
(a)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:
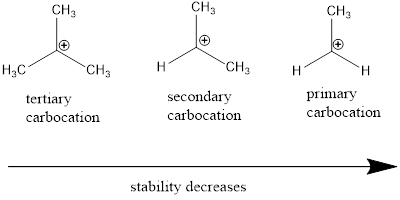
(b)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

(c)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Acid Catalyzed Hydration Reaction: The reaction involves breaking of phi bonds between carbon-carbon multiple bonds and addition of alcohol to more substituted position of carbon in the molecule.
First step is the acid donates proton to the
Then, the water is added to the given alkene through acid catalyzed reaction where the water gets added to the carbo cation finally, the removal of one proton from oxonium ion (oxygen with one positive charge) using water results in the formation of product.
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

(d)
Interpretation:
The major product for the given reaction has to be determined.
Concept introduction:
Nucleophile: Nucleophiles are electron rich compounds which donates electrons to electrophilic compounds which results in bond formation.
Electrophile: Electrophiles are electron deficient compounds which accepts electrons from nucleophiles that results in bond formation.
Electrophilic addition: It is a type of addition reaction in which the pi bond present in the molecule breaks as the electrophile approaches and results in the formation of product with sigma bond.
Addition of halogen to an alkene: The addition of halogen to an alkene compound forms cyclic 3 membered intermediate as the first step which then the leads to the product formation. Example for this is as follows,
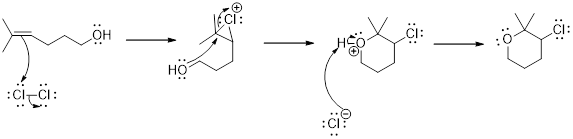
Carbocation: it is carbon ion that bears a positive charge on it.
Carbocation stability order:

Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIAL ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardDraw a Newman projection for the molecule below from the perspective indicated. Which of the groups (letters A-H) are methyl groups? CH3 H H H A H B ☑ >> H. ABCDEFG I H -H CH3 G D CH F E Numeric 4 points How many gauche interactions exist in the conformation shown in the previous problem? 1arrow_forward
- HELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardHELP NOW PLEASE ! ASAP! URGENT!arrow_forwardWould the following organic synthesis occur in one step? Add any missing products, required catalysts, inorganic reagents, and other important conditions. Please include a detailed explanation and drawings showing how the reaction may occur in one step.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward13) When solid barium phosphate is in equilibrium with its ions, the ratio of barium ions to phosphate ions would be: a. 1:1 b. 2:3 c. 3:2 d. 2:1 14) The pH of a 0.05 M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is 15) The pH of a 0.20 M solution of KOH at 25°C isarrow_forwardPls help.arrow_forward
- Pls help.arrow_forward16) A 2.0 L flask containing 2.0 x 10-3 mol H2(g), 3.0 x 10-3 mol Cl2(g), and 4.0 x 10-3 mol HCl(g) at equilibrium. This system is represented by the following chemical equation: H2 (g) + Cl2 (g) → 2HCl(g) Calculate the equilibrium constant for this reaction.arrow_forward7) The pH of a 0.05M solution of HCl(aq) at 25°C is a. 1.3 b. 2.3 c. 3.3 d. 12.7arrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
