
Concept explainers
A concrete mix includes the following ingredients per cubic foot:
a. Cement = 25 lb
b. Water = 11 lb
c. No admixture
Table P6.31 shows possible changes that can be made to the mix ingredients. Indicate in the appropriate boxes in the table what will happen in each case for the workability and the ultimate compressive strength as increase, decrease, or approximately the same. 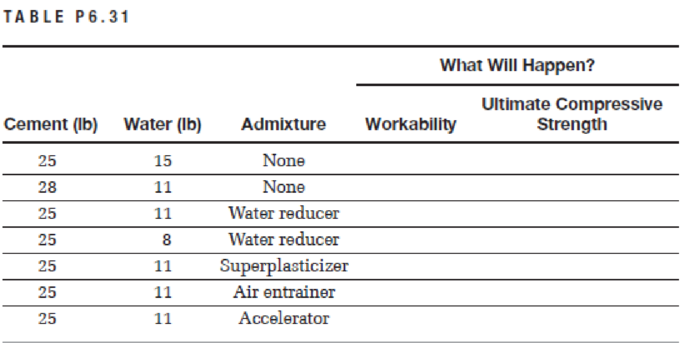
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

Chapter 6 Solutions
Materials for Civil and Construction Engineers (4th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Modern Database Management
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Computer Science: An Overview (13th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Starting Out with C++ from Control Structures to Objects (9th Edition)
- 4. Draw a free body diagram of the loading and forces. Solve for the reaction A at the wall support. Check your answer using the summation of forces. 10k A w=2 k/ft 40ft 10ft 5karrow_forwardA reinforced concrete beam with b=300mm, h=670mm,and d=600 mm, having a span of 7.3 m, can be considered as a fully fixed at the left support and simply supported at the right end. It is reinforced for positive bending with 8-16 and for negative bending with 4816 plus 418. Calculate the collapse load using the plastic hinge method. (20%)arrow_forwardA reinforced concrete beam with b=300mm, h=670mm,and d=600 mm, having a span of 7.3 m, can be considered as a fully fixed at the left support and simply supported at the right end. It is reinforced for positive bending with 8-16 and for negative bending with 4816 plus 418. Calculate the collapse load using the plastic hinge method.arrow_forward
- Calculate the collapse load (P) for the two fixed ended beam shown below. Use equilibrium method P 2 m 4 m L=6 marrow_forwardPlease use virtual work/ force method as I am struggling with that particular concept.arrow_forwardThe anchor from Part A can also fail in shear in the circular head, as shown (Figure 3). What is the minimum thickness tt required for the head to support the allowed load PallowPallow = 15 kNkN if the material fails in shear at τfailτfail = 30 MPaMPa ? Use a factor of safety F.S.F.S. = 2.2.arrow_forward
- Find three sites on the www related to reinforced concrete (other than thoselinked to the Syllabus). For each site, provide a written description of the sitecontent and the site’s URL.arrow_forwardVisit the course web page on Canvas. Find the document where the advantagesand disadvantages of reinforced concrete are listed. Provide at least three additionaladvantages and three additional disadvantages. Justify your answer.arrow_forwardMax. Flow rate from catchment area=0.25 m³/s drain to road (one side road) having roof section with longitudinal slope %1, n=0.016, cross-section slope %1, 24 m width of road, 0.15 m curb stone. Gutter data: 7 cm high of water. 1-What is the capacity (or Max. flow rate) for this road? 2- With 0.5 m3 /s is it flood? 3-Whate is the clear zone in case Q=0.5 m³/s?arrow_forward
- Estimate Q inlet for curb inlet in sump, If y=5 cm, L=0.5 m and %13 clogging.arrow_forward3020,220 30 30m 120 Design inlet system for the road in figure below. C=0.93, i=65 mm/hr, Gutter data: y max.=9 cm, n=0.016, k=0.38, slope %1, Z=40, (space-bar-2 cm). Estimate inlet type. elevation in points (a-82.1, b=82 m), in point t rain water depth in point f>3 cm in u turn >5.5 cm. Sag point in S. Drow curbstone DATE DATE 5 100 Median strip 10 %1 d 72arrow_forwardEstimate Q inlet for grate inlet in sump, If w=0.4 m, L-0.5 m, y=5 cm and opining space 3 cm and bar width= 2.5 cm %12 clogging.arrow_forward
 Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage, Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Materials Science And Engineering PropertiesCivil EngineeringISBN:9781111988609Author:Charles GilmorePublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Solid Waste EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305635203Author:Worrell, William A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,





