
Concept explainers
The Bunchberry
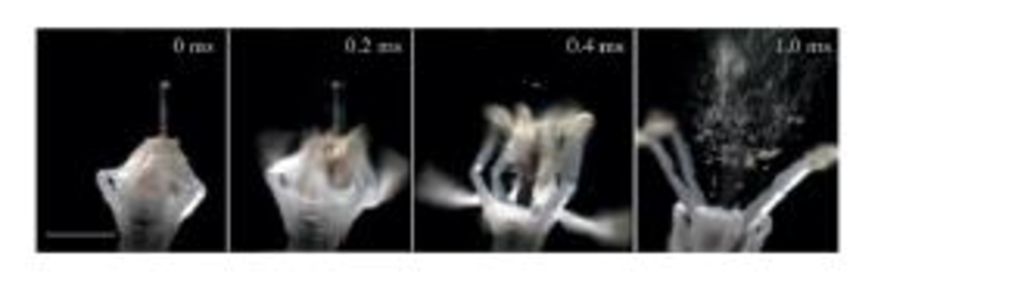
The bunchberry flower has the fastest-moving parts ever seen in a plant. Initially, the stamens are held by the petals in a bent position, storing energy like a coiled spring. As the petals release, the tips of the stamens fly up and quickly release a burst of pollen.
Figure P7. 72 shows the details of the motion. The tips of the stamens act like a catapult, flipping through a 60° angle; the times on the earlier photos show that this happens in just 0.30 ms. We can model a stamen tip as a 1.0-mm-Jong, 10 μg rigid rod with a 10 μg anther sac at one end and a pivot point at the opposite end. Though an oversimplification, we will model the motion by assuming the
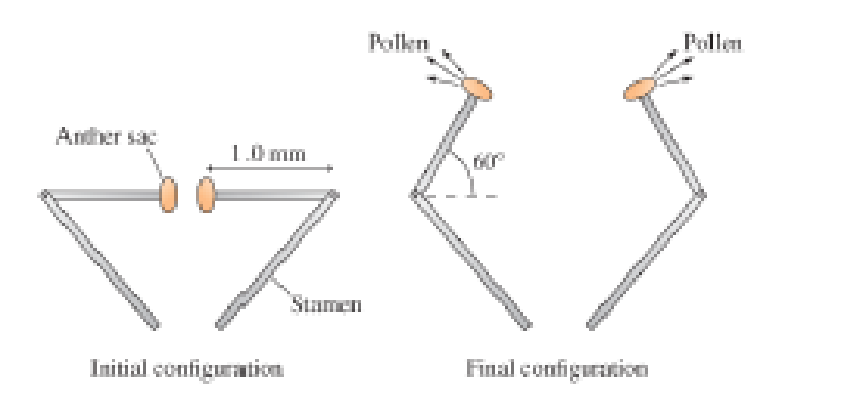
Figure P7.72
74. How large is the “straightening torque”? (You can omit gravitational forces from your calculation; the gravitational torque is much Jess than this.)
A. 2.3 × 10–7 N · m
B. 3.1 × 10–7 N · m
C. 2.3 × 10–5 N · m
D. 3.1 × 10–5 N · m
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 7 Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
Chemistry: An Introduction to General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry (13th Edition)
Campbell Biology (11th Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
- 1. The average KE and temperature in Kelvin of the molecules of a gas are related by the equation KE = 3/2 KT where k is the Boltzmann constant 1.38 x 10 m² kg s². The diagram shows the energy levels for a Hydrogen atom. Energy/eV 0.00 -1.51 3.39 13.58 Use this information to show that Hydrogen at room temperature will not emit light. 2. When hydrogen burns in oxygen 241.8 kJ of energy are released per mole. Show that this reaction can produce light.arrow_forward3. By using the fact that around any closed loop the sum of the EMFS = the sum of the PDs. Write equations for the two loops shown in the cct below. 40 ΔΩ I₂ 4V (loop1 20 (loop2) 2v I+12 Use these equations to show that the current flowing through the 20 resistor is 0.75Aarrow_forward5. A potential divider circuit is made by stretching a 1 m long wire with a resistance of 0.1 per cm from A to B as shown. 8V A 100cm B sliding contact 5Ω A varying PD is achieved across the 5 Q resistor by moving the slider along the resistance wire. Calculate the distance from A when the PD across the 5 Q resistor is 6 V.arrow_forward
- 4. A voltmeter with resistance 10 kQ is used to measure the pd across the 1 kQ resistor in the circuit below. 6V 5ΚΩ 1ΚΩ V Calculate the percentage difference between the value with and without the voltmeter.arrow_forward1. A 9V battery with internal resistance 5 2 is connected to a 100 2 resistor. Calculate: a. the Power dissipated in the 100 2 resistor b. The heat generated per second inside the battery. C. The rate of converting chemical to electrical energy by the battery. 2. A 230 V kettle is rated at 1800 W. Calculate the resistance of the heating element.arrow_forward2. If each of the resistors in the circuit below has resistance R show that the total resistance between A and B is 5R/11 A Barrow_forward
- 1. At 0°C a steel cable is 1km long and 1cm diameter when it is heated it expands and its resistivity increases. Calculate the change in resistance of the cable as it is heated from 0-20°C The temperature coefficient of resistance a, gives the fractional increase in resistance per °C. So increase in resistance AR = Ra.AT Where R, is the resistance at 0°C For steel a, 0.003 °C The coefficient of linear expansion a- gives the fractional increase in length per °C temperature rise. So increase in Length AL La-AT Where L, is the length at 0°C For steel a₁ = 12 x 10 °C-1 The resistivity of steel at 0°C = 1.2 x 10 Qmarrow_forward1. F E 6V 10 1.1. B a 6V b C C Apply Kirchoff's 1st law to point C for the circuit above Apply Kirchoff's 2nd Law to loops: a. ABCFA b. ABDEA C. FCDEF d. Find values for currents a,b and c Darrow_forward2. The results of the Rutherford experiment can be categorized in 3 statements. Fill in the missing words Most 11. Some III. A few State which result gives evidence that the nucleus is a. heavier than an alpha particle b. very small compared to the size of the atom c. positively charged 3. Using values in the diagram derive an expression for r .0 e marrow_forward
- 3. A 100 W light bulb is connected to 230 V mains supply by a cable with resistance 0.12. Determine the heat loss per second by the cable.arrow_forward1. The image shows electrons flowing in a conductor with cross sectional area 1mm². A electron flow • Add an arrow showing the direction of current. B • Which end has the highest potential? • Calculate the current when 1019 electrons flow through the wire in 10 s. If there are 1026 electrons per unit volume what is the drift velocity of the electrons?arrow_forwardpls helparrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





