
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781260028355
Author: Carey
Publisher: MCG CUSTOM
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 8, Problem 42P
The heats of reaction were measured for addition of
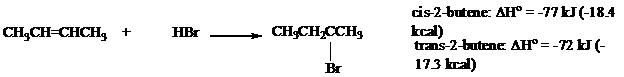
Use these data to calculate the energy difference between
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
I want to know how to do it , please help
Help me i dont know how to do it
Can you explain how to draw a molecular orbital diagram for the given molecule? It is quite difficult to understand. Additionally, could you provide a clearer illustration? Furthermore, please explain how to draw molecular orbital diagrams for any other given molecule or compound as well.
Chapter 8 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-PACKAGE >CUSTOM<
Ch. 8.1 - What three alkenes yield 2-methylbutane on...Ch. 8.2 - Prob. 2PCh. 8.2 - Prob. 3PCh. 8.3 - Prob. 4PCh. 8.4 - Prob. 5PCh. 8.4 - Give a structural formula for the carbocation...Ch. 8.5 - Prob. 7PCh. 8.6 - Instead of the three-step process of Mechanism...Ch. 8.6 - The rates of hydration of the two alkenes shown...Ch. 8.6 - Is the electrophilic addition of hydrogen chloride...
Ch. 8.7 - You can calculate the equilibrium constant for the...Ch. 8.7 - Does the presence or absence of a catalyst such as...Ch. 8.7 - The gas phase reaction of ethanol with hydrogen...Ch. 8.8 - Prob. 14PCh. 8.8 - Hydroborationoxidation of -pinene, like its...Ch. 8.10 - Arrange the compounds 2-methyl-1-butene,...Ch. 8.10 - Give the structure of the product formed when each...Ch. 8.11 - Prob. 18PCh. 8.11 - Prob. 19PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 20PCh. 8.12 - Prob. 21PCh. 8.13 - Prob. 22PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 23PCh. 8.14 - Prob. 24PCh. 8 - How many alkenes yield...Ch. 8 - Prob. 26PCh. 8 - Catalytic hydrogenation of...Ch. 8 - Prob. 28PCh. 8 - Prob. 29PCh. 8 - Prob. 30PCh. 8 - Prob. 31PCh. 8 - A single epoxide was isolated in 7984% yield in...Ch. 8 - Prob. 33PCh. 8 - Prob. 34PCh. 8 - On catalytic hydrogenation over a rhodium...Ch. 8 - Prob. 36PCh. 8 - Prob. 37PCh. 8 - Prob. 38PCh. 8 - Prob. 39PCh. 8 - 1-Butene has a higher heat of hydrogenation than...Ch. 8 - Match the following alkenes with the appropriate...Ch. 8 - The heats of reaction were measured for addition...Ch. 8 - Complete the following table by adding + and -...Ch. 8 - Match the heats of hydrogenation (107 kJ/mol,...Ch. 8 - The iodination of ethylene at 25 C is...Ch. 8 - Specify reagents suitable for converting...Ch. 8 - (a) Which primary alcohol of molecular formula...Ch. 8 - Identify compounds A and B in the retrosynthesis...Ch. 8 - Identify compounds A and B in the retrosynthesis...Ch. 8 - Prob. 50PCh. 8 - On being heated with a solution of sodium ethoxide...Ch. 8 - Compound A (C7H15Br) is not a primary alkyl...Ch. 8 - Prob. 53PCh. 8 - Prob. 54PCh. 8 - A mixture of three alkenes (A, B, and C) was...Ch. 8 - Reaction of 3,3-dimethyl-1-butene with hydrogen...Ch. 8 - Dehydration of 2,2,3,4,4-pentamethyl-3-pentanol...Ch. 8 - Prob. 58PCh. 8 - East Indian sandalwood oil contains a hydrocarbon...Ch. 8 - Prob. 60PCh. 8 - Prob. 61PCh. 8 - Prob. 62PCh. 8 - Prob. 63PCh. 8 - Prob. 64PCh. 8 - On the basis of the mechanism of acid-catalyzed...Ch. 8 - As a method for the preparation of alkenes, a...Ch. 8 - Which of the following is the most reasonable...Ch. 8 - Prob. 68PCh. 8 - Oxymercuration Concerns about mercurys toxicity...Ch. 8 - Prob. 70DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 71DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 72DSPCh. 8 - Prob. 73DSPCh. 8 - Oxymercuration Concerns about mercurys toxicity...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Prob 10: Select to Add Arrows THEarrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons using the provided starting and product structures draw the curved electron pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic steps Ether(solvent)arrow_forwardThis deals with synthetic organic chemistry. Please fill in the blanks appropriately.arrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. What is the IUPAC name of each of the the following? 0 CH3CHCNH₂ CH3 CH3CHCNHCH2CH3 CH3arrow_forwardYou have now performed a liquid-liquid extraction protocol in Experiment 4. In doing so, you manipulated and exploited the acid-base chemistry of one or more of the compounds in your mixture to facilitate their separation into different phases. The key to understanding how liquid- liquid extractions work is by knowing which layer a compound is in, and in what protonation state. The following liquid-liquid extraction is different from the one you performed in Experiment 4, but it uses the same type of logic. Your task is to show how to separate apart Compound A and Compound B. . Complete the following flowchart of a liquid-liquid extraction. Handwritten work is encouraged. • Draw by hand (neatly) only the appropriate organic compound(s) in the boxes. . Specify the reagent(s)/chemicals (name is fine) and concentration as required in Boxes 4 and 5. • Box 7a requires the solvent (name is fine). • Box 7b requires one inorganic compound. • You can neatly complete this assignment by hand and…arrow_forwardb) Elucidate compound D w) mt at 170 nd shows c-1 stretch at 550cm;' The compound has the ff electronic transitions: 0%o* and no a* 1H NMR Spectrum (CDCl3, 400 MHz) 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 ppm 13C{H} NMR Spectrum (CDCl3, 100 MHz) Solvent 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 ppm ppm ¹H-13C me-HSQC Spectrum ppm (CDCl3, 400 MHz) 5 ¹H-¹H COSY Spectrum (CDCl3, 400 MHz) 0.5 10 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 10 15 20 20 25 30 30 -35 -1.0 1.5 -2.0 -2.5 3.0 -3.5 0.5 ppm 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 0.5 ppmarrow_forward
- Part I. a) Elucidate the structure of compound A using the following information. • mass spectrum: m+ = 102, m/2=57 312=29 • IR spectrum: 1002.5 % TRANSMITTANCE Ngg 50 40 30 20 90 80 70 60 MICRONS 5 8 9 10 12 13 14 15 16 19 1740 cm M 10 0 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 1800 1600 13 • CNMR 'H -NMR Peak 8 ppm (H) Integration multiplicity a 1.5 (3H) triplet b 1.3 1.5 (3H) triplet C 2.3 1 (2H) quartet d 4.1 1 (2H) quartet & ppm (c) 10 15 28 60 177 (C=0) b) Elucidate the structure of compound B using the following information 13C/DEPT NMR 150.9 MHz IIL 1400 WAVENUMBERS (CM-1) DEPT-90 DEPT-135 85 80 75 70 65 60 55 50 45 40 35 30 25 20 ppm 1200 1000 800 600 400arrow_forward• Part II. a) Elucidate The structure of compound c w/ molecular formula C10 11202 and the following data below: • IR spectra % TRANSMITTANCE 1002.5 90 80 70 60 50 40 30 20 10 0 4000 3600 3200 2800 2400 2000 1800 1600 • Information from 'HAMR MICRONS 8 9 10 11 14 15 16 19 25 1400 WAVENUMBERS (CM-1) 1200 1000 800 600 400 peak 8 ppm Integration multiplicity a 2.1 1.5 (3H) Singlet b 3.6 1 (2H) singlet с 3.8 1.5 (3H) Singlet d 6.8 1(2H) doublet 7.1 1(2H) doublet Information from 13C-nmR Normal carbon 29ppm Dept 135 Dept -90 + NO peak NO peak 50 ppm 55 ppm + NO peak 114 ppm t 126 ppm No peak NO peak 130 ppm t + 159 ppm No peak NO peak 207 ppm по реак NO peakarrow_forwardCould you redraw these and also explain how to solve them for me pleasarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: The Molecular Science
Chemistry
ISBN:9781285199047
Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. Stanitski
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry: An Atoms First Approach
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079243
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Principles of Modern Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079113
Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. Butler
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 2; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=AL_CM_Btef4;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY
Chapter 4 Alkanes and Cycloalkanes Lesson 1; Author: Linda Hanson;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPIa6EHJMJw;License: Standard Youtube License