
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the given reaction has to be given.
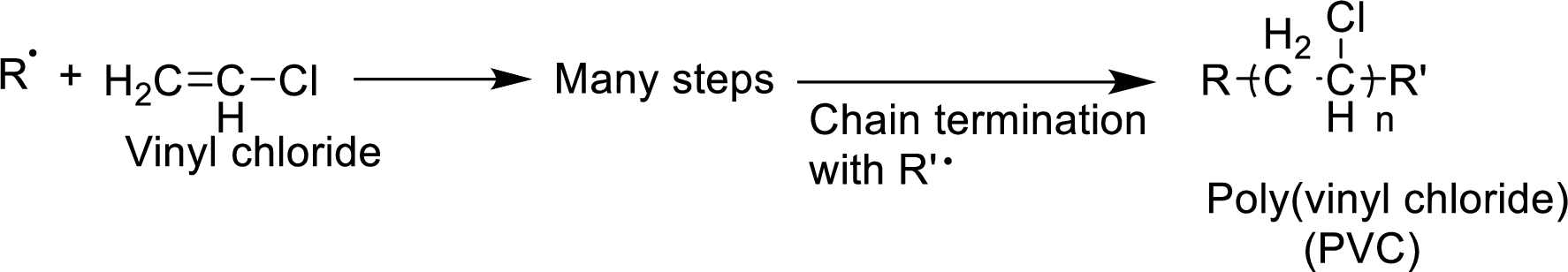
Concept Introduction:
The
- 1. Chain initiation
- 2. Chain propagation and
- 3. Chain termination.
Chain initiation occurs by the formation of radical from one of the monomer units. Propagation occurs by the reaction of the radicals with molecules. Chain termination occurs by neutralization of radicals.
(b)
Interpretation:
The mechanism for the formation of poly(styrene) from styrene has to be given and at which end of the styrene double bond, the
Concept Introduction:
The polymers are formed from the repetition monomer units. The polymerization process occurs in three steps.
- 1. Chain initiation
- 2. Chain propagation and
- 3. Chain termination.
Chain initiation occurs by the formation of radical from one of the monomer units. Propagation occurs by the reaction of the radicals with molecules. Chain termination occurs by neutralization of radicals.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw the structure of the aldol, self condensation product for each of the following compounds if a compound does not undergo aldol self condensation explain why it does notarrow_forwardShow how each of the following transformations might be best accomplished. More than one step may required. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. [4 only] CH3 A. CH CH2 C Br CH3 B OH only source of carbon CH3 CH CH2 C NHz CH 3 Harrow_forward. Choose a structure from the list provided below that best fits each of the following escriptions. Place the letter of the structure in the blank to the left of the description. There is nly one correct answer for each question. starch HO CH₂OH b. cellulose d. CH₂OH HO OH HO HO OH OH OH f. sucrose CH₂OH OH OH HO OCH₂ OH a monosaccharide that gives a negative Benedict's Test. a ẞ-1,4'-glycoside a disaccharidearrow_forward
- Show how each of the following transformations might be best accomplished. More than one step may required. Show all reagents and all intermediate structures. [4 only] CH3 A. CH CH2 C Br CH3 CH3 CH3CH2 C NH2 CH3 B OH any source of carbon N MIHarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions. 0 0 25 PS ES 1919sds-III msx H H + 5% NaOCH 3, CH3OHA O CH₂OH Jeiniog 2E1 gniwool of mor]. Ignibuloni 9vil 19 A B 11 >buoqm gniwollol so dass 101 tomboy boo-11Coble or to r ton auch i viw ninlaxs, noitsausbroo 152 lobla ogsbau ton 250b br A. Which carbonyl compound functions as the electrophile in this reaction? B. Draw the structure of the enolate ion that is generated during the course of this reaction. C. This reaction is an example of: a. a mixed Claisen condensation. b. C. d. a Dieckman condensation. a Michael reaction. a mixed aldol reaction. HD HDarrow_forwardConsider the reaction below to answer the following questions: 847 Acetoacetic ester can be prepared by the Claisen self-condensation reaction of ethyl acetate. H₁C 0 H 0 IL 유 || OCH2CH3 1. NaOEt, EtOH C 2. H₂O H3C CH₂ Cold not tobizmo. S OCH2CH3 A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for this reaction. Show all electron flow with arrows and draw all intermediate structures. B. Ethyl acetate can be prepared from ethanol as the only organic starting material. Show all reagents and structures for all intermediates in this preparation. C. Give the structures of the ester precursors for the following Claisen condensation product and formulate the reaction. ou OELarrow_forward
- A. What is the correct structure for a-D-glucopyranose? CH₂OH a HO HO- OH b HO HO- OH HOH₂C OH OH OH CH₂OH HO C. HO HO- OH OH CH₂OH OH OH B. Draw structures for the products you would expect to obtain from reaction of B-D-galactopyranose with each of the following reagents. Be sure to include all relevant stereochemistry. [FOUR only] A. CH, Ag₂O B. warm dilute HNO3 C. (CH3CO)20, pryridine D. NaBH in H₂O E. CH₂OH, HCI F. Br₂, H₂O HO CH₂OH HO- OH OH B-D-galactopyranosearrow_forwardGive the major organic product(s) for each of the following reactions or reaction sequences. CH₂CN 5% NaOEt, EIOH سجد سی . بلی H 1. NaOCH, CH,OH CH3 OCH3 2 H₂O*arrow_forwardDraw the structures for each of the intermediates in the boxes provided for the synthesis below. 004 HNO F HO CHCO) D Dydre R.SO. 1.1 NO fe HO H.SO. 2. CC1 NOH HO MCL HNO, H.50.arrow_forward
- . Each of the following compounds can be prepared by a mixed aldol condensation reaction. Give the Cructures of the aldehyde and/or ketone precursors for each aldol product and formulate the reaction. 0 CH=CHCCH 3. Ph 1arrow_forward. Consider the reaction below to answer the following question: H NaOEt H BOH بلی H + H₂O A. Write the complete stepwise mechanism for the reaction above. Show all intermediate structures and all electron flow with arrows. B. This reaction is an example of: an intramolecular aldol condensation a. an intramolecular Claisen condensation b. C. d. a Robinson annulation a Michael reaction C. The product of this reaction is: a. b. C. d. a ẞ. y-unsaturated aldehyde an a, B-unsaturated ketone an a, B-unsaturated aldehyde an enolarrow_forwardClassify each of the following nitrogen atoms in the following compounds as primary, secondary, tiary, or quaternary. A. B. C. CH3 HO-CHCHNHCH3 ephedrine CH CHCH3 amphetamine NH₂ D. CF H3C CH3 mapiquat chloride HO fexofenadine OH H3C CH3 CO₂Harrow_forward
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning

