
Concept explainers
The hydroxyl radical
(d) The radical is generated when sunlight hits water vapor. Calculate the maximum wavelength (in nm) required to break an
Interpretation:
The Lewis structure of hydroxyl radical is to be drawn; the reason for radical’s high affinity for H atoms, enthalpy change for the given reaction, and the maximum wavelength required to break given bond in given compound are to be calculated.
Concept introduction:
The standard enthalpy of a reaction is the enthalpy change that occurs under standard conditions.
The standard enthalpy of a reaction is determined using the equation as given below:
Here, the stoichiometric coefficients are represented by m for reactants and n for products, and enthalpy of formation at standard conditions is represented by
The standard enthalpy of formation is the amount of heat change that arises as a result of one mole of compound formation at the standard states from its integral elements.
The value of enthalpy of formation of an element is zero at its most stable state.
Bond Enthalpy is the energy required to break a bond of 1 mole of a substance. It is given in
The Lewis dot symbols contain dots, which give information about valence electrons.
According to Planck’s energy–frequency law, energy is given by:
Here, h is Planck’s constant,
Answer to Problem 142AP
Solution:
(a)
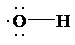
(b) The reason for radical
(c)
(d)
Explanation of Solution
a) Lewis structure for radical (OH)
The skeletal structure for
The number of valence electrons is as follows:
Now, only two electrons are used in bond formation. So, the number of remaining electrons is 5.
The oxygen atom has only one electron used in bond formation, so it will have 5 remaining electrons.
So, the Lewis structure for
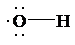
b) The radical has high affinity for H atom, refer table 8.6.
From table 8.6, the bond enthalpy of oxygen–hydrogen bond:
Since the value of oxygen–hydrogen bond is very high, the radical
Hence, the reason for radical
c) The enthalpy change for the following given reaction:
The enthalpy of reaction can be calculated as follows:
From table 8.6, the enthalpy of formation values are as follows:
Now, the standard enthalpy of the given reaction is as follows:
Substitute
Hence, the enthalpy of the given reaction from the bond enthalpy values is
d) The maximum wavelength (in nm) required to break an
From table 8.6, the bond enthalpy for oxygen–hydrogen bond is as follows:
This can be written as the energy of oxygen–hydrogen bond as
According to Planck’s energy–frequency law, energy is given as follows:
This can be written as follows:
Substitute
Hence, the maximum wavelength required to break the oxygen–hydrogen bond is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry
- if the answer is no reaction than state that and please hand draw!arrow_forward"I have written solutions in text form, but I need experts to rewrite them in handwriting from A to Z, exactly as I have written, without any changes."arrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forward
- Please correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardreciprocal lattices rotates along with the real space lattices of the crystal. true or false?arrow_forwardDeducing the reactants of a Diels-Alder reaction vn the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ O If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. • If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Product can't be made in one step. Explanation Checkarrow_forward
- Predict the major products of the following organic reaction: Δ ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Larrow_forward> Can the molecule on the right-hand side of this organic reaction be made in good yield from no more than two reactants, in one step, by moderately heating the reactants? ? Δ • If your answer is yes, then draw the reactant or reactants in the drawing area below. You can draw the reactants in any arrangement you like. If your answer is no, check the box under the drawing area instead. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Х © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accesarrow_forwardPredict the major products of the following organic reaction: O O + A ? Some important notes: • Draw the major product, or products, of the reaction in the drawing area below. • If there aren't any products, because no reaction will take place, check the box below the drawing area instead. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products that are enantiomers. Explanation Check Click and drag to start drawing a structure. eserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center >arrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
