
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
A second chain propagation step in the given reaction has to be proposed.
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of
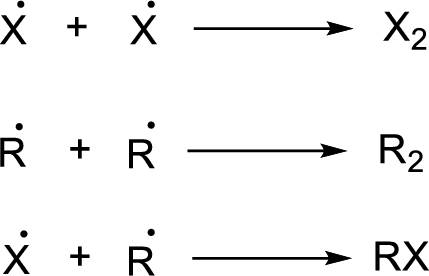
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 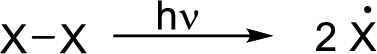
Chain propagation: 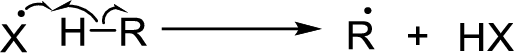
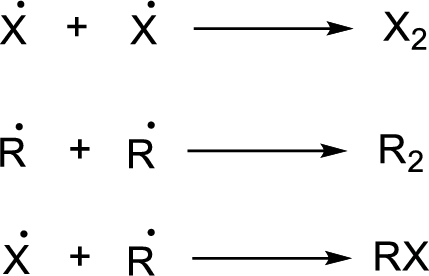
Chain termination:
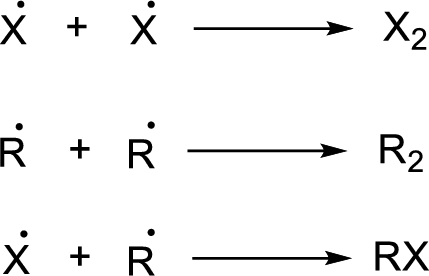
(b)
Interpretation:
Heat of the reaction,
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of alkanes: The replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by halogen. When alkanes is heated or irradiated with the light of specific wavelength, the alkyl halide are formed by radical chain reaction.
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 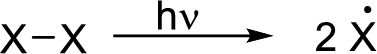
Chain propagation: 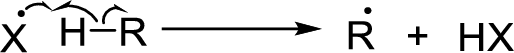
Chain termination:
It is a change in enthalpy of a homolysis reaction at absolute zero where a molecule is broken down into two free radicals.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energies and relative rates of the set chain propagation steps in section 8.5B with given reaction has to be compared.
Concept introduction:
Halogenation of alkanes: The replacement of one or more hydrogen atoms by halogen. When alkanes is heated or irradiated with the light of specific wavelength, the alkyl halide are formed by radical chain reaction.
Radical chain reaction:
Initiation reaction: 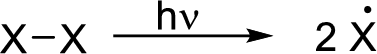
Chain propagation: 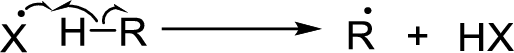
Chain termination:
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Please help me figure out the mechanism with arrows of the following reactionarrow_forwardOrganic Functional Groups Predicting the reactants or products of acetal hydrolysis termine the structures of the missing organic molecules in the following reaction: H* H* + H₂O Y ☑ Note: Molecules that share the same letter have the exact same structure. In the drawing area below, draw the skeletal ("line") structures of the missing organic molecules X, Y, and Z. You may draw that you like, so long as they aren't touching. Molecule X shows up in multiple steps, but you only have to draw its structure Explanation Check @2 W Click and drag to start drawing a structure. #4 # 3 LU E % 67 olo 5 66 R T Y & 7 AcGraw Hill LLC. All Rights R Xarrow_forward8. (16 pts) Provide the stepwise mechanism for the synthesis of the following compound via an enaminearrow_forward
- Draw the titration curve of (i) weak acid vs. strong base; (ii) weak acid vs. weakbase; (iii) diprotic acid with strong base (iii) triprotic acid with strong base.arrow_forwardComplete the reaction in the drawing area below by adding the major products to the right-hand side. If there won't be any products, because nothing will happen under these reaction conditions, check the box under the drawing area instead. Note: if the products contain one or more pairs of enantiomers, don't worry about drawing each enantiomer with dash and wedge bonds. Just draw one molecule to represent each pair of enantiomers, using line bonds at the chiral center. More... No reaction. my ㄖˋ + 1. Na O Me Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 2. H +arrow_forwardPredict the intermediate 1 and final product 2 of this organic reaction: NaOMe H+ + 1 2 H H work up You can draw 1 and 2 in any arrangement you like. Note: if either 1 or 2 consists of a pair of enantiomers, just draw one structure using line bonds instead of 3D (dash and wedge) bonds at the chiral center. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $ dmarrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning


