
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780133918922
Author: Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 6.6, Problem 93P
Determine the compressive force P that is exerted on the piston for equilibrium as a function of θ. Plot the results of P (vertical axis) versus θ (horizontal axis 0° ≤ θ ≤ 90°.
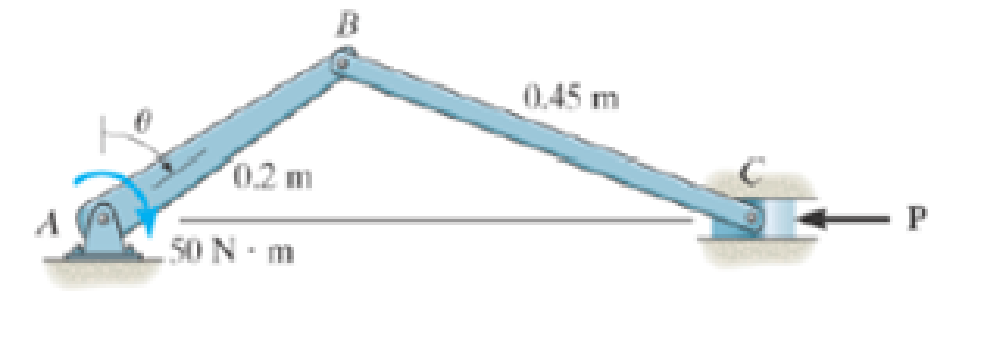
Prob. 6-93
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3-141
(3-113)
I just want to know the units of C_dot. Would it be rad/sec?
Chapter 6 Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Ch. 6.3 - In each case, calculate the support reactions and...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in each truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the greatest load P that can be applied...Ch. 6.3 - Identify the zero-force members in the truss....Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 20 kN, P2 = 10 kN. Probs. 6-1/2Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 45 kN, P2 = 30 kN. Probs. 6-1/2
Ch. 6.3 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss,...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 6 kN, P2 = 9 kN. Probs. 6-9/10Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the Pratt...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Members AB and BC can each support a maximum...Ch. 6.3 - If a = 6 ft, determine the greatest load P the...Ch. 6.3 - State whether the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.3 - If the maximum force that any member can support...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 10 kN, P2 = 8 kN. Probs. 6-18/19Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Set P1 = 9 kN, P2 = 15 kN. Probs. 6-20/21Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the double...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the force in each member of the truss in...Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude of load P that can...Ch. 6.3 - Take P = 2 kN. Probs. 6-25/26Ch. 6.3 - Determine the maximum magnitude P of the two loads...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CF, and FE....Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if the members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members DC, HC, and HI of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members ED, EH, and GH of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HG, HE and DE of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, HI, and CH of...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GF, CD, and GC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members GH, BC, and BG of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members EF, CF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members AF, BF, and BC, and...Ch. 6.4 - State if these members are in tension or...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CF, and CG and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force developed in members FE, EB,...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, HC, and HG....Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, GJ, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BE, EF, and CB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BF, BG, and AB, and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members BC, CH, GH, and CG...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members CD, CJ, and KJ and...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members JK, CJ, and CD of...Ch. 6.4 - Determine the force in members HI, FI, and EF of...Ch. 6.6 - In each case, identify any two-force members, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P needed to hold the 60-lb...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - If a 100-N force is applied to the handles of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the normal force that the 100-lb plate A...Ch. 6.6 - Also, determine the proper placement x of the hook...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and B....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at D. Prob. F6-20Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at A and C....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at C. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at E. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the components of reaction at D and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 100-lb...Ch. 6.6 - The block weighs 100 lb. Prob. 6-62Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 50-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P required to hold the 150-kg...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at supports A and B. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - The suspended cylinder has a mass of 75 kg. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports A, C, and...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant force at pins A, B, and C...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the reactions at the supports at A, E,...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - There is a hinge (pin) at D. Determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force P exerted on each of the...Ch. 6.6 - The toggle clamp is subjected to a force F at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force the load creates in member DB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force developed on the...Ch. 6.6 - Also, find the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Also, what are the horizontal and vertical...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the guy cable AI and the...Ch. 6.6 - When the walking beam ABC is horizontal, the force...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force that the jaws J of the metal...Ch. 6.6 - It consists of two toggles ABC and DBF, which are...Ch. 6.6 - The 600-N load is applied to the pin. Prob. 6-89Ch. 6.6 - If the wheel at A exerts a normal force of FA = 80...Ch. 6.6 - The shovel load has a mass of 1.25 Mg and a center...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the compressive force P that is exerted...Ch. 6.6 - If each coin weighs 0.0235 lb, determine the...Ch. 6.6 - Assuming the blades are pin connected at B and the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the total force he must exert on bar AB...Ch. 6.6 - The cable is attached to D, passes over the smooth...Ch. 6.6 - The grip at B on member DAB resists both...Ch. 6.6 - If the compression in the spring is 20 mm when the...Ch. 6.6 - If a clamping force of 300 N is required at A,...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 350 N is applied to the handle...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in the hydraulic cylinder AB...Ch. 6.6 - The spring has a stiffness of k = 6 kN/m. Prob....Ch. 6.6 - If d = 0.75 ft and the spring has an unstretched...Ch. 6.6 - If a force of F = 50 lb is applied to the pads at...Ch. 6.6 - If there is a 300-kg stone in the bucket, with...Ch. 6.6 - when the mechanism is in the position shown. The...Ch. 6.6 - Prob. 110PCh. 6.6 - Prob. 111PCh. 6.6 - If the sprig has a stiffness of k = 15 lb/in., and...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - Through this arrangement, a small weight can...Ch. 6.6 - If only vertical forces are supported at the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in each member of the truss...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in member GJ and GC of the...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the force in members GF, FB, and BC of...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the horizontal and vertical components...Ch. 6.6 - Determine the resultant forces at pins B and C on...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- (read image)arrow_forwardQu 2 Schematically plot attractive, repulsive, and net energies versus interatomic separation for two atoms or ions. Note on this plot the equilibrium separation (distance) ro and the bonding energy Eo. Qu 3 How many atoms (or molecules) are in one mole of the substance? Qu 4 Mole, in the context of this book, is taken in units of gram-mole. On this basis, how many atoms are there in a pound-mole of a substance? Qu 5 The atomic radii of Mg* and F ions are 0.072 and 0.133 nm, respectively. Calculate the force of attraction between these two ions at their equilibrium interionic separation (i.e., when the ions just touch one another). What is the force of repulsion at this same separation distance?show all work step by step problems formulaarrow_forwardQu 4 Silver has FCC crystal structure at room temperature, and a lattice constant, a, of 0.407 nm. Draw a reduced sphere silver unit cell in the grids provided below, clearly label the lattice dimensions. Within the unit cell you drew, shade the (1 0 0) plane. How many atoms are contained within the (1 0 0) plane? Calculate the area of (1 0 0) plane in [nm?]. Express your answer in [nm?] to three significant figures. Calculate the planar density of the (1 0 0) plane in [atoms/nm?]. Express the answer in atoms/nm to three significant figures. show all work step by steparrow_forward
- Can I get help on this question?arrow_forwardDuring some actual expansion and compression processes in piston–cylinder devices, the gases have been observed to satisfy the relationship PVn = C, where n and C are constants. Calculate the work done when a gas expands from 350 kPa and 0.03 m3 to a final volume of 0.2 m3 for the case of n = 1.5. The work done in this case is kJ.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide contained in a piston–cylinder device is compressed from 0.3 to 0.1 m3. During the process, the pressure and volume are related by P = aV–2, where a = 6 kPa·m6. Calculate the work done on carbon dioxide during this process. The work done on carbon dioxide during this process is kJ.arrow_forward
- The volume of 1 kg of helium in a piston–cylinder device is initially 5 m3. Now helium is compressed to 3 m3 while its pressure is maintained constant at 130 kPa. Determine the initial and final temperatures of helium as well as the work required to compress it, in kJ. The gas constant of helium is R = 2.0769 kJ/kg·K. The initial temperature of helium is K. The final temperature of helium is K. The work required to compress helium is kJ.arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder device initially contains 0.4 kg of nitrogen gas at 160 kPa and 140°C. Nitrogen is now expanded isothermally to a pressure of 80 kPa. Determine the boundary work done during this process. The properties of nitrogen are R= 0.2968 kJ/kg-K and k= 1.4. N₂ 160 kPa 140°C The boundary work done during this process is KJ.arrow_forward! Required information An abrasive cutoff wheel has a diameter of 5 in, is 1/16 in thick, and has a 3/4-in bore. The wheel weighs 4.80 oz and runs at 11,700 rev/min. The wheel material is isotropic, with a Poisson's ratio of 0.20, and has an ultimate strength of 12 kpsi. Choose the correct equation from the following options: Multiple Choice о σmax= (314) (4r2 — r²) - о σmax = p² (3+) (4r² + r²) 16 σmax = (314) (4r² + r²) σmax = (314) (4² - r²)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY
Physics 33 - Fluid Statics (1 of 10) Pressure in a Fluid; Author: Michel van Biezen;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=mzjlAla3H1Q;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY