
a)
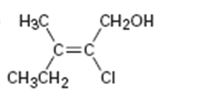
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
b)
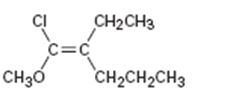
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
c)
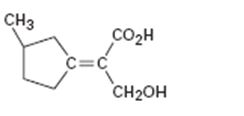
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
d)
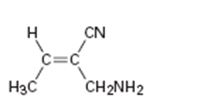
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- Draw the mechanism (including all curved arrows for electron movement) showing how the maleicanhydride is attacked by the anthracene and formation of the final Diels Alder product.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
- Provide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forwardI have a bottle of butanal that has been improperly used by lab workers. They allowed a traceamount NaOH (aq) to contaminate the bottle. What is now in my bottle of “butanal? What is the molecular name and functional group name? Draw the structure.arrow_forwardProvide the missing information. *see imagearrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning


