
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
The products of the proton transfer reaction shown below is to be drawn.
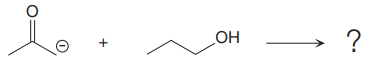
Concept introduction:
In a proton transfer reaction, Bronsted-Lowry base reacts with Bronsted-Lowry acid. Here, Bronsted-Lowry acid donates a proton and forms a conjugate base while Bronsted-Lowry base accepts a proton and forms a conjugate acid. The proton transfer reaction consists of a single elementary step.
(b)
Interpretation:
A free energy diagram for the following reaction, indicating whether it is endothermic or exothermic, is to be drawn.

Concept introduction:
When comparing two acids, the acid with the lower
A reaction tends to be spontaneous if
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Problem 54, could you please explain it in detail? Thank you! Step by step, I'm really confused, so please don't make it overly complex. My question is to visually draw it out and demonstrate it to me; I'm confused about that problem, please (not just in words) but demonstrate it to me in all due essence (visually) with descriptions.arrow_forwardExplain the types of electromeric effects +E and -E.arrow_forwardBriefly describe the electromeric effect (Organic Chemistry)arrow_forward
- Draw the major product of this reaction. Ignore inorganic byproducts. Assume that the water side product is continuously removed to drive the reaction toward products. (CH3)2NH, TSOH Drawingarrow_forwardSo, the first image is what I'm trying to understand regarding my approach. The second image illustrates my teacher's method, and the third image includes my notes on the concepts behind these types of problems.arrow_forwardHAND DRAWarrow_forward
- Draw a mental model for calcium chloride mixed with sodium phosphatearrow_forwardhere is my question (problem number 20) please explain to me thanks!arrow_forwardThe bromination of anisole is an extremely fast reaction. Complete the resonance structures of the intermediate arenium cation for the reaction (Part 1), and then answer the question that follows (Part 2).arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
