
Concept explainers
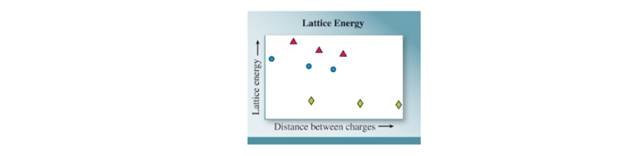
Lattice energies are graphed for three series of compounds in which the ion charges are
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 8 Solutions
Chemistry
- Check How many signals would you expect to find in the H NMR spectrum of each given compound? Part 1 of 2 Part 2 of 2 Br Br 2. Cl X 2 © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Resarrow_forwardcalculate the pH of 0.015 M H2SO4. Remember stoichiometry.arrow_forwardin VSEPR Theory AX2 isa) tetrahedralb) octahedralc) lineard) trigonal bipyramidarrow_forward
- true or false, Gibbs Free Energy is the measure of randomness of a systemarrow_forwardtrue or false, enthalpy determines whether a reaction in endothermic or exothermicarrow_forwardCheck Consider the 13 C NMR spectrum below. 140 120 100 80 60 60 PPM 40 20 0 The spectrum belongs to which one of the following constitutional isomers of the compound C 10H14? Select the single best answer. ✓ Save © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved.arrow_forward
- The structure of compound 1,1,2-trichloropropane is given below. Cl Cl Cl 1 How many signals would you expect to find in the 'H NMR spectrum of 1,1,2-trichloropropane? ×arrow_forward1, How many signals do you expect in the H NMR spectrum for this molecule? Write the answer below. Also, in each of the drawing areas below is a copy of the molecule, with Hs shown. In each copy, one of the H atoms is colored red. Highlight in red all other H atoms that would contribute to the same signal as the H already highlighted red. Note for advanced students: In this question, any multiplet is counted as one signal. Number of signals in the 'H NMR spectrum. For the molecule in the top drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in top molecule For the molecule in the bottom drawing area, highlight in red any other H atoms that will contribute. to the same signal as the H atom already highlighted red. If no other H atoms will contribute, check the box at right. No additional Hs to color in bottom molecule Check…arrow_forwardIncorrect Row 2: Your answer is incorrect. Consider this molecule: How many H atoms are in this molecule? 22 How many different signals could be found in its 'H NMR spectrum? 12 Note: A multiplet is considered one signal.arrow_forward
- 13 How many signals would you expect to see in the Check O signal(s) X § 'C NMR spectrum for the following compound? © 2025 McGraw Hillarrow_forward13 Consider the "C NMR spectrum below. 140 120 100 80 60 40 20 20 PPM 0 The spectrum belongs to which one of the following constitutional isomers of the compound C,H12? Select the single best answer. Check ✓ G Save For Later 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forwardThe structure of compound 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene) is given below. How many signals would you expect to find in the 'H NMR spectrum of 1,3,5-trimethylbenzene (mesitylene)? Check ×arrow_forward

 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Modern ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305079113Author:David W. Oxtoby, H. Pat Gillis, Laurie J. ButlerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





