
a)
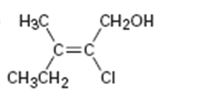
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
b)
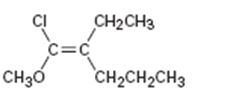
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
c)
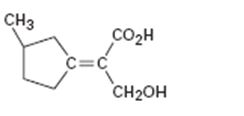
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
d)
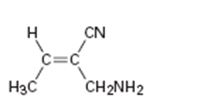
Interpretation:
To assign E or Z configuration for the compound given.
Concept introduction:
The two groups attached to the carbons in double bond are to be ranked first. The member that ranks higher can be determined by considering the atomic number of the first atom of the two substituents separately. The atom with highest atomic number gets the higher rank. If a decision cannot be made by considering the atomic number of the first atom in each substituent then the second, third, fourth atoms away from double bond are considered until the first difference is found. Multiple bonded atoms are considered as equivalent to the same number of single bonded atoms. The isomer that has the higher ranked groups on each carbon on the same side of the double bond is said to have Z configuration. If the higher ranked groups are on the opposite sides, the alkene is said to have E configuration.
To assign:
The configuration for the compound given as E or Z.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!

Chapter 7 Solutions
OWLv2 with Student Solutions Manual eBook, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card for McMurry's Organic Chemistry, 9th
- A mixture of C7H12O2, C9H9OCl, biphenyl and acetone was put together in a gas chromatography tube. Please decide from the GC resutls which correspond to the peak for C7,C9 and biphenyl and explain the reasoning based on GC results. Eliminate unnecessary peaks from Gas Chromatography results.arrow_forwardIs the molecule chiral, meso, or achiral? CI .CH3 H₂C CIarrow_forwardPLEASE HELP ! URGENT!arrow_forward
- Identify priority of the substituents: CH3arrow_forwardHow many chiral carbons are in the molecule? OH F CI Brarrow_forwardA mixture of three compounds Phen-A, Acet-B and Rin-C was analyzed using TLC with 1:9 ethanol: hexane as the mobile phase. The TLC plate showed three spots of R, 0.1 and 0.2 and 0.3. Which of the three compounds (Phen-A; Acet-B or Rin-C) would have the highest (Blank 1), middle (Blank 2) and lowest (Blank 3) spot respectively? 0 CH: 0 CH, 0 H.C OH H.CN OH Acet-B Rin-C phen-A A A <arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
