
Concept explainers
Akron Manufacturing Co. manufactures a cement-sealing compound called Seal-Rite. The process requires that the product pass through three departments. In Dept. 1, all materials are put into production at the beginning of the process; in Dept. 2, materials are put into production evenly throughout the process; and in Dept. 3, all materials are put into production at the end of the process. In each department, it is assumed that the labor and factory
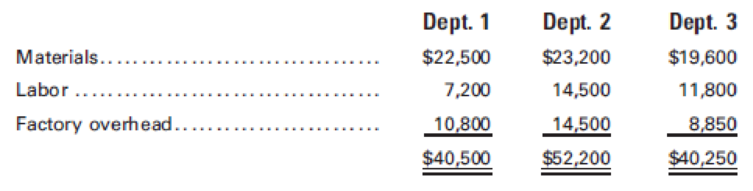
At the end of January, the production reports for the month show the following:
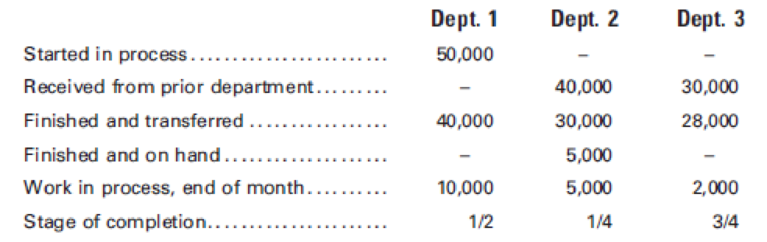
Required:
- 1. Prepare a cost of production summary for each department for January, using the weighted average cost method.
- 2. Prepare the
journal entries to record the January transactions. - 3. Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured for the month ended January 31.
1.
Prepare a cost of production summary for each department for the month January by using the weighted average method.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a cost of production summary for Department 1.
| A M Co. | ||
| Cost of production summary | ||
| Department 1 | ||
| For the month ended January 31 | ||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Cost of production for month: | ||
| Materials | $22,500 | |
| Labor | 7,200 | |
| Factory overhead | 10,800 | |
| Total costs accounted for | $40,500 | |
| Unit output for month: | ||
| Materials: | ||
| Finished and transferred to Department 2 during month | 40,000 | |
| Equivalent units of work-in process, end of month | 10,000 | |
| Total equivalent production | 50,000 | |
| Labor and factory overhead | ||
| Finished and transferred to Department 2 during month | 40,000 | |
| Equivalent units of work-in process, end of month | 5,000 | |
| Total equivalent production | 45,000 | |
| Unit cost for month: | ||
| Materials | $0.45 | |
| Labor | 0.16 | |
| Factory overhead | 0.24 | |
| Total | $0.85 | |
| Inventory cost: | ||
| Cost of goods finished and transferred to department 2 during month | $34,000 | |
| Cost of work-in process, end of month: | ||
| Materials | $4,500 | |
| Labor | 800 | |
| Factory overhead | 1,200 | 6,500 |
| Total production costs accounted for | $40,500 | |
Table (1)
Prepare a cost of production summary for Department 2.
| A M Co. | |||
| Cost of production summary | |||
| Department 2 | |||
| For the month ended January 31 | |||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Cost of goods received from dept. 1. during month | $34,000 | ||
| Cost of production for month: | |||
| Materials | $23,200 | ||
| Labor | 14,500 | ||
| Factory overhead | 14,500 | 52,200 | |
| Total costs accounted for | $86,200 | ||
| Unit output for month: | |||
| Materials, labor, and factory overhead | |||
| Finished and transferred to Department 3 during month | 30,000 | ||
| Finished and on hand | 5,000 | 35,000 | |
| Equivalent units of work-in process, end of month | 1,250 | ||
| Total equivalent production | 36,250 | ||
| Unit cost for month: | |||
| Materials | $0.64 | ||
| Labor | 0.4 | ||
| Factory overhead | 0.4 | ||
| Total | $1.44 | ||
| Inventory cost: | |||
| Cost of goods finished and transferred to department 3 during month | |||
| Cost in department 1 | $25,500 | ||
| Cost in department 2 | 43,200 | $68,700 | |
| Cost of goods finished and on hand: | |||
| Cost in Dept. 1 | $4,250 | ||
| Cost in Dept. 2 | 7,200 | 11,450 | |
| Cost of work-in process, end of month: | |||
| Cost in dept. 1. | $4,250 | ||
| Cost in dept. 2: | |||
| Materials | $800 | ||
| Labor | 500 | ||
| Factory overhead | 500 | 1,800 | 6,050 |
| Total production costs accounted for | $86,200 | ||
Table (2)
Prepare a cost of production summary for Department 3.
| A M Co. | |||
| Cost of production summary | |||
| Department 3 | |||
| For the month ended January 31 | |||
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Cost of goods received from dept. 2. during month | $68,700 | ||
| Cost of production for month: | |||
| Materials | $19,600 | ||
| Labor | 11,800 | ||
| Factory overhead | 8,850 | 40,250 | |
| Total costs accounted for | $108,950 | ||
| Unit output for month: | |||
| Materials: | |||
| Finished and transferred to finished goods during the month | 28,000 | ||
| Equivalent units of work-in process, end of month | 0 | ||
| Total equivalent production | 28,000 | ||
| Labor and factory overhead: | |||
| Finished and transferred to finished goods during the month | 28,000 | ||
| Equivalent units of work-in process, end of month | 1,500 | ||
| Total equivalent production | 29,500 | ||
| Unit cost for month: | |||
| Materials | $0.70 | ||
| Labor | 0.4 | ||
| Factory overhead | 0.3 | ||
| Total | $1.40 | ||
| Inventory cost: | |||
| Cost of goods finished and transferred to finished during month | |||
| Cost in department 1 | $23,800 | ||
| Cost in department 2 | 40,320 | ||
| Cost in department 3 | 39,200 | $103,320 | |
| Cost of work-in process, end of month: | |||
| Cost in dept. 1. | $1,700 | ||
| Cost in dept. 2: | 2,880 | ||
| Cost in dept. 3: | |||
| Materials | 0 | ||
| Labor | $600 | ||
| Factory overhead | 450 | 1,050 | 5,630 |
| Total production costs accounted for | $108,950 | ||
Table (3)
Summary from cost of production reports:
| Particulars | Amount($) | Amount($) |
| Materials: | ||
| Dept. 1 | $22,500 | |
| Dept. 2 | 23,200 | |
| Dept. 3 | 19,600 | $65,300 |
| Labor: | ||
| Dept. 1 | $7,200 | |
| Dept. 2 | 14,500 | |
| Dept. 3 | 11,800 | 33,500 |
| Factory overhead: | ||
| Dept. 1 | $10,800 | |
| Dept. 2 | 14,500 | |
| Dept. 3 | 8,850 | 34,150 |
| Total production costs for January | $ 132,950 | |
| Deduct work in process, end of month: | ||
| Dept. 1 | $6,500 | |
| Dept. 2 | 17,500 | |
| Dept. 3 | 5,630 | 29,630 |
| Cost of production, goods fully manufactured during January | $103,320 |
Table (4)
2.
Prepare the journal entry to record the transaction.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the journal entry to record the transaction.
| Particulars | Post ref. | Debit($) | Credit($) |
| Work in process Dept. 1 | 22,500 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 2 | 23,200 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 3 | 19,600 | ||
| Materials | 65,300 | ||
| (To record the materials transaction) | |||
| Work in process Dept. 1 | 7,200 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 2 | 14,500 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 3 | 11,800 | ||
| Payroll | 33,500 | ||
| (To record the payroll transaction) | |||
| Work in process Dept. 1 | 10,800 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 2 | 14,500 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 3 | 8,850 | ||
| Factory overhead | 34,150 | ||
| (To record the factory overhead) | |||
| Work in process Dept. 2 | 34,000 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 1 | 34,000 | ||
| (To record the goods transferred to department 2) | |||
| Work in process Dept. 3 | 68,700 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 2 | 68,700 | ||
| (To record the goods transferred to department 3) | |||
| Finished goods | 1,03,320 | ||
| Work in process Dept. 3 | 1,03,320 | ||
| (To record the goods transferred to finished goods) |
Table (5)
3.
Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured for the January month.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare a statement of cost of goods manufactured.
| A M Co. | |
| Statement of cost of goods manufactured | |
| For the month end January | |
| Particulars | Amount($) |
| Materials | $65,300 |
| Labor | 33,500 |
| Factory overhead | 34,150 |
| Total manufacturing cost | $132,950 |
| Add: Work in process inventory, January 1 | 0 |
| $132,950 | |
| Less: Work in process inventory, January 31 | 29,630 |
| Cost of goods manufactured during the month | $103,320 |
Table (6)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Cost Accounting
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Accounting Information Systems (14th Edition)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis (16th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
Marketing: An Introduction (13th Edition)
- I need help with this general accounting question using standard accounting techniques.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardI am searching for the correct answer to this general accounting problem with proper accounting rules.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub
Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337912020Author:Carl Warren, Ph.d. Cma William B. TaylerPublisher:South-Western College Pub


