
Concept explainers
The Bunchberry
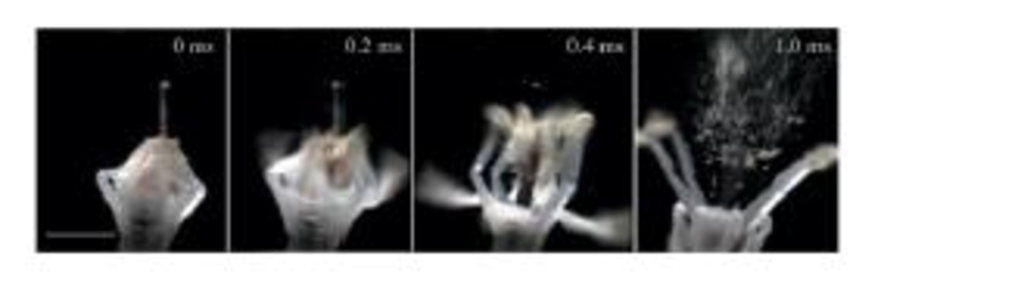
The bunchberry flower has the fastest-moving parts ever seen in a plant. Initially, the stamens are held by the petals in a bent position, storing energy like a coiled spring. As the petals release, the tips of the stamens fly up and quickly release a burst of pollen.
Figure P7. 72 shows the details of the motion. The tips of the stamens act like a catapult, flipping through a 60° angle; the times on the earlier photos show that this happens in just 0.30 ms. We can model a stamen tip as a 1.0-mm-Jong, 10 μg rigid rod with a 10 μg anther sac at one end and a pivot point at the opposite end. Though an oversimplification, we will model the motion by assuming the
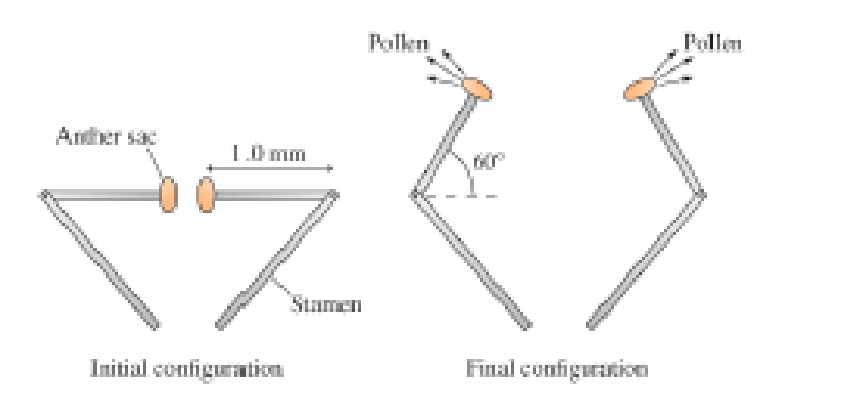
Figure P7.72
72. What is the angular acceleration of the anther sac during the motion?
A. 3.5 × 103 rad/s2
B. 7.0 × 103 rad/s2
C. 1.2 × 107 rad/s2
D. 2.3 × 107 rad/s2
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics
Introduction to Electrodynamics
The Cosmic Perspective (8th Edition)
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern Physics
Life in the Universe (4th Edition)
Glencoe Physical Science 2012 Student Edition (Glencoe Science) (McGraw-Hill Education)
- A force, P, is applied so that the two wheels contact each other. Each wheel spins at 300 rpm before contact. After 6 seconds of contact, wheel A reaches a final angular velocity of 60 rpm clockwise. What will be: A. The final angular velocity of wheel B? B. The angular acceleration of each wheel during contact?arrow_forwardA lawn mower has a flat, rod-shaped steel blade that rotates about its center. The mass of the blade is 0.65 kg and its length is 0.55 m. You may want to review (Pages 314 - 318) . a. What is the rotational energy of the blade at its operating angular speed of 3550 rpm? Express your answer using two significant figures. Kr = J B. If all of the rotational kinetic energy of the blade could be converted to gravitational potential energy, to what height would the blade rise? y= _____ marrow_forwardTwo horizontal rods are each held up by vertical strings tied to their ends. Rod 1 has length L and mass M; rod 2 has length 2L and mass 2M. Each rod then has one of its supporting strings cut, causing the rod to begin pivoting about the end that is still tied up. Which rod has a larger initial angular acceleration?A. Rod 1 B. Rod 2C. The initial angular acceleration is the same for both.arrow_forward
- 909090 A particle moves that is defined by the parametric equations x = 3t² - 1 y = t³ - 3t² + t - 3 (where x and y are in meters, and t is in seconds). a. Compute the angular velocity (rad/s) at t = 2 seconds.arrow_forwardAs shown, force F→2 acts half as far from the pivot as F→1 .What magnitude of F→2 causes the net torque on the rod to be zero?arrow_forwardTwo horizontal rods are each held up by vertical strings tied to their ends. Rod 1 has length L and mass M; rod 2 has length 24 and mass 2M. Each rod then has one of its supporting strings cut, causing the rod to begin pivoting about the end that is still tied up. Which rod has a larger initial angular acceleration? A. Rod 1 B. Rod 2 C. The initial angular acceleration is the same for both.arrow_forward
- Figure OQ10.8 shows a system of four particles joined by light, rigid rods. Assume a = b and M is larger than m. About which of the coordinate axes does the system have (i) the smallest and (ii) the largest moment of inertia? (a) the x axis (b) the y axis (c) the z axis. (d) The moment of inertia has the same small value for two axes. (e) The moment of inertia is the same for all three axes. Figure OQ10.8arrow_forwardA ball rolls to the left along a horizontal surface, up the slope, and then continues along a horizontal surface (Fig. P12.70). Sketch the angular speed and the magnitude of the angular acceleration of the ball as functions of time. FIGURE P12.70arrow_forwardA rotating objects angular position is given by (t) = (1.54t2 7.65t + 2.75) rad, where t is measured in seconds. Find a. the objects angular speed when t = 3.50 s and b. the magnitude of the angular acceleration when t = 3.50 s.arrow_forward
- A long, thin rod of mass m = 5.00 kg and length = 1.20 m rotates around an axis perpendicular to the rod with an angularspeed of 3.00 rad/s. a. What is the angular momentum of therod if the axis passes through the rods midpoint? b. What is theangular momentum of the rod if the axis passes through a pointhalfway between its midpoint and its end?arrow_forwardA cam of mass M is in the shape of a circular disk of diameter 2R with an off-center circular hole of diameter R is mounted on a uniform cylindrical shaft whose diameter matches that of the hole (Fig. P1 3.78). a. What is the rotational inertia of the cam and shaft around the axis of the shaft? b. What is the rotational kinetic energy of the cam and shaft if the system rotates with angular speed around this axis?arrow_forwardA pulsar is a rapidly rotating neutron star. The Crab nebula pulsar in the constellation Taurus has a period of 33.510-3s , radius 10.0 km, and mass 2.81030kg . The pulsar’s rotational period will increase over time due to the release of electromagnetic radiation, which doesn’t change its radius but reduces its rotational energy. (a) What is the angular momentum of the pulsar? (b) Suppose the angular velocity decreases at a rate of 1014rad/s2 . What is the torque on the pulsar?arrow_forward
 University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning




