
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
The unsaturation has to be located and how it will be represented in the name of the compound has to be given.
Concept Introduction:
All the molecules have their unique names. These names must be known in order to communicate. But remembering all the chemical names is impossible as there are many numbers of molecules. To avoid this, the
| Stereoisomerism | Substituents | Parent | Unsaturation | Functional Group |
Stereoisomerism indicate if the considered molecule has any stereocenters are present (R,S) and if double bond is present are cis/trans.
The groups that are connected to the main carbon chain is known as substituents.
The longest carbon chain is known as the parent.
Unsaturation indicates that if any triple or double bonds are present in the molecule. If a compound contains a double bond it is named as “-en-” and if a triple bond is present “-yn-” is used. If a compound contains two double bonds, then it is named as “-dien-”. If three double bonds are present in the given compound, then it is named as “-trien-”. This same rule applies for the compound that contains multiple triple bonds also.
Functional group is the one after which the considered compound is being named.
| Functional Group | Class of compound | Suffix |
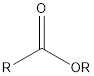 | Ester | -oate |
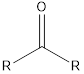 | -one | |
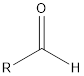 | -al | |
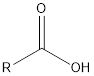 | -oic acid | |
 | Alcohol | -ol |
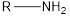 | -amine |
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry As a Second Language: First Semester Topics
- QUESTION: Find the standard deviation for the 4 different groups 5.298 3.977 223.4 148.7 5.38 4.24 353.7 278.2 5.033 4.044 334.6 268.7 4.706 3.621 305.6 234.4 4.816 3.728 340.0 262.7 4.828 4.496 304.3 283.2 4.993 3.865 244.7 143.6 STDEV = STDEV = STDEV = STDEV =arrow_forwardQUESTION: Fill in the answers in the empty green boxes regarding 'Question 5: Calculating standard error of regression' *The images of the data showing 'coefficients for the standard curve' have been providedarrow_forwardUsing the Nernst equation to calculate nonstandard cell voltage Try Again Your answer is wrong. In addition to checking your math, check that you used the right data and DID NOT round any intermediate calculations. A galvanic cell at a temperature of 25.0 °C is powered by the following redox reaction: 2+ 2+ Sn²+ Ba(s) (aq) + Ba (s) Sn (s) + Ba²+ (aq) →>> Suppose the cell is prepared with 6.10 M Sn 2+ 2+ in one half-cell and 6.62 M Ba in the other. Calculate the cell voltage under these conditions. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 1.71 V ☐ x10 ☑ 5 0/5 ? 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
- Question: Find both the b (gradient) and a (y-intercept) value from the list of data below: (x1 -x̄) 370.5 (y1 - ȳ) 5.240 (x2 - x̄) 142.5 (y2 - ȳ) 2.004 (x3 - x̄) 28.5 (y3 - ȳ) 0.390 (x4 - x̄) -85.5 (y4 - ȳ) -1.231 (x5 - x̄) -199.5 (y5 - ȳ) -2.829 (x6 - x̄) -256.5 (y6 - ȳ) -3.575arrow_forwardCalculating standard reaction free energy from standard reduction... Using standard reduction potentials from the ALEKS Data tab, calculate the standard reaction free energy AG° for the following redox reaction. Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 3Cu+ (aq) + Cro²¯ (aq) +4H₂O (1) → 3Cu²+ (aq) +Cr(OH)3 (s)+5OH˜¯ (aq) 0 kJ ☐ x10 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 241.7 mL of a 0.4900M solution of methylamine (CH3NH2) with a 0.7800M solution of HNO3. The pK of methylamine is 3.36. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 17.7 mL of the HNO3 solution to it. Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HNO3 solution added. Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = ☑ ? 18 Ararrow_forward
- The following is two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 223.4 148.7 353.7 278.2 334.6 268.7 305.6 234.4 340.0 262.7 304.3 283.2 244.7 143.6 QUESTION: For both groups of data calculate the answers attached in the image.arrow_forwardThe following is a two groups (Regular tomato sauce & Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce) of data recorded by a team analysising salt content in tomato sauce using the MOHR titration method: Regular Tomato Sauce Salt Reduced Tomato Sauce 340.0mmol/L 262.7mmol/L QUESTION: For both groups (Regular & Salt Reduced tomato sauce) of data provide answers to the following calculations below: 1. Standard Deviation (Sx) 2. T Values (t0.05,4) 3. 95% Confidence Interval (mmol/L) 4. [Na+] (mg/100 mL) 5. 95% Confidence Interval (mg/100 mL)arrow_forwardIf we have leucine (2-amino-4-methylpentanoic acid), alanine (2-aminopropanoic acid) and phenylalanine (2-amino-3-phenylpropanoic acid), indicate the tripeptides that can be formed (use the abbreviated symbols Leu., Ala and Phe).arrow_forward
- Briefly state why trifluoroacetic acid is more acidic than acetic acid.arrow_forwardExplain why acid chlorides are more reactive than amides in reactions with nucleophiles.arrow_forwardCalculating the pH of a weak base titrated with a strong acid An analytical chemist is titrating 101.7 mL of a 0.3500M solution of piperidine (C5H10NH) with a 0.05700M solution of HClO4. The pK of piperidine is 2.89. Calculate the pH of the base solution after the chemist has added 682.9 mL of the HClO solution to it. 4 Note for advanced students: you may assume the final volume equals the initial volume of the solution plus the volume of HClO solution added. 4 Round your answer to 2 decimal places. pH = .11 00. 18 Ararrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





