
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The groups that has to be considered as substituents and the name for them has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
All the molecules have their unique names. These names must be known in order to communicate. But remembering all the chemical names is impossible as there are many numbers of molecules. To avoid this, the
| Stereoisomerism | Substituents | Parent | Unsaturation | Functional Group |
Stereoisomerism indicate if the considered molecule has any stereocenters are present (R,S) and if double bond is present are cis/trans.
The groups that are connected to the main carbon chain is known as substituents. The substituents are identified after the carbon chain is identified and the functional group present in the given compound also identified. The substituents are named by adding “yl” to the end of the name which indicate that it is a substituent is an alkyl. The
The longest carbon chain is known as the parent. Parent carbon chain is the lengthiest carbon chain in the molecule that must include the functional group that is present in the compound. The longest carbon chain is identified and the parent name is given by the number of carbon atoms that is present in it. It must be remembered that even though functional group is not present in parent carbon chain, the double bond, triple bond if present has to be included.
| Number of carbon atoms in chain | Parent |
| 1 | Meth |
| 2 | Eth |
| 3 | Prop |
| 4 | But |
| 5 | Pent |
| 6 | Hex |
Unsaturation indicates that if any triple or double bonds are present in the molecule. If a compound contains a double bond it is named as “-en-” and if a triple bond is present “-yn-” is used. If a compound contains two double bonds, then it is named as “-dien-”. If three double bonds are present in the given compound, then it is named as “-trien-”. This same rule applies for the compound that contains multiple triple bonds also.
Functional group is the one after which the considered compound is being named.
| Functional Group | Class of compound | Suffix |
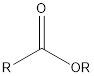 | Ester | -oate |
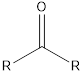 | Ketone | -one |
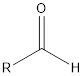 | Aldehyde | -al |
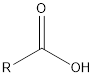 | -oic acid | |
 | Alcohol | -ol |
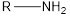 | -amine |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
- 7.5 1.93 2.05 C B A 4 3 5 The Joh. 9 7 8 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 0.86 OH 10 4 3 5 1 2 7.5 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 1.5 1.0 ppm 9 7 8 CI 4 3 5 1 2 7.0 6.5 6.0 5.5 5.0 4.5 4.0 3.5 3.0 2.5 2.0 2.21 4.00 1.5 2.00 2.07 1.0 ppm 2.76arrow_forwardAssign the functional group bands on the IR spectra.arrow_forwardFind the pH of a 0.120 M solution of HNO2. Find the pH ignoring activity effects (i.e., the normal way). Find the pH in a solution of 0.050 M NaCl, including activityarrow_forward
- Please help me answer these three questions. Required info should be in data table.arrow_forwardDraw the major organic substitution product or products for (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane reacting with the given nucleophile. Clearly drawn the stereochemistry, including a wedged bond, a dashed bond and two in-plane bonds at each stereogenic center. Omit any byproducts. Bri CH3CH2O- (conc.) Draw the major organic product or products.arrow_forwardTartaric acid (C4H6O6) is a diprotic weak acid. A sample of 875 mg tartaric acid are dissolved in 100 mL water and titrated with 0.994 M NaOH. How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the first equivalence point? How many mL of NaOH are needed to reach the second equivalence point?arrow_forward
- Including activity, calculate the solubility of Pb(IO3)2 in a matrix of 0.020 M Mg(NO3)2.arrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M KBr.arrow_forwardIncluding activity, calculate the pH of a 0.010 M HCl solution with an ionic strength of 0.10 M.arrow_forward
- Can I please get the graph 1: Concentration vs. Density?arrow_forwardOrder the following series of compounds from highest to lowest reactivity to electrophilic aromatic substitution, explaining your answer: 2-nitrophenol, p-Toluidine, N-(4-methylphenyl)acetamide, 4-methylbenzonitrile, 4-(trifluoromethyl)benzonitrile.arrow_forwardOrdene la siguiente serie de compuestos de mayor a menor reactividad a la sustitución aromática electrofílica, explicando su respuesta: ácido bencenosulfónico, fluorobenceno, etilbenceno, clorobenceno, terc-butilbenceno, acetofenona.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





