
Concept explainers
The diagram shows a "relaxation" oscillator. The charge
(a) The charge
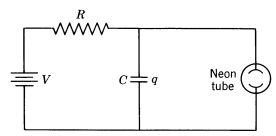
(b) Suppose the neon tube fires at
(c) Expand the periodic
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
Mathematical Methods in the Physical Sciences
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
Elementary Statistics
College Algebra (7th Edition)
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Thinking Mathematically (6th Edition)
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
- A smallish urn contains 16 small plastic bunnies - 9 of which are pink and 7 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X=6)[Select] (b) P(X>7) ≈ [Select]arrow_forward. Find how many years it takes for $1786 to grow to $2063 if invested at 2.6% annual interest compounded monthly. 12+arrow_forwardK=3, Gauss Seidel Fill in only 4 decimal places here in Canvas. Make sure in exam and homework, 6 decimal places are required. X1 = X2 = X3 =arrow_forward
- A smallish urn contains 25 small plastic bunnies - 7 of which are pink and 18 of which are white. 10 bunnies are drawn from the urn at random with replacement, and X is the number of pink bunnies that are drawn. (a) P(X = 5)=[Select] (b) P(X<6) [Select]arrow_forwardThe fox population in a certain region has an annual growth rate of 8 percent per year. It is estimated that the population in the year 2000 was 22600. (a) Find a function that models the population t years after 2000 (t = 0 for 2000). Your answer is P(t) = (b) Use the function from part (a) to estimate the fox population in the year 2008. Your answer is (the answer should be an integer)arrow_forwardrarrow_forward
- The solutions are 1 where x1 x2- ● Question 11 Solve: x 54 Give your answer as an interval. Question 12arrow_forwardA population of deer in Pierce County currently has 1875 deer, but due to urban development, the population is decreasing at a rate of 1.1% a year. a) Assuming this growth rate continues, find the formula for a function f(t) describing this population. b) In how many years will the population reach 1300? Do the problems on your own paper, show all your work, and submit your scanned work below. Choose File No file chosenarrow_forward● Question 7 Solve the equation. log2(3m - 5) = log2(m +8) m n = Question 8arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning

