
It requires 799 kJ of energy to break one mole of carbon-oxygen double bonds in carbon dioxide. What
Interpretation:
The energy required to rupture one mole of
Concept introduction:
Bohr developed a rule for quantization of energy that could be applicable to the electron of an atom in motion. By using this he derived a formula for energy levels of electron in H-atom.
Relation between frequency and wavelength is,
C is the speed of light.
h is Planck’s constant (
E is energy of light particle.
The distance between any two similar points of a wave is called wavelength
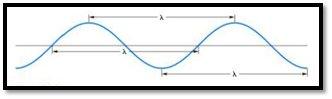
Figure 1
Frequency is defined as number of wavelengths of a wave that can pass through a point in one second.
Answer to Problem 7.108QP
The wavelength of light used to break per bond is
Explanation of Solution
To calculate: The wavelength of light used to break per bond.
The energy of each photon is calculated as follows,
The wave length of light used to break per bond is
The obtained wavelength is in range of near UV region of electromagnetic spectrum which corresponds to lyman series of H-atom. The minimum energy required in this region for transition corresponds to
The obtained energy is more than required energy to break the
By using the formula for energy levels of electron in H-atom, the wavelength of light used to break per bond was calculated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 7 Solutions
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Course List)
- So I'm working on molecular geometry. Can you help me with this stuff here and create three circles: one that's 120, one that’s 180, and one that’s 109.5?arrow_forwardCurved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Problem 164 of N Select to Add Arrows CHI CH 1 1 1 Parrow_forwardusing these can you help me , I guess convert them to lewis dit structures or full drawn out skeletal and I guess is that what would help me depict the bond angle.arrow_forward
- Please answer the questions and provide detailed explanation. Please also include the Hydrogens that are on the molecule to show how many signals there are.arrow_forwardCapp aktiv.com Part of Speech Table for Assi x Aktiv Learning App K Curved arrows are used to illustrate the flow of electrons. Using the provided starting and product structures, draw the curved electron-pushing arrows for the following reaction or mechanistic step(s). Be sure to account for all bond-breaking and bond-making steps. Problem 232 of 10 10: Mg Select to Add Arrows Br O H :0 CI:O H Mg THE + dy Undo Reset Done Brarrow_forwardPlease answer the question and provide a detailed drawing of the structure. If there will not be a new C – C bond, then the box under the drawing area will be checked. Will the following reaction make a molecule with a new C – C bond as its major product: Draw the major organic product or products, if the reaction will work. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning





