
Concept explainers
Consider the following
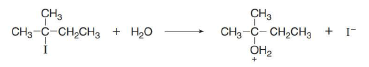
a. Draw a mechanism for this reaction using curved arrows.
b. Draw an energy diagram. Label the axes, the reactants, products,
c. Draw the structure of any transition states.
d. What is the rate equation for this reaction?
e. What happens to the reaction rate in each of the following instances? [1] The leaving group is changed from
(a)
Interpretation: The mechanism of the given reaction is to be drawn by the use of curved arrows.
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The electron rich chemical species that contains negative charge or lone pair of electrons are known as a nucleophile. In a nucleophilic substitution reaction, nucleophile takes the position of leaving group by attacking the electron deficient carbon atom.
Answer to Problem 7.64P
The mechanism of the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
Explanation of Solution
The structure of the given alkyl halide shows that carbon atom, on which bromine is present, is bonded to three other carbon atoms. Hence, the bromine atom is bonded to tertiary carbon atom and the given alkyl halide is
In
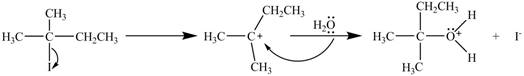
Figure 1
The mechanism of the given reaction is shown in Figure 1.
(b)
Interpretation: The energy diagram is to be drawn. The axes, reactants, products,
Concept introduction: The replacement or substitution of one functional group with another different functional group in any chemical reaction is termed as substitution reaction. The graphical representation of chemical reaction in which x-axis represents energy of the reaction and y-axis represents the reaction coordinate is called energy profile diagram.
Answer to Problem 7.64P
The energy diagram of the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
Explanation of Solution
In
The energy of products is equal to the energy of reactants. Therefore, the energy diagram of the given reaction is,
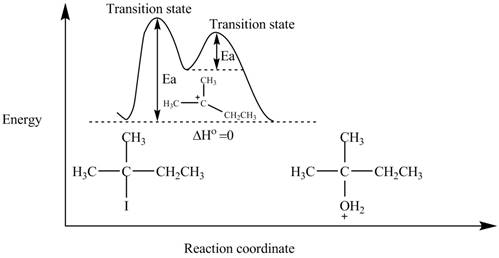
Figure 2
The x-axes of the energy diagram represent the energy of reactants and products and y-axes represent the reaction coordinate.
The energy diagram of the given reaction is shown in Figure 2.
(c)
Interpretation: The structure of the transition state is to be drawn.
Concept introduction: In
Answer to Problem 7.64P
The structure of the transition states is shown in Figure 3.
Explanation of Solution
In
Therefore, the transition states of the given reaction are,
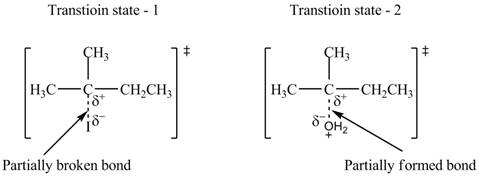
Figure 3
The structure of the transition states is shown in Figure 3.
(d)
Interpretation: The rate equation of the given reaction is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: The rate of
The rate of
Answer to Problem 7.64P
The rate equation of the given reaction is,
Explanation of Solution
The rate of
The rate of
The alkyl halide of given reaction is
Therefore, the rate equation of given reaction is,
The rate equation of the given reaction is,
(e)
Interpretation: The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is to be stated.
Concept introduction: The rate of
The rate of
Answer to Problem 7.64P
The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is,
[1] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[2] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[3] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[4] The rate of the reaction remains unchanged.
[5] The rate of the reaction increases by five times.
Explanation of Solution
[1]
The tertiary halide undergoes nucleophilic substitution by
[2]
The polar protic solvent favors
[3]
The tertiary halide undergoes nucleophilic substitution by
[4]
The rate of
The rate of
According the given statement, the concentration of
Therefore, the rate of the reaction remains unchanged when the concentration of
[5]
The rate of
The rate of
According the given statement, the concentration of
Therefore, the rate of the reaction increases by five times when the concentration
The change that occurs to the reaction rate in given instances is,
[1] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[2] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[3] The rate of the reaction will decrease.
[4] The rate of the reaction remains unchanged.
[5] The rate of the reaction increases by five times.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- 2. Provide reagents/conditions to accomplish the following syntheses. More than one step is required in some cases. a. H3C Br .CH3 H3C NH2arrow_forwarda. OH H₂N-O -Ph H+ acyclic productarrow_forwardeks.com/aleksogi/x/sl.exe/1o_u-IgNslkr7j8P3jH-IQs_pBanHhvTCeeBZbufuBYTI0Hz7m7D3ZS17Hd6m-HIl6n52njJN-TXdQA2X9yID-1SWQJTgnjARg30 111 States of Matter Understanding conceptual components of the enthalpy of solution 0/5 Ge A small amount of acetonitrile (CH, CN) is dissolved in a large amount of water. Imagine separating this process into the four stages sketched below. (These sketches show only a portion of the substances, so you can see the density and distribution of atoms and molecules in them.) CH,CN H₂O B 88 C Use these sketches to answer the questions in the table below. The enthalpy of solution AH is negative soln when CH3CN dissolves in water. Use this information to list the stages in order of increasing enthalpy. Would heat be absorbed or released if the system moved from Stage C to D? What force would oppose or favor the system moving from Stage C to D? Check all that apply. 1 absorbed O released neither absorbed nor released. none O ionic bonding force covalent bonding force…arrow_forward
- In a system with an anodic overpotential, the variation of ŋ as a function of the current density: 1. at low fields is linear 2. at higher fields, it follows Tafel's law Find the range of current densities for which the overpotential has the same value as when calculated for cases 1 and 2 (maximum relative difference of 5% with respect to the behavior for higher fields). To which overpotential range does this correspond? Data: 10 = 1.5 mA cm², T = 300°C, ẞ = 0.64, R = 8.314 J K 1 mol¹ and F = 96485 C mol-1.arrow_forwardIndicate 10.6 with only one significant figure.arrow_forwardIf I have 10 data points for variables x and y, when I represent y versus x I obtain a line with the equation y = mx + b. Is the slope m equal to dy/dx?arrow_forward
- The data for the potential difference of a battery and its temperature are given in the table. Calculate the entropy change in J mol-1 K-1 (indicate the formulas used).Data: F = 96485 C mol-1arrow_forwardIn a cell, the change in entropy (AS) can be calculated from the slope of the E° vs 1/T graph. The slope is equal to -AS/R, where R is the gas constant. Is this correct?arrow_forwardUsing the Arrhenius equation, it is possible to establish the relationship between the rate constant (k) of a chemical reaction and the temperature (T), in Kelvin (K), the universal gas constant (R), the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). This equation is widely applied in studies of chemical kinetics, and is also widely used to determine the activation energy of reactions. In this context, the following graph shows the variation of the rate constant with the inverse of the absolute temperature, for a given chemical reaction that obeys the Arrhenius equation. Based on the analysis of this graph and the concepts acquired about the kinetics of chemical reactions, analyze the following statements: I. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the temperature of the system. II. The activation energy (Ea) varies with the concentration of the reactants. III. The rate constant (K) varies proportionally with temperature. IV. The value of the…arrow_forward
- In an electrolytic cell, indicate the formula that relates E0 to the temperature T.arrow_forward-- 14:33 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 11. Compound A can transform into compound B through an organic reaction. From the structures below, mark the correct one: HO A تھے۔ די HO B ○ A) Compounds A and B are isomers. B) Both have the same number of chiral carbons. C) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 and H2O to form compound B. D) Compound A underwent a substitution reaction forming the intermediate chlorohydrin to obtain compound B. E) Compound A underwent an addition reaction of Cl2 forming the chloronium ion and then added methanol to obtain compound B. 60arrow_forward-- 14:40 A Candidate Identification docs.google.com 13. The compound 1-bromo-hex-2-ene reacts with methanol to form two products. About this reaction, mark the correct statement: OCH3 CH3OH Br OCH3 + + HBr A B A) The two products formed will have the same percentage of formation. B) Product B will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of an allylic carbocation. C) Product A will be formed by SN1 substitution reaction with the formation of a more stable carbocation than product B. D) Product A will be formed by an SN2 substitution reaction occurring in two stages, the first with slow kinetics and the second with fast kinetics. E) The two compounds were obtained by addition reaction, with compound B having the highest percentage of formation. 57arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
