
(a)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Answer to Problem 7.45P
Given the structure name is isopropyl bromide
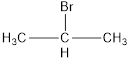
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
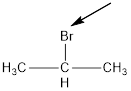
The bromide is in the middle carbon make it into a isopropyl.
Thus given the structure name is isopropyl bromide

(b)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
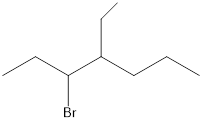
Given the structure name is 3-bromo-4-ethylheptane
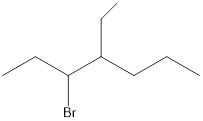
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
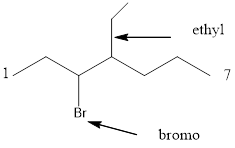
Starting from first carbon the bromide is in the third carbon and ethyl is in fourth carbon, and there are total of seven carbon so 3-bromo-4-ethylheptane.
Thus given the structure name is 3-bromo-4-ethylheptane
(c)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
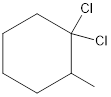
Given the structure name is 1, 1-dichloro-2-methylcyclohexane
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
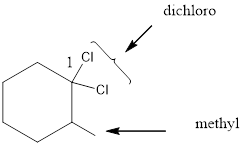
Starting from first carbon the two chlorine is in the first carbon and methyl is in second carbon, and there are total of six carbon and ring so 1, 1-dichloro-2-methylcyclohexane.
Thus Given the structure name is 1, 1-dichloro-2-methylcyclohexane

(d)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
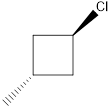
Given the structure name is trans-1-chloro-3-iodocyclobutane
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
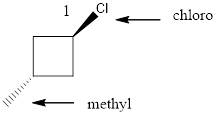
Starting from first carbon the chlorine is in the first carbon and methyl is in third carbon, and there are total of four carbon and ring so trans-1-chloro-3-iodocyclobutane.
Thus Given the structure name is trans-1-chloro-3-iodocyclobutane

(e)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
Given the structure name is 1-bromo-4-ethyl-3-fluorooctane
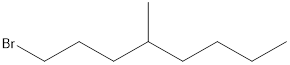
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
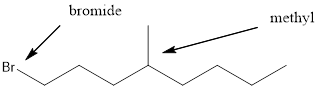
Starting from first carbon the bromide is in the first carbon and methyl is in fourth carbon, and there are total of eight carbon so 1-bromo-4-ethyl-3-fluorooctane.
Thus Given the structure name is 1-bromo-4-ethyl-3-fluorooctane

(f)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
Given the structure name is (3S)-3-iodo-2-methylnonane
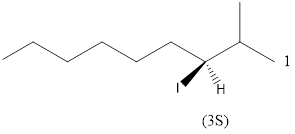
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
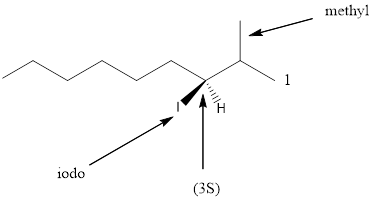
Starting from first carbon the iodo is in the third carbon and methyl is in second carbon, and there are total of nine carbon so (3S)-3-iodo-2-methylnonane.
Thus Given the structure name is (3S)-3-iodo-2-methylnonane

(g)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
Given the structure name is (1 R, 2R)-trans-1-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexane
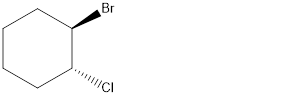
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
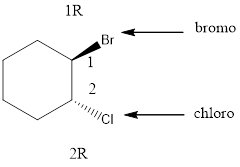
Starting from first carbon the chloro and bromo is in the first carbon and there are total of six carbon so (1 R, 2R)-trans-1-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexane.
Thus Given the structure name is (1 R, 2R)-trans-1-bromo-2-chlorocyclohexane
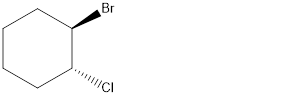
(h)
Interpretation:
To draw the given structure corresponding to each name.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl halides are organic molecules that contains a halogen atom X bonded to sp3 hybridized carbon atom. Alkyl halides are classified as primary (1°), secondary (2°), and tertiary (3°) depending on the number of carbons bonded to the carbon with the halogen. An alkyl halide is named as an alkane with a halogen substituent-that is, as a halo alkane. To name a halogen substituent, change the -ine ending of the name of the halogen to the suffix -o (chlorine-chloro).
Answer to Problem 7.45P
Given the structure name is (5R)-4, 4, 5-trichloro-3, 3-dimethyldecane
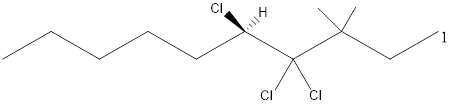
Explanation of Solution
To write the corresponding structure. To work backward from a name to the structure.
First find the parent name and draw it according to the number of carbons. Use the suffix to identify the functional group.
Then arrange the number of carbon in the chain. Finally add the substituent to the appropriate carbon.
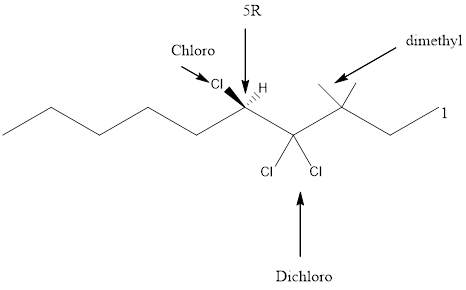
Starting from first carbon the chloro is in the fourth and fifth carbon and there are total of ten carbons so (5R)-4, 4, 5-trichloro-3, 3-dimethyldecane.
Thus Given the structure name is (5R)-4, 4, 5-trichloro-3, 3-dimethyldecane

Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
Organic Chemistry-Package(Custom)
- Determine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. NaN₃arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forwardCan I please get help with this?arrow_forward
- Use the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation to calculate pH of a buffer containing 0.050M benzoic acidand 0.150M sodium benzoate. The Ka of benzoic acid is 6.5 x 10-5arrow_forwardA. Draw the structure of each of the following alcohols. Then draw and name the product you would expect to produce by the oxidation of each. a. 4-Methyl-2-heptanol b. 3,4-Dimethyl-1-pentanol c. 4-Ethyl-2-heptanol d. 5,7-Dichloro-3-heptanolarrow_forwardWhat is the pH of a 1.0 L buffer made with 0.300 mol of HF (Ka = 6.8 × 10⁻⁴) and 0.200 mol of NaF to which 0.160 mol of NaOH were added?arrow_forward
- Can I please get help with this.arrow_forwardDetermine if the following salt is neutral, acidic or basic. If acidic or basic, write the appropriate equilibrium equation for the acid or base that exists when the salt is dissolved in aqueous solution. If neutral, simply write only NR. Be sure to include the proper phases for all species within the reaction. N₂H₅ClO₄arrow_forwardPlease help me with identifying these.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





