
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The standard enthalpy of reaction has to be calculated using the values of bond dissociation enthalpies.
Concept Introduction:
The value of standard enthalpy change
Where,
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction (1):
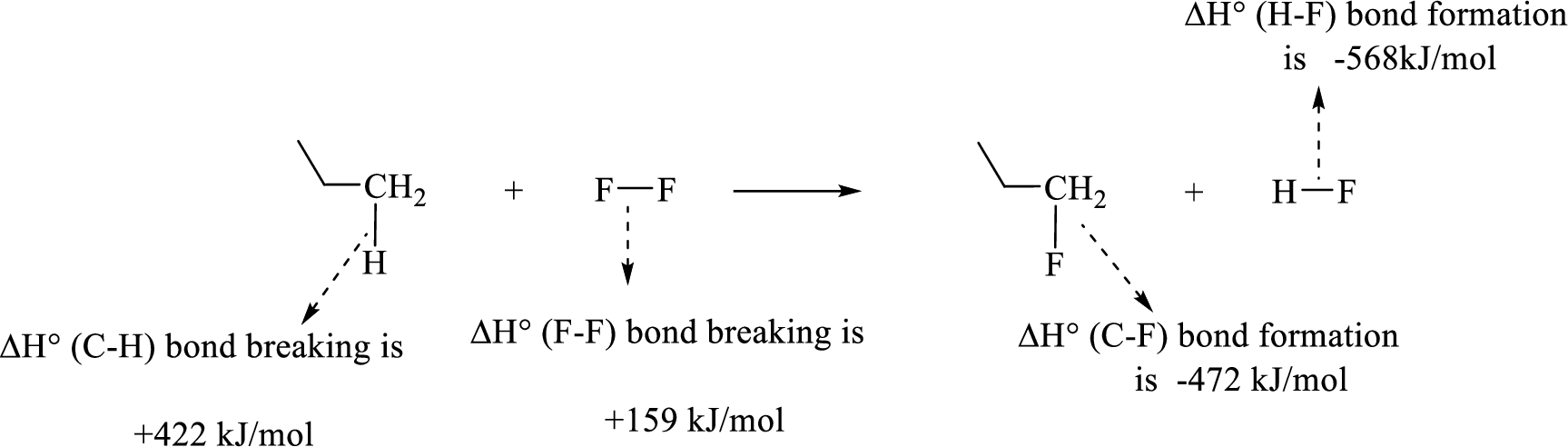
The reaction is given below:
Therefore, standard enthalpy of given reaction is
Given reaction (2):
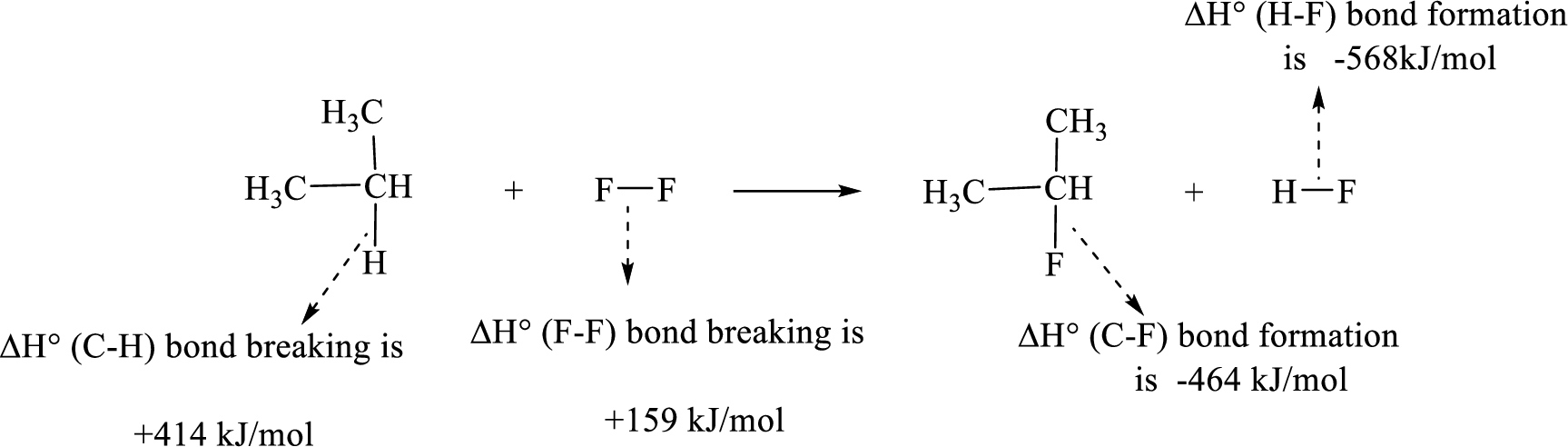
The reaction is given below:
Therefore, standard enthalpy of given reaction is
(b)
Interpretation:
A pair of chain propagation steps for each reaction has to be proposed; the value of
Concept Introduction:
Radical Bromination: A type of halogenation reaction in which the bromine atom gets bonded with the
Radical reaction of
Stability of Radicals: Radicals are highly unstable due to its unpaired valence electron of an atom.
The increasing order of radical stability is given below,
Benzylic > allylic > tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 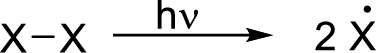
Chain propagation: 
Chain termination:
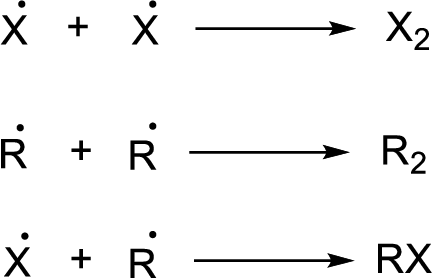
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction (1):
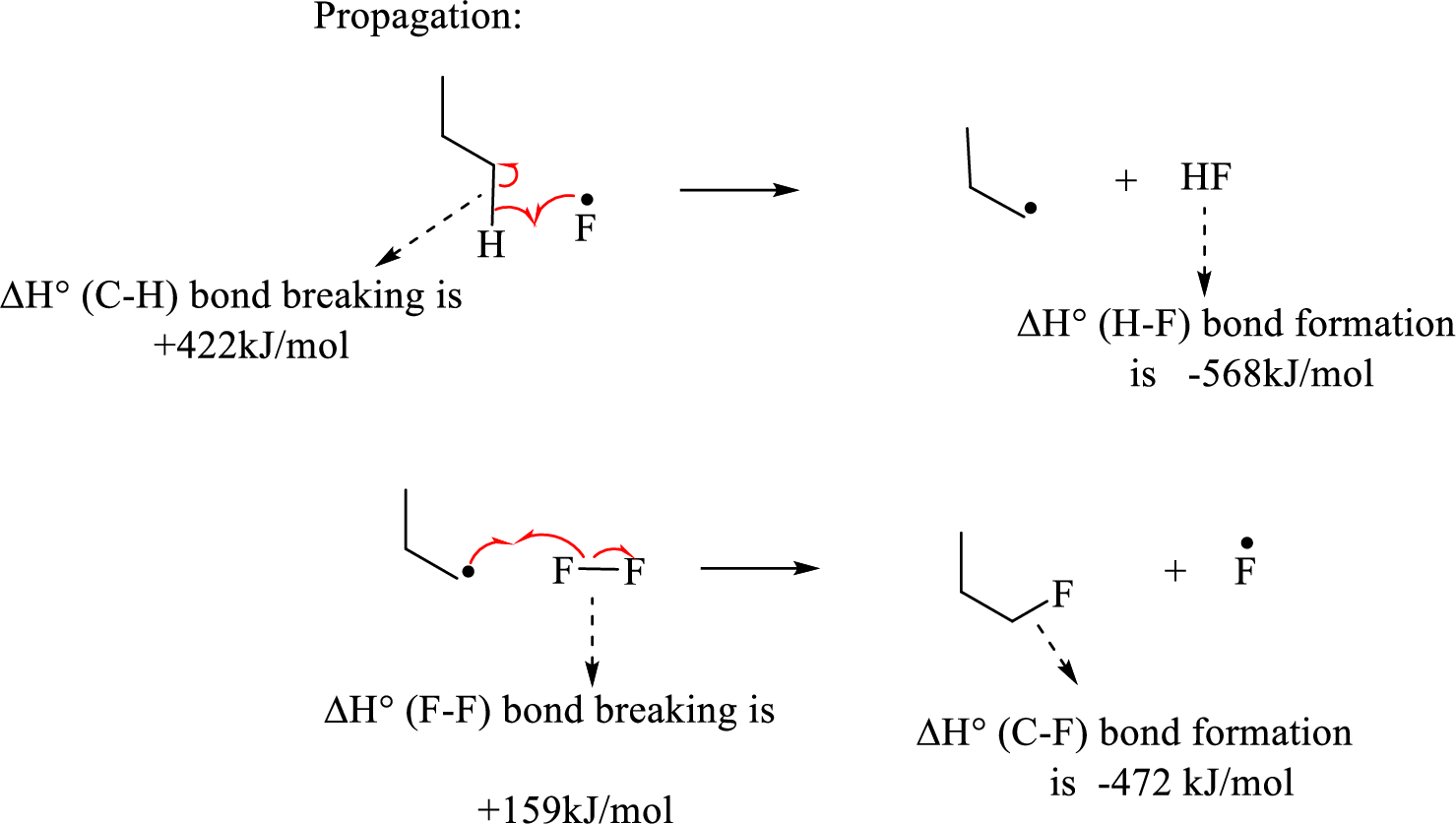
The propagation step involves extremely reactive fluorine radicals react towards the propane by abstracting the terminal hydrogen forming primary radical and
Hence, the pair of propagation steps is shown above.
Given reaction (2):
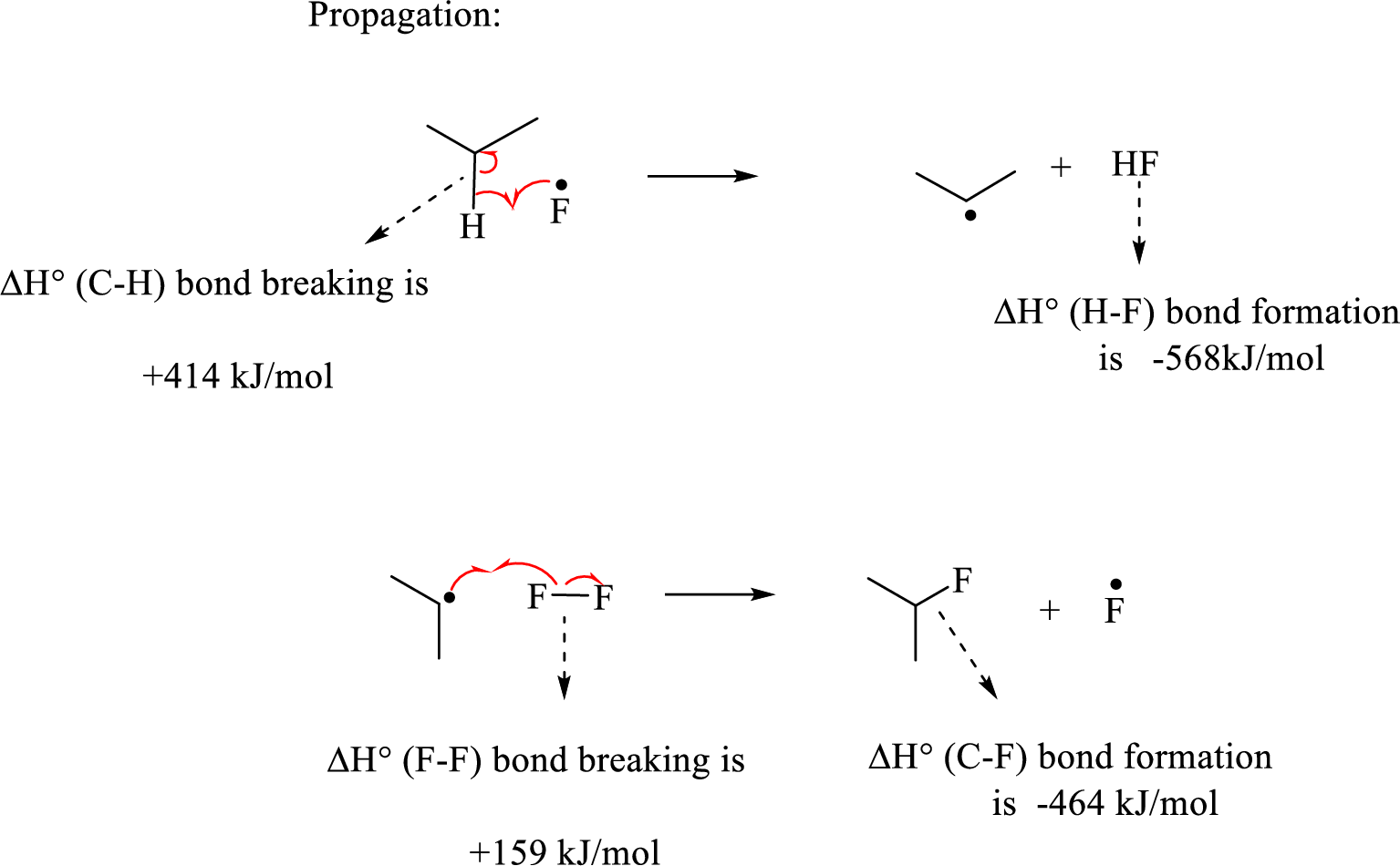
Initiation step involves the homolytic bond cleavage of fluorine molecule by irradiation of light or heat leads to the formation of two Fluorine radicals.
The propagation step involves extremely reactive fluorine radicals react towards the propane by abstracting the secondary hydrogen forming secondary radical and
Hence, the pair of propagation steps is shown above.
Therefore, for each reaction step the value of
(c)
Interpretation:
The regioselectivity of radical fluorination relative to that of radical chlorination and Bromination has to be predicted using Hammond’s postulate.
Concept Introduction:
Radical Bromination: A type of halogenation reaction in which the fluorine atom gets bonded with the alkane or alkyl substituents resulting to the product with added fluorine atom via radical mechanism.
Radical reaction of
Stability of Radicals: Radicals are highly unstable due to its unpaired valence electron of an atom.
The increasing order of radical stability is given below,
Benzylic > allylic > tertiary > secondary > primary > methyl
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 
Chain propagation: 
Chain termination:
(c)
Explanation of Solution
In each radical fluorination sequence, the hydrogen abstraction step is highly exothermic, thus the transition state is reached too early and the transition state more closely resembles the reactant; so the intermediate has very little radical character of product. Therefore, the relative stabilities of primary versus secondary radical is of little of importance in determination of product.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Give the expected major product of reaction of 2,2-dimethylcyclopropane with each of the following reagents. 2. Reaction with dilute H₂SO, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More CHC Erase QQQ c. Reaction with dilute aqueous HBr. Select Drew Templates More Era c QQQ b. Reaction with NaOCH, in methanol. Select Draw Templates More d. Reaction with concentrated HBr. Select Draw Templates More En a QQQ e. Reaction with CH, Mg1, then H*, H₂O 1. Reaction with CH,Li, then H', H₂Oarrow_forwardWrite the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure O OH OH name X ☐arrow_forwardMacmillan Learning One of the molecules shown can be made using the Williamson ether synthesis. Identify the ether and draw the starting materials. А со C Strategy: Review the reagents, mechanism and steps of the Williamson ether synthesis. Determine which of the molecules can be made using the steps. Then analyze the two possible disconnection strategies and deduce the starting materials. Identify the superior route. Step 6: Put it all together. Complete the two-step synthesis by selecting the reagents and starting materials. C 1. 2. Answer Bank NaH NaOH NaOCH, снен, сен, он Сиси, Сне (СН), СОН (Сн, Свarrow_forward
- Write the systematic name of each organic molecule: structure CH3 O CH3-CH-CH-C-CH3 OH HV. CH3-C-CH-CH2-CH3 OH CH3 O HO—CH, CH–CH—C CH3 OH 오-오 name X G ☐arrow_forwardHI Organic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of esterification What is the missing reactant in this organic reaction? HO OH H +回 + H₂O 60013 Naomi V Specifically, in the drawing area below draw the skeletal ("line") structure of R. If there is more than one reasonable answer, you can draw any one of them. If there is no reasonable answer, check the No answer box under the drawing area. No answer Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Explanation Check 1 2 #3 $ 4 2025 % ala5 'a :☐ G & 67 8 Ar K enter Accessible 9 Q W E R TY U 1 tab , S H J Karrow_forwardPlease help me with number 5 using my data and graph. I think I might have number 3 and 4 but if possible please check me. Thanks in advance!arrow_forward
- dict the major products of this organic reaction. C Explanation Check 90 + 1.0₂ 3 2. (CH3)2S Click and drag f drawing a stru © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. • 22 4 5 7 8 Y W E R S F H Bilarrow_forwardcan someone draw out the reaction mechanism for this reaction showing all the curly arrows and 2. Draw the GPNA molecule and identify the phenylalanine portion. 3. Draw L-phenylalanine with the correct stereochemistryarrow_forwardWhat is the reaction mechanism for this?arrow_forward
- Predict the major products of both organic reactions. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds to show the stereochemistry of the products when it's important, for example to distinguish between two different major products. esc esc Explanation Check 2 : + + X H₁₂O + Х ง WW E R Y qab Ccaps lock shift $ P X Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil T FR F18 9 G t K L Z X V B N M control opption command command T C darrow_forwardDraw the Markovnikov product of the hydrohalogenation of this alkene. this problem. Note for advanced students: draw only one product, and don't worry about showing any stereochemistry. Drawing dash and wedge bonds has been disabled for caps lock Explanation Check 2 W E R + X 5 HCI Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility Bil Y F G H K L ZZ X C V B N M control opption command F10 F10 command 4 BA Ar Carrow_forwardI don't understand why the amide on the top left, with the R attached to one side, doesn't get substituted with OH to form a carboxylic acid. And if only one can be substituted, why did it choose the amide it chose rather than the other amide?arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning

