
Concept explainers
a)
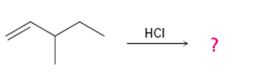
Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the hydrogen of the
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
b)
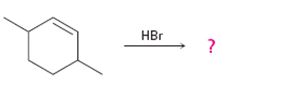
Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the hydrogen of the alkyl halide to yield a carbocation. One of the carbon in C=C gets attached to hydrogen while the other acquires a positive charge. In the second step, the carbocation formed can rearrange to give another more stable carbocation either by a hydride shift (shift of hydrogen atom with its electron pair) or by an alkyl shift (shift of an alkyl group with its electron pair) between neighboring carbons. In the last step the carbocation produced reacts with the halide ion to give the alkyl halide.
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
c)

Interpretation:
The product and the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Concept introduction:
In electrophilic addition reactions, the first step is the attack of the π electrons of the double bond on the H+ of the acid to yield a carbocation. One of the carbon in C=C gets attached to hydrogen while the other acquires a positive charge. In the second step, the carbocation formed can rearrange to give a more stable carbocation either by a hydride shift (shift of hydrogen atom with its electron pair) or by an alkyl shift (shift of an alkyl group with its electron pair) between neighboring carbons. In the last step the carbocation produced reacts with the halide ion to give the alkyl halide.
To predict:
The product and to show the complete arrow-pushing mechanism for the electrophilic reaction given which involves a carbocation rearrangement.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY-EBOOK>I<
- help 20arrow_forwardProvide the drawing of the unknown structure that corresponds with this data.arrow_forward20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forward
- 3) Draw a detailed mechanism and predict the product of the reaction shown? 1) EtMgBr 2) H3O+arrow_forwardHow to draw the mechanism for this reaction?arrow_forward> H₂C=C-CH2-CH3 B. H₂O Pt C. + H2 + H₂O H D. 16. Give the IUPAC name for each of the following: B. Cl Cl c. Cl Cl 17. Draw the line-angle formula for each of the following compounds: 1. phenol 2. 1,3-dichlorobenzene 3. 4-ethyltoluene < Previous Submit Assignment Next ▸arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
