
(a) Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of
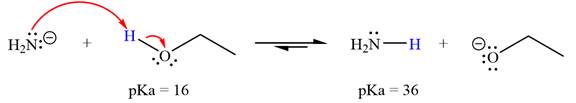
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(b)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of the acetate ion
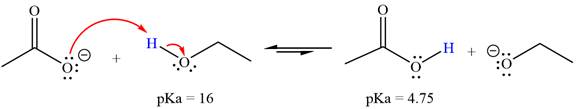
Acetic acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(c)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving chloride ion
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of chloride ion
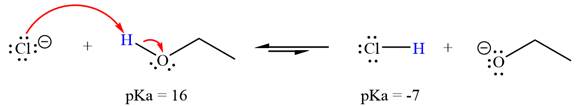
Hydrochloric acid,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(d)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving phenoxide ion (
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of phenoxide ion (
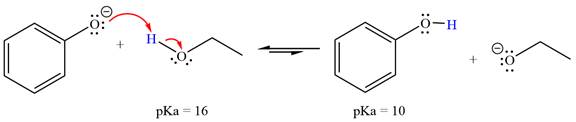
Phenol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(e)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of cyanide ion
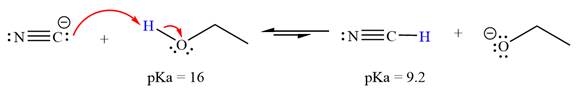
Acetylene,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
(f)
Interpretation:
It is to be determined whether the given reactant is suitable for a reaction involving ethanol as a solvent with respect to leveling effect.
Concept introduction:
The solvent affects the properties of bases and acids. This effect is referred as leveling effect. For an acid-base reaction, the basicity of the solvent levels or limits the strength of the strong acid. Similarly, the acidity of the solvent levels the strength of the strong base. With respect to the leveling effect, a solvent is unsuitable for a particular reactant R if R is a stronger acid that the solvent’s conjugate acid (i.e., R has the lower pKa) or if R is a stronger base than the solvent’s conjugate base (i.e., the conjugate acid of R has a higher pKa than the solvent).
Answer to Problem 6.45P
With respect to the leveling effect, ethanol is not a suitable solvent for a reaction involving
Explanation of Solution
The reaction of propyl group
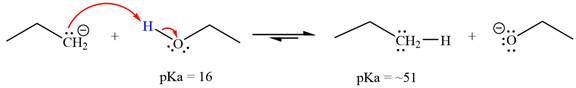
Ethanol,
The solvent effect on the reactant is determined with respect to the leveling effect.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Organic Chemistry: Principles and Mechanisms (Second Edition)
- Please draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forwardA 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardFirefly luciferin exhibits three rings. Identify which of the rings are aromatic. Identify which lone pairs are involved in establishing aromaticity. The lone pairs are labeled A-D below.arrow_forward
- A 0.10 M solution of acetic acid (CH3COOH, Ka = 1.8 x 10^-5) is titrated with a 0.0250 M solution of magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2). If 10.0 mL of the acid solution is titrated with 10.0 mL of the base solution, what is the pH of the resulting solution?arrow_forwardGiven a complex reaction with rate equation v = k1[A] + k2[A]2, what is the overall reaction order?arrow_forwardPlease draw the structure in the box that is consistent with all the spectral data and alphabetically label all of the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. The integrations are computer generated and approximate the number of equivalent protons. Molecular formula: C13H1802 14 13 12 11 10 11 (ppm) Structure with assigned H peaks 2.08 3.13arrow_forward
- CHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the steady-state approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. One of the approximation methods for solving the rate equation is the limiting or determining step approximation method. Explain what it consists of.arrow_forwardCHEMICAL KINETICS. Indicate the approximation methods for solving the rate equation.arrow_forward
- TRANSMITTANCE เบบ Please identify the one structure below that is consistent with the 'H NMR and IR spectra shown and draw its complete structure in the box below with the protons alphabetically labeled as shown in the NMR spectrum and label the IR bands, including sp³C-H and sp2C-H stretch, indicated by the arrows. D 4000 OH LOH H₂C CH3 OH H₂C OCH3 CH3 OH 3000 2000 1500 HAVENUMBERI-11 1000 LOCH3 Draw your structure below and label its equivalent protons according to the peak labeling that is used in the NMR spectrum in order to assign the peaks. Integrals indicate number of equivalent protons. Splitting patterns are: s=singlet, d=doublet, m-multiplet 8 3Hb s m 1Hd s 3Hf m 2Hcd 2Had 1He 鄙视 m 7 7 6 5 4 3 22 500 T 1 0arrow_forwardRelative Transmittance 0.995 0.99 0.985 0.98 Please draw the structure that is consistent with all the spectral data below in the box and alphabetically label the equivalent protons in the structure (Ha, Hb, Hc ....) in order to assign all the proton NMR peaks. Label the absorption bands in the IR spectrum indicated by the arrows. INFRARED SPECTRUM 1 0.975 3000 2000 Wavenumber (cm-1) 1000 Structure with assigned H peaks 1 3 180 160 140 120 100 f1 (ppm) 80 60 40 20 0 C-13 NMR note that there are 4 peaks between 120-140ppm Integral values equal the number of equivalent protons 10.0 9.0 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0 3.0 2.0 1.0 0.0 fl (ppm)arrow_forwardCalculate the pH of 0.0025 M phenol.arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

