
Concept explainers
Successive substitution of F atoms for H atoms in the molecule NH3 produces the molecules NH2F, NHF2, and NF3.
- a. Draw Lewis structures for each of the four molecules.
- b. Using VSEPR theory, predict the geometry of each of the four molecules.
- c. Specify the polarity (polar or nonpolar) for each of the four molecules.
(a)
Interpretation:
Lewis structures for the four molecules that are formed by successive substitution of
Concept Introduction:
Lewis structure clearly depicts the bonding and nonbonding electrons in the atom. This is only partially useful for the molecule that contains one or more multiple bonds and when coordinate covalent bond is present in the molecule. For drawing Lewis structure a systematic procedure is followed. They are,
- The total number of valence electrons that is present in molecule is calculated by adding all the valence electrons of the atoms present in the molecule.
- The chemical symbols for the atoms that is present in the molecule is written in the order that they are bonded. After this a single covalent bond is placed between each atoms as two electrons.
- The nonbonding electrons are added to each atom that is bonded to the central atom so that it contains octet of electrons. For hydrogen alone the “octet” is only two electrons.
- The remaining electrons has to be placed on the central atom in the structure.
- If there is no octet of electrons present in the central atom, then use one or more pairs of nonbonding electrons that is bonded to the central atom to form double or triple bonds.
- The total number of electrons has to be counted and it has to be confirmed whether the count is same as that of the number of valence electrons that is available for bonding.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecules are
For
Given molecule is
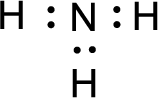
The nonbonding electrons are added to the nitrogen atom. This results in the structure as,
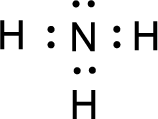
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 8 and it is same as the valence electrons of
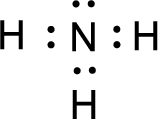
For
Given molecule is
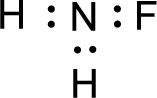
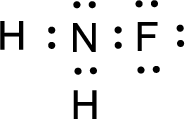
The nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom and nitrogen atom. This results in the structure as,
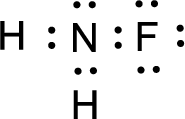
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 14 and it is same as the valence electrons of
For
Given molecule is
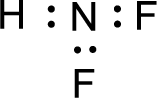
The nonbonding electrons are added to the fluorine atom and nitrogen atom. This results in the structure as,
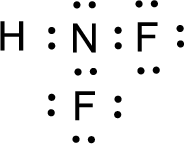
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 20 and it is same as the valence electrons of
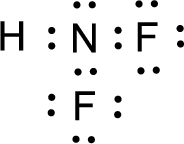
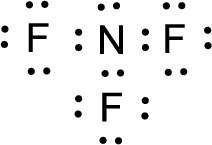
For
Given molecule is
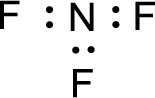
The nonbonding electrons are added to the nitrogen atom and fluorine atoms. This results in the structure as,
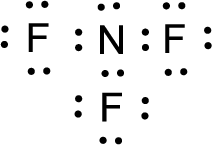
All the atoms present in the above structure contains octet of electrons. The total number of electron dots present in the above structure is 26 and it is same as the valence electrons of
(b)
Interpretation:
Molecule geometry has to be predicted for the four molecules using VSEPR theory.
Concept Introduction:
Information about the number of bonds and types of bonds can be obtained from Lewis structure but the molecular geometry cannot be obtained. Three dimensional arrangement of atoms in a molecule can be given by molecular geometry. Physical and chemical properties are determined by the molecular geometry of the molecule.
Using VSEPR theory and Lewis structure, the molecular geometry of the molecule that contain less number of atoms can be predicted. VSEPR theory uses the information from Lewis structure of the molecule to predict the molecular geometry of the molecule. Main concept of VSEPR theory is that electron pairs that are present in the valence shell adopt arrangement in a way that minimize the repulsion between like charges.
If the central atom contains two electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on opposite side of the nucleus. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains three electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be on corner of a triangle. This means the angle has to be
If the central atom contains four electron pairs, then it has to be far apart means, it has to be in a tetrahedral arrangement. This means the angle has to be
The collection of valence electron that is present in localized region about central atom in a molecule is known as VSEPR electron group. This may contain two electrons, four electrons, or six electrons. The electron group that contain four and six electrons repel each other.
Tetrahedral VSEPR electron group:
The four electron pairs can be of three VSEPR electron groups. They are 4 bonding electron groups, 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 4 bonding electron groups is tetrahedral. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is trigonal pyramidal. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 2 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Trigonal planar VSEPR electron group:
The three electron pairs can be of two VSEPR electron groups. They are 3 bonding electron groups, and 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups. The molecular geometry that is associated with 3 bonding electron groups is trigonal planar. The molecular geometry that is associated with 2 bonding and 1 nonbonding electron groups is angular.
Linear VSEPR electron group:
The two electron pairs can be of only one VSEPR electron groups. It is only 2 bonding electron groups and the geometry associated with it is linear geometry.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecule is
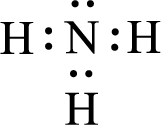
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be nitrogen. This has three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is trigonal pyramidal. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups and it has trigonal pyramidal geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
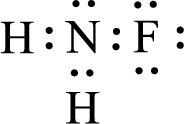
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be nitrogen. This has three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is trigonal pyramidal. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups and it has trigonal pyramidal geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
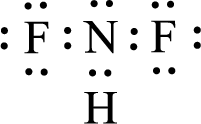
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be nitrogen. This has three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is trigonal pyramidal. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups and it has trigonal pyramidal geometry as per VSEPR theory.
Given molecule is
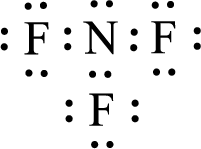
The central atom in the above molecule is found to be nitrogen. This has three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups. The arrangement around the central atom is trigonal pyramidal. Looking for molecular geometry, the central atom that contains three bonding electron groups and one nonbonding electron groups and it has trigonal pyramidal geometry as per VSEPR theory.
(c)
Interpretation:
The four molecules that are given has to be classified as polar and nonpolar.
Concept Introduction:
Measure of the degree of inequality in attraction of the bonding electrons to the various locations present within a molecule is known as molecular polarity. This can also be said in terms of electron attraction and that is in a molecule one part is favored than the other parts of the molecule.
If in a molecule there is an uneven distribution of electronic charges means it is known as polar molecule. If there is a symmetrical distribution of electron charge over the molecule means it is known as nonpolar molecule. Two factors that decide molecular polarity is bond polarity and geometry of molecule. If a molecule is symmetrical means then there won’t be any molecular polarity because the effect given by the polar bonds may cancel out each other.
The polarity of the bonds, arrangement of the bonds determines the degree of molecular polarity. If the electronegativity difference is more, then the molecule will be more polar.
Explanation of Solution
Given molecules are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Study Guide with Selected Solutions for Stoker's General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th
- Could you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but color-coded or step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you!arrow_forwardCould you please solve the first problem in this way and present it similarly but (color-coded) and step by step so I can understand it better? Thank you! I want to see what they are doingarrow_forward
- Can you please help mne with this problem. Im a visual person, so can you redraw it, potentislly color code and then as well explain it. I know im given CO2 use that to explain to me, as well as maybe give me a second example just to clarify even more with drawings (visuals) and explanations.arrow_forwardPart 1. Aqueous 0.010M AgNO 3 is slowly added to a 50-ml solution containing both carbonate [co32-] = 0.105 M and sulfate [soy] = 0.164 M anions. Given the ksp of Ag2CO3 and Ag₂ soy below. Answer the ff: Ag₂ CO3 = 2 Ag+ caq) + co} (aq) ksp = 8.10 × 10-12 Ag₂SO4 = 2Ag+(aq) + soy² (aq) ksp = 1.20 × 10-5 a) which salt will precipitate first? (b) What % of the first anion precipitated will remain in the solution. by the time the second anion starts to precipitate? (c) What is the effect of low pH (more acidic) condition on the separate of the carbonate and sulfate anions via silver precipitation? What is the effect of high pH (more basic)? Provide appropriate explanation per answerarrow_forwardPart 4. Butanoic acid (ka= 1.52× 10-5) has a partition coefficient of 3.0 (favors benzene) when distributed bet. water and benzene. What is the formal concentration of butanoic acid in each phase when 0.10M aqueous butanoic acid is extracted w❘ 25 mL of benzene 100 mL of a) at pit 5.00 b) at pH 9.00arrow_forward
- Calculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 Group of answer choices 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0 choices: 0.0269 kJ/mole 2610 kJ/mole 27.6 kJ/mole 0.215 kJ/mole 20.8 kJ/molearrow_forwardCalculate activation energy (Ea) from the following kinetic data: Temp (oC) Time (s) 23.0 180. 32.1 131 40.0 101 51.8 86.0arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning
World of Chemistry, 3rd editionChemistryISBN:9781133109655Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan L. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Brooks / Cole / Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





