
Concept explainers
Draw structures corresponding to the following systematic names:
(a) (4E)-2, 4-Dimethyl-l, 4-hexadiene
(b) cis-3, 3-Dimethyl-4-propyl-l, 5-octadiene
(c) 4-Methyl-l, 2-pentadiene
(d) (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-Dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene
(e) 3-Butyl-2-heptene
(f) trans-2, 2, 5, 5-Tetramethyl-3-hexene
a) (4E)-2, 4-Dimethyl-1, 4-hexadiene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (4E)-2, 4-dimethyl-1, 4-hexadiene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–alkene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon are on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (4E)-2, 4-dimethyl-1, 4-hexadiene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (4E)-2, 4-dimethyl-1, 4-hexadiene is
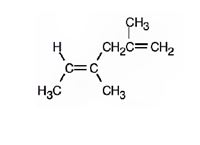
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain six carbons with two double bonds between C2 & C3 and C4 & C5. There should be two methyl substituents one on C2 and other on C4. Further higher ranked groups on each carbon should be in the opposite sides of the double bonds.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (4E)-2, 4-dimethyl-1, 4-hexadiene is

b) cis-3, 3-Dimethyl-4-isopropyl-1, 5-octadiene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name cis-3, 3-dimethyl-4-isopropyl-1, 5-octadiene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as thetrans isomer.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name cis-3, 3-dimethyl-4-isopropyl-1, 5-octadiene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name cis-3, 3-dimethyl-4-isopropyl-1, 5-octadiene is
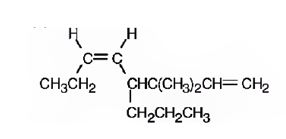
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with two double bonds between C1 & C2 and C5 & C6. There should be two methyl substituents on C3 and an isopropyl group on C4. Further similar groups in each carbon should be on the same sides of the double bonds.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name cis-3, 3-dimethyl-4-isopropyl-1, 5-octadiene is

c) 4-Methyl-1, 2-pentadiene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name4-methyl-1, 2-pentadiene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 4-methyl-1, 2-pentadiene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 4-methyl-1, 2-pentadiene is
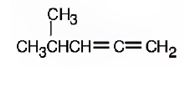
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain five carbons with two double bonds between C1 & C2 and C2 & C3. There should be amethyl substituent on C4.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 4-methyl-1, 2-pentadiene is
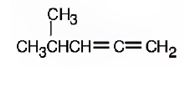
d) (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-Dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon are on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene is
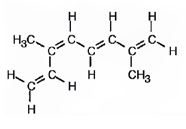
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain eight carbons with two double bonds between C2 & C3 and C6 & C7. There should be two methyl substituents one on C2 and other on C6. Further higher ranked groups on C2 & C3 must be placed on the opposite sides of the double bond. The higher ranked groups on C6 & C7 must be placed on the same side of the double bond.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name (3E, 5Z)-2, 6-dimethyl-1, 3, 5, 7-octatetraene is

e) 3-Butyl-2-heptene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name3-butyl-2-heptene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 3-butyl-2-heptene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 3-butyl-2-heptene is
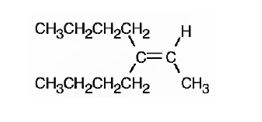
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain seven carbons with a double bond between C2 & C3. There should be a butyl substituent on C3.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name 3-butyl-2-heptene is

f) trans-2, 2, 5, 5-Tetramethyl-3-hexene.
Interpretation:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name trans-2, 2, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-hexene is to be drawn.
Concept introduction:
The longest carbon chain containing the double bond to be chosen. Based on the name of the parent compound–the alkene name ends with the suffix–ene. The chain is to be numbered from the end that gives the lowest number to the carbon in double bond. Substituents are to be numbered according to their positions in the chain and listed alphabetically. The position of the double bond is indicated by giving the number of the first alkene carbon before the name of the parent name. If more than one double bond is present, their positions are indicated with the suffixes -diene, -triene and so on. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is called as the cis isomer. The isomer that has similar groups on each carbon on the opposite side of the double bond is called as the trans isomer.
To draw:
The structure corresponding to the systematic name trans-2, 2, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-hexene.
Answer to Problem 38AP
The structure corresponding to the systematic name trans-2, 2, 5, 5-tetramethyl-3-hexene is
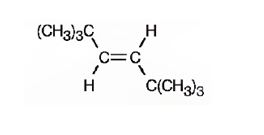
Explanation of Solution
The name shows that the longest carbon chain should contain six carbons with a double bond between C3 & C4. There should be four methyl substituents two on C3 and two on C5. Further similar groups in each carbon should be on the opposite sides of the double bonds.
The structure corresponding to the systematic name trans-2,2,5,5-tetramethyl-3-hexene is

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- ASP please....arrow_forwardNonearrow_forwardConsider the structure of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane. Part 1 of 2 Draw the Newman projection for the anti conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. ✡ ぬ Part 2 of 2 H H F Br H H ☑ Draw the Newman projection for the gauche conformation of 1-bromo-2-fluoroethane, viewed down the C1-C2 bond. H F Br H Harrow_forward
- Please help me answer this question. I don't understand how or where the different reagents will attach and it's mostly due to the wedge bond because I haven't seen a problem like this before. Please provide a detailed explanation and a drawing showing how it can happen and what the final product will look like.arrow_forwardWhich of the following compounds is the most acidic in the gas phase? Group of answer choices H2O SiH4 HBr H2Sarrow_forwardWhich of the following is the most acidic transition metal cation? Group of answer choices Fe3+ Sc3+ Mn4+ Zn2+arrow_forward
- Based on the thermodynamics of acetic acid dissociation discussed in Lecture 2-5, what can you conclude about the standard enthalpy change (ΔHo) of acid dissociation for HCl? Group of answer choices You cannot arrive at any of the other three conclusions It is a positive value It is more negative than −0.4 kJ/mol It equals −0.4 kJ/molarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure corresponding to the following IUPAC name: 7-isopropyl-3-methyldecanearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





