
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The given compound has to be named.
Concept Introduction:
All the molecules have their unique names. These names must be known in order to communicate. But remembering all the chemical names is impossible as there are many numbers of molecules. To avoid this, the
| Stereoisomerism | Substituents | Parent | Unsaturation | Functional Group |
Stereoisomerism indicate if the considered molecule has any stereocenters are present (R,S) and if double bond is present are cis/trans. In order to name a double bond as cis/trans, the important condition is that, an identical group has to be present on either side of the double bond. If the identical groups are present on the same side of double bond, then it is known as cis. If the identical groups are present on the opposite side of the double bond then it is known as trans.
The groups that are connected to the main carbon chain are known as substituents. The substituents are identified after the carbon chain is identified and the functional group present in the given compound also identified. The substituents are named by adding “yl” to the end of the name which indicate that it is a substituent is an alkyl. The
The longest carbon chain is known as the parent. Parent carbon chain is the lengthiest carbon chain in the molecule that must include the functional group that is present in the compound. The longest carbon chain is identified and the parent name is given by the number of carbon atoms that is present in it. It must be remembered that even though functional group is not present in parent carbon chain, the double bond, triple bond if present has to be included. Numbering becomes a part of all the parts in IUPAC name. After identifying the parent chain, the numbering is done. If functional group is present in the given compound, the numbering is given in such a way that the functional group gets the least number. Then the double bond, triple bond.
| Number of carbon atoms in chain | Parent |
| 1 | Meth |
| 2 | Eth |
| 3 | Prop |
| 4 | But |
| 5 | Pent |
| 6 | Hex |
Unsaturation indicates that if any triple or double bonds are present in the molecule. If a compound contains a double bond it is named as “-en-” and if a triple bond is present “-yn-” is used. If a compound contains two double bonds, then it is named as “-dien-”. If three double bonds are present in the given compound, then it is named as “-trien-”. This same rule applies for the compound that contains multiple triple bonds also.
Functional group is the one after which the considered compound is being named.
| Functional Group | Class of compound | Suffix |
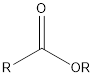 | Ester | -oate |
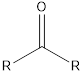 | Ketone | -one |
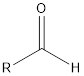 | Aldehyde | -al |
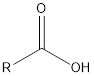 | -oic acid | |
 | Alcohol | -ol |
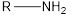 | -amine |
For naming a given compound, the reverse order has to be followed. First the functional group is considered followed by unsaturation, parent chain, substituents, and then the stereoisomerism.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
- What is the final product when D-galactose reacts with hydroxylamine?arrow_forwardIndicate the formula of the product obtained by reacting methyl 5-chloro-5-oxopentanoate with 1 mole of 4-penten-1-ylmagnesium bromide.arrow_forwardIn the two chair conformations of glucose, the most stable is the one with all the OH groups in the equatorial position. Is this correct?arrow_forward
- please help me with my homeworkarrow_forwardhelparrow_forwardThe temperature on a sample of pure X held at 1.25 atm and -54. °C is increased until the sample boils. The temperature is then held constant and the pressure is decreased by 0.42 atm. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 2 0 0 200 400 temperature (K) Xarrow_forward
- QUESTION: Answer Question 5: 'Calculating standard error of regression' STEP 1 by filling in all the empty green boxes *The values are all provided in the photo attached*arrow_forwardpressure (atm) 3 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. 0 0 200 temperature (K) 400 аarrow_forwarder your payment details | bar xb Home | bartleby x + aleksogi/x/isl.exe/1o u-lgNskr7j8P3jH-1Qs_pBanHhviTCeeBZbufuBYT0Hz7m7D3ZcW81NC1d8Kzb4srFik1OUFhKMUXzhGpw7k1 O States of Matter Sketching a described thermodynamic change on a phase diagram 0/5 The pressure on a sample of pure X held at 47. °C and 0.88 atm is increased until the sample condenses. The pressure is then held constant and the temperature is decreased by 82. °C. On the phase diagram below draw a path that shows this set of changes. pressure (atm) 1 3- 0- 0 200 Explanation Check temperature (K) 400 X Q Search L G 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved Terms of Use Privacy Cearrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





