
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
thumb_up100%
Chapter 6.3, Problem 1PP
In each case, calculate the support reactions and then draw the free-body diagrams of joints A, B, and C of the truss.
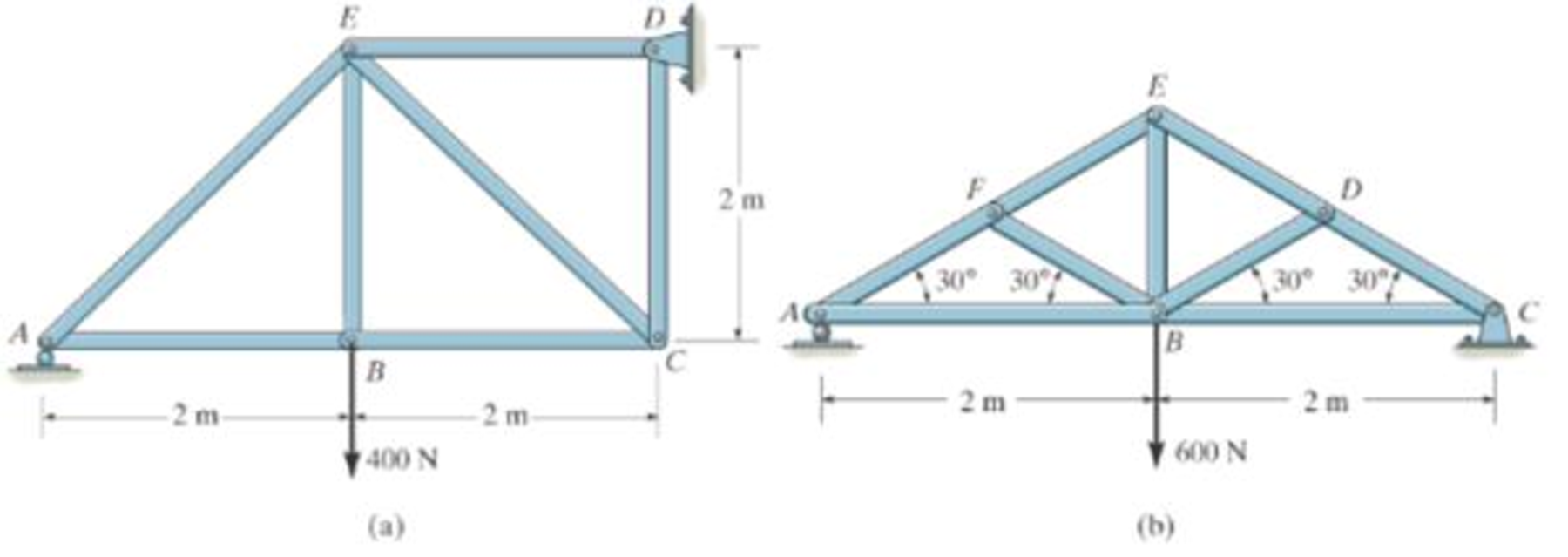
Prob. P6-1
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule08:39
Students have asked these similar questions
=
MMB 241 Tutorial 2.pdf
3/3
75%
+ +
6. A particle is traveling along the parabolic path y = 0.25 x². If x = 8 m, vx=8 m/s, and ax=
4 m/s² when t = 2 s, determine the magnitude of the particle's velocity and acceleration at
this instant.
y = 0.25x²
-x
7. Determine the speed at which the basketball at A must be thrown at the angle of 30° so
that it makes it to the basket at B.
30°
-x
1.5 m
B
3 m
-10 m-
8. The basketball passed through the hoop even though it barely cleared the hands of the
player B who attempted to block it. Neglecting the size of the ball, determine the
2
Adhesives distribute loads across the interface, whereas fasteners create areas of localized stresses.
True or False
A continuous column flash system is separating 100 kmol/h of a saturated liquid feed that is 45 mol% methanol and 55 mol% water at 1.0 atm. Operate with L/V = 1.5 and the outlet bottoms at xN = 0.28.
Find the values of FL, FV, y1, and the number of equilibrium stages required.
Find the value of Q used to vaporize FV.
For a normal flash with the same feed and the same V/F, find the values of x and y.
Chapter 6 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 20 kN, P2 = 10 kN. Probs. 6-1/2Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 45 kN, P2 = 30 kN. Probs. 6-1/2
Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 6 kN, P2 = 9 kN. Probs. 6-9/10Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - If a = 6 ft, determine the greatest load P the...Ch. 6.3 - State whether the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. Probs. 6-18/19Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 9 kN, P2 = 15 kN. Probs. 6-20/21Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude of load P that can...Ch. 6.3 - Take P = 2 kN. Probs. 6-25/26Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the two loads...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, CD, and GC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GH, BC, and BG of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BF, BG, and AB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members JK, CJ, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Also, determine the proper placement x of the hook...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and B....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at D. Prob. F6-20Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - The block weighs 100 lb. Prob. 6-62Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - The suspended cylinder has a mass of 75 kg. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - There is a hinge (pin) at D. Determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P exerted on each of the...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force the load creates in member DB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force developed on the...Ch. 6.6 - Also, find the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the guy cable AI and the...Ch. 6.6 - When the walking beam ABC is horizontal, the force...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - It consists of two toggles ABC and DBF, which are...Ch. 6.6 - The 600-N load is applied to the pin. Prob. 6-89Ch. 6.6 - If the wheel at A exerts a normal force of FA = 80...Ch. 6.6 - The shovel load has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force P that is exerted...Ch. 6.6 - If each coin weighs 0.0235 lb, determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Assuming the blades are pin connected at B and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - The cable is attached to D, passes over the smooth...Ch. 6.6 - The grip at B on member DAB resists both...Ch. 6.6 - If the compression in the spring is 20 mm when the...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder AB...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has a stiffness of k = 6 kN/m. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - If d = 0.75 ft and the spring has an unstretched...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with...Ch. 6.6 - when the mechanism is in the position shown. The...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 110PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 111PCh. 6.6 - If the sprig has a stiffness of k = 15 lb/in., and...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - If only vertical forces are supported at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Given a persons year of birth, the Birthday Wizard can compute the year in which the persons nth birthday will ...
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
The ________ object is assumed to exist and it is not necessary to include it as an object when referring to it...
Web Development and Design Foundations with HTML5 (8th Edition)
Determine the magnitude of the resultant force and its direction measured counterclockwise from the positive x ...
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Porter’s competitive forces model: The model is used to provide a general view about the firms, the competitors...
Management Information Systems: Managing The Digital Firm (16th Edition)
What is a local variable? What statements are able to access a local variable?
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A beer still is being used to separate ethanol from water at 1.0 atm. The saturated liquid feed flow rate is F = 840.0 kmol/h. The feed is 44.0 mol% ethanol. The saturated vapor steam is pure water with ratio of steam flow rate S to feed rate, S/F = 2/3. We desire a bottoms product that is 4.0 mol% ethanol. CMO is valid. Find the mole fraction of ethanol in the distillate vapor, yD,E. Find the number of equilibrium stages required. If the feed is unchanged and the S/F ratio is unchanged, but the number of stages is increased to a very large number, what is the lowest bottoms mole fraction of ethanol that can be obtained?arrow_forward3.1 Convert the following base-2 numbers to base-10: (a) 1011001, (b) 110.0101, and (c) 0.01011.arrow_forwardConsider the forces acting on the handle of the wrench in (Figure 1). a) Determine the moment of force F1={−F1={−2i+i+ 4 jj −−8k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures. b) Determine the moment of force F2={F2={3i+i+ 7 jj −−6k}lbk}lb about the zz axis. Express your answer in pound-inches to three significant figures.arrow_forward
- I need you to explain each and every step (Use paper)arrow_forwardCalculate the Moment About the Point A -20"- 5 lb 40 N D 1.5 m 40 N 4.5 m A 15 lb. 150 mm 52 N 5 12 100 mm 15 lb. 26 lb. 12 5 34 lb. 13 8 15 77777 36 lb.arrow_forwardCalculate the Moment About the Point A -20"- 5 lb 40 N D 1.5 m 40 N 4.5 m A 15 lb. 150 mm 52 N 5 12 100 mm 15 lb. 26 lb. 12 5 34 lb. 13 8 15 77777 36 lb.arrow_forward
- Formala for Hunzontal component= + cos & Vertical Component: Fsin t Find the vertical and horizontal components for the figure bellow: 30° 200 N 77 200 cos 30 = 173 N // 200 sin 30 = 100 N YA a₂+b₂ b₂ (b₁,b₂) a+b 20haits (a+b₁,a+b) Magnitude a and b a = lbl = 2o unite rugle of vector a wt Horisontal Axis = 30 11 vector & wt Honzontal Axis - 60° b b a= |a| Cas 30 a2 (a1, a2) ag = 10 bx = /b/ cos a 1 20 cos 80 = 17.32 Sia 30 = 20 sin 30. 60 = 10 = 20 Cos 60 = It by = 161 sin 60 = 20 sia 60 = 17.32 b₁ Rx ax +bx = 17.32 +10=2732 a₁ a₁+b₁ X By = ou + by= + + by = 10 + 17.32 =27.32 Magnitude = 38.637 Find the Vector a +b the Resultans The angle of the vector with the horizontal axle is 30 degrees while the angle of the vector b is 60 degrees. The magnitude of both vectors is 20 (units) angle of the Resultant vector = tam- " (14) 45arrow_forwardThe net force exerted on the piston by the exploding fuel-air mixture and friction is 5 kN to the left. A clockwise couple M = 200 N-m acts on the crank AB. The moment of inertia of the crank about A is 0.0003 kg-m2 . The mass of the connecting rod BC is 0.36 kg, and its center of mass is 40 mm from B on the line from B to C. The connecting rod’s moment of inertia about its center of mass is 0.0004 kg-m2 . The mass of the piston is 4.6 kg. The crank AB has a counterclockwise angular velocity of 2000 rpm at the instant shown. Neglect the gravitational forces on the crank, connecting rod, and piston – they still have mass, just don’t include weight on the FBDs. What is the piston’s acceleration?arrow_forwardSolve only no 1 calculations,the one with diagram,I need handwritten expert solutionsarrow_forward
- Problem 3 • Compute the coefficient matrix and the right-hand side of the n-parameter Ritz approximation of the equation d du (1+x)· = 0 for 0 < x < 1 dx dx u (0) = 0, u(1) = 1 Use algebraic polynomials for the approximation functions. Specialize your result for n = 2 and compute the Ritz coefficients.arrow_forwardFinite Element Analysis. Solve step by steparrow_forwardDraw the top view In autoCAD from graphicsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY