
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.6, Problem 100P
If the compression in the spring is 20 mm when the valve is open as shown, determine the normal force acting, on the cam lobe at C. Assume the cam and bearings at H, I, and J are smooth. The spring has a stiffness of 300 N/m.
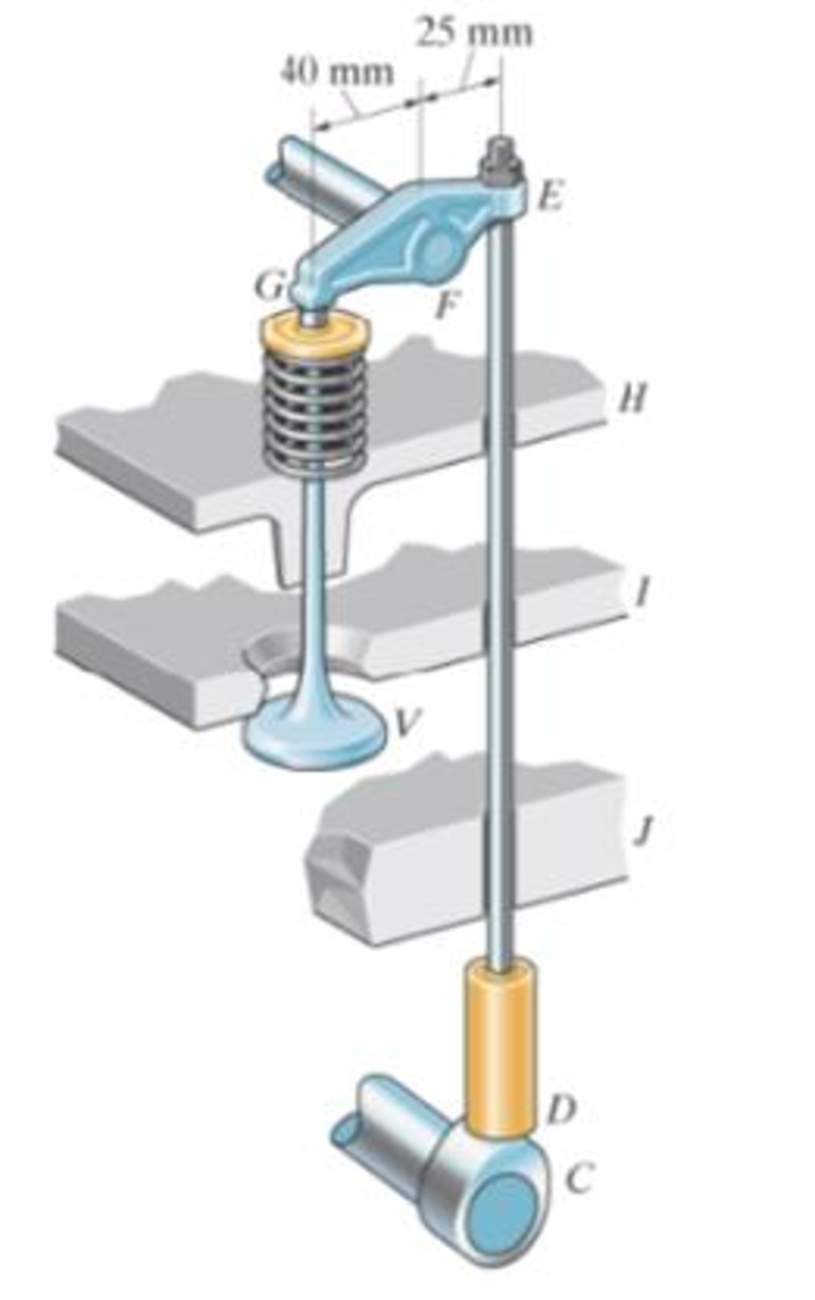
Prob. 6-100
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Answer all the calculations questions, if you are not not expert please don't attempt, don't use artificial intelligence
Please measure the size of the following object, and then
draw the front, top and side view in the AutoCAD
(including the printing)
just one arrow
for this one
30
Question 5
Calculate the Moment about the point B in
Nx m
B
500 N
A
2 m
1.2 m
0.8 m
300 N
7
Chapter 6 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 20 kN, P2 = 10 kN. Probs. 6-1/2Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 45 kN, P2 = 30 kN. Probs. 6-1/2
Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 6 kN, P2 = 9 kN. Probs. 6-9/10Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - If a = 6 ft, determine the greatest load P the...Ch. 6.3 - State whether the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. Probs. 6-18/19Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 9 kN, P2 = 15 kN. Probs. 6-20/21Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude of load P that can...Ch. 6.3 - Take P = 2 kN. Probs. 6-25/26Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the two loads...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, CD, and GC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GH, BC, and BG of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BF, BG, and AB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members JK, CJ, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Also, determine the proper placement x of the hook...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and B....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at D. Prob. F6-20Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - The block weighs 100 lb. Prob. 6-62Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - The suspended cylinder has a mass of 75 kg. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - There is a hinge (pin) at D. Determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P exerted on each of the...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force the load creates in member DB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force developed on the...Ch. 6.6 - Also, find the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the guy cable AI and the...Ch. 6.6 - When the walking beam ABC is horizontal, the force...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - It consists of two toggles ABC and DBF, which are...Ch. 6.6 - The 600-N load is applied to the pin. Prob. 6-89Ch. 6.6 - If the wheel at A exerts a normal force of FA = 80...Ch. 6.6 - The shovel load has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force P that is exerted...Ch. 6.6 - If each coin weighs 0.0235 lb, determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Assuming the blades are pin connected at B and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - The cable is attached to D, passes over the smooth...Ch. 6.6 - The grip at B on member DAB resists both...Ch. 6.6 - If the compression in the spring is 20 mm when the...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder AB...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has a stiffness of k = 6 kN/m. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - If d = 0.75 ft and the spring has an unstretched...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with...Ch. 6.6 - when the mechanism is in the position shown. The...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 110PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 111PCh. 6.6 - If the sprig has a stiffness of k = 15 lb/in., and...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - If only vertical forces are supported at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given that an L-shaped member (OAB) can rotate about OA, determine the moment vector created by the force about the line OA at the instant shown in the figure below. OA lies in the xy-plane, and the AB part is vertical. Express your answer as a Cartesian vector.arrow_forwardDetermine the magnitude of the moment created by the force about the point A.arrow_forward= MMB 241- Tutorial 1.pdf 2/3 80% + + 10. Determine a ats = 1 m v (m/s) 4 s (m) 2 11. Draw the v-t and s-t graphs if v = 0, s=0 when t=0. a (m/s²) 2 t(s) 12. Draw the v-t graph if v = 0 when t=0. Find the equation v = f(t) for each a (m/s²) 2 segment. 2 -2 13. Determine s and a when t = 3 s if s=0 when t = 0. v (m/s) 2 t(s) t(s) 2arrow_forward
- Q.5) A cylinder is supported by spring AD and cables AB and AC as shown. The spring has an at rest length (unstretched length) of 4 meters. If the maximum allowable tension in cables AB and AC is 200 N, determine (a) the largest mass (kg) of cylinder E the system can support, (b) the necessary spring constant (stiffness) to maintain equilibrium, and (b) the tension (magnitude) in each cable when supporting the maximum load found in part (a). B 4 m 3 m A E 1 m 3 m D 5 marrow_forwardDetermine the moment created by the force about the point O. Express your answer as a Cartesian vector.arrow_forward4. An impeller rotating at 1150 rpm has the following data: b, = 1 ¼ in., b2 = ¾ in., d, = 7 in., d2 = 15 in., B1 = 18", B2 = 20°, cross-sectional area A = Db if vane thickness is neglected. Assuming radial inlet flow, determine the theoretical capacity in gpm head in ft horsepower 5. If the impeller in Problem (4) develops an actual head of 82 ft and delivers 850 gpm at the point of maximum efficiency and requires 22 BHP. Determine overall pump efficiency virtual velocities V2 and W2arrow_forward
- (30 pts) Problem 1 A thin uniform rod of mass m and length 2r rests in a smooth hemispherical bowl of radius r. A moment M mgr 4 is applied to the rod. Assume that the bowl is fixed and its rim is in the horizontal plane. HINT: It will help you to find the length l of that portion of the rod that remains outside the bowl. M 2r a) How many degrees of freedom does this system have? b) Write an equation for the virtual work in terms of the angle 0 and the motion of the center of mass (TF) c) Derive an equation for the variation in the position of the center of mass (i.e., Sŕƒ) a. HINT: Use the center of the bowl as the coordinate system origin for the problem. d) In the case of no applied moment (i.e., M 0), derive an equation that can be used to solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation e) In the case of an applied moment (i.e., M = mgr = -) derive an equation that can be used to 4 solve for the equilibrium angle of the rod. DO NOT solve the equation. f) Can…arrow_forwardPlease show all work step by steparrow_forwardCopyright 2013 Pearson Education, publishing as Prentice Hall 2. Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal cutters exert on the smooth cable C if 100-N forces are applied to the handles. The jaws are pinned at E and A, and D and B. There is also a pin at F. E 400 mm 15° D B 30 mm² 80 mm/ 20 mm 15° $15° 20 mm 400 mm 15° 100 N 100 N 15°arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Mechanical SPRING DESIGN Strategy and Restrictions in Under 15 Minutes!; Author: Less Boring Lectures;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dsWQrzfQt3s;License: Standard Youtube License