
Review of Selected Concepts Related to Nomenclature
Write the chemical formula of each of the following. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
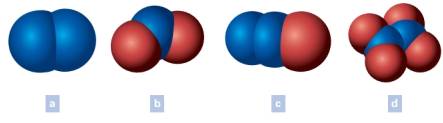
(a)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (a) is written as N2
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. The number of each kind of atom which makes up the particle generally called as the composition, is denoted by the chemical formula. Commonly, elements can be madeup of molecules having single atom, two atoms or complex multi-atoms. Coversely, when the substance itself is an element it should have all atoms of the same element. In the above example (a), the two lobes are having the same blue color which is for the element nitrogen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Chemical formula = N2
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (a) is written.
(b)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (b) is written as NO2
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (b), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element oxygen and one lobe is having the color for nitrogen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 1
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 2
Chemical formula = NO2
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (b) is written.
(c)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (c) is written as N2O
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (c), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element nitrogen and one lobe is having the color for oxygen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 1
Chemical formula = N2O
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (c) is written.
(d)
Interpretation:
The chemical formula of each of the following is to be written. The blue spheres represent nitrogen atoms and the red spheres oxygen atoms. Oxygen is written last in the formulas that include oxygen.
Concept introduction:
The particle of an element or compound in the written format is denoted by the chemical formulas. The symbols of elements in a particular substance covers the formula of the required substance.
Answer to Problem 1E
The chemical formula of (d) is written as N2O4
Explanation of Solution
Generally, in a formula, the total number of atoms of the element under study is shown by a subscript number immediately following the symbol. Notably, the subscript does not have the number when only one atom of an element present in the formula. In the above example (d), the two lobes are having the same color which is for the element nitrogen and other four lobes are having the color for oxygen.
Total number of lobes of nitrogen (N) = 2
Total number of lobes of oxygen (O) = 4
Chemical formula = N2O4
Thus, the chemical formula of the colored lobes (d) is written.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approach
- टे Predict the major products of this organic reaction. Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between different major products. ☐ ☐ : ☐ + NaOH HO 2 Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardShown below are five NMR spectra for five different C6H10O2 compounds. For each spectrum, draw the structure of the compound, and assign the spectrum by labeling H's in your structure (or in a second drawing of the structure) with the chemical shifts of the corresponding signals (which can be estimated to nearest 0.1 ppm). IR information is also provided. As a reminder, a peak near 1700 cm-1 is consistent with the presence of a carbonyl (C=O), and a peak near 3300 cm-1 is consistent with the presence of an O–H. Extra information: For C6H10O2 , there must be either 2 double bonds, or 1 triple bond, or two rings to account for the unsaturation. There is no two rings for this problem. A strong band was observed in the IR at 1717 cm-1arrow_forwardPredict the major products of the organic reaction below. : ☐ + Х ك OH 1. NaH 2. CH₂Br Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- NG NC 15Show all the steps you would use to synthesize the following products shown below using benzene and any organic reagent 4 carbons or less as your starting material in addition to any inorganic reagents that you have learned. NO 2 NC SO3H NO2 OHarrow_forwardDon't used hand raiting and don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardShow work...don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- 1 Please provide an efficient synthesis of the product below from the starting material. Use the starting material as the ONLY source of carbon atoms. Show the synthesis of each compound that would be used in the overall synthesis of the product. [This synthesis uses alkyne and alcohol chemistry.]arrow_forward10- 4000 20 20 30- %Reflectance 60 50- 09 60- 40- Date: Thu Feb 06 17:30:02 2025 (GMT-05:0(UnknownP Scans: 8 Resolution: 2.000 70 70 88 80 3500 3000 2500 90 100 00 Wavenumbers (cm-1) 2000 1500 2983.10 2359.13 1602.52 1584.22 1451.19 1391.87 1367.07 1314.37 1174.34 1070.13 1027.33 1714.16 1269.47 1000 1106.08 1001.14 937.02 873.60 850.20 780.22 686.91 674.38 643.09 617.98 02/06/25 16:38:20arrow_forwardd. Draw arrow-pushing mechanism for an enzymatic retro-aldol reaction of the following hexose. Use B: and/or HA as needed. OH OH سية HO OH OHarrow_forward
 Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning





