
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.4P
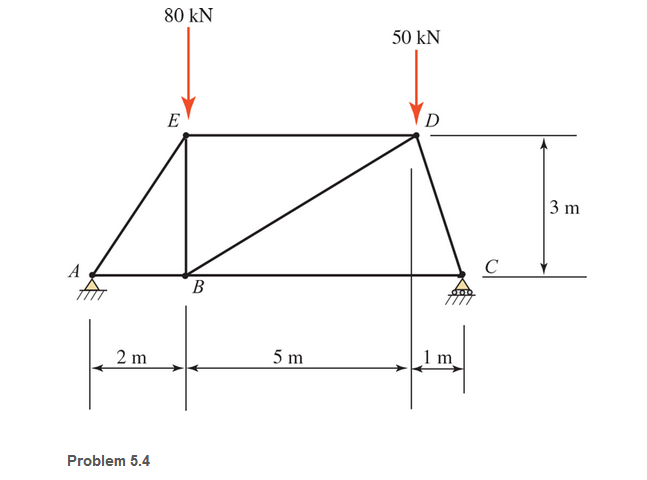
Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses shown, using the method of joints.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule10:21
Students have asked these similar questions
For the truss shown below:
1. Calculate the force in all members (Using the method of joints).
2. Indicate if members AB, BE, and DE are compression or tension members.
3. Calculate the force in member BE (Using the method of sections).
4. Compare the results for part (1) and part (2)
4 m
A
3 m
12 kN
D
B
3 m
E 3 kN
C
Problem 2 (Pro 3.25 Textbook):
Identify the zero-force members in the trusses below
1. USING THE METHOD OF JOINTS TO COMPUTE THE FORCE IN MEMBERS DF, EF, DE, CE, AND BE OF THE LOADED HOWE ROOF TRUSS
AS SHOWN IN FIG. 1
2. USING THE METHOD OF SECTIONS , DETERMINE THE FORCE IN MEMBER CE, BE, EF, BF AND AF OF LOADED CANTILEVER TRUSS AS SHOWN IN FIG. 2
3. USE METHOD OF SECTIONS TO COMPUTE FORCES ACTING IN MEMBERS BD, BE, CE, DE, AND DF OF THE LOADED PINK TRUSS AS SHOWN IN FIG. 3
4. THE X-FRAME AS SHOWN IN FIG. 4 IS HINGED AT D AND ON ROLLER AT E. DETERMINE THE RESULTANT HINGED FORCES AT A, B AND C
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 5 - through 5.7 Calculate the forces in all members of...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, DH, and HI for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, BE, and FE for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, CH, and CG in...
Ch. 5 - For the Howe roof truss shown, determine the...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members DE, CE, and BC in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in members BC, BG, and FG for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, BD, BE, and CB...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected A-frame supports a load, as shown....Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - A bracket is pin connected at points A, B, and D...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected frame is loaded, as shown....Ch. 5 - The cylinder shown has a mass of 500 kg. Determine...Ch. 5 - A simple frame is pin connected at points A, B,...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - through 5.31 Calculate the forces in all members...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38, Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38 , Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected crane framework is loaded and...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at pins A, B, and D in...Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - The wall bracket shown is pin-connected at points...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - The A-frame shown is pin-connected at A,B,C, and...Ch. 5 - The tongs shown are used to grip an object. For an...Ch. 5 - A toggle joint is a mechanism by which a...Ch. 5 - In the toggle joint of Problem 5.46 , assume that...Ch. 5 -
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
Determine the resultant internal loadings acting on the cross sections at points F and G of the frame. Probs. 7...
Statics and Mechanics of Materials (5th Edition)
The assembly consists of two red brass C83400 copper rods AB and CD of diameter 30 mm, a stainless 304 steel al...
Mechanics of Materials
Determine the largest angle that will cause the wedge to be self-locking regardless of the magnitude of horizo...
Engineering Mechanics: Statics
What parts are included in the vehicle chassis?
Automotive Technology: Principles, Diagnosis, And Service (6th Edition) (halderman Automotive Series)
The sports car is traveling along a 30 banked road having a radius of curvature of = 500ft. If the coefficient...
Engineering Mechanics: Dynamics (14th Edition)
Draw the free-body diagram for the following problems. a. The truss in Prob. 5-15. b. The beam in Prob. 5-16. c...
INTERNATIONAL EDITION---Engineering Mechanics: Statics, 14th edition (SI unit)
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 7 Compute the reaction forces in B and D. Hint: in this case, since you have to determine the external reactions only, you can consider the truss as a single rigid body 4.5 m 4.5 m B 2.8 m A 8.4 kN 8.4 kNarrow_forwardFor the truss loaded as shown in the figure, determine; a. the magnitude and type of forces in members AB, AC, BC, BD, BE, CE, DE, DF, DG and E by method of joints. b. the magnitude and type of forces in members FH, GH, GI, HJ, JI and IK by method of sections.arrow_forward8. For the plane truss loaded as shown below, use the method of joints to calculate the force in members AB, BC,AG, BC and GC. 10 mm 7.5 m 30 kN 8 4.5 m 30 kN 4.5 m f 30 KN 7.5 m 3 m 3 marrow_forward
- 3. In the given truss below calculate the forces in members CG and CF. Indicate if tension of compression. 2 kN 2 m B 2 m 2 m A 4 kN G 3 marrow_forwardThe given structure was supported by pin supports at points D and E. Member EF, DFG and BGC are connected to each other by internal hinges at B and F and a slider at G. (The slider at G allows relative horizontal motions of members BGC and DFG but constrains the vertical movement of members BGC and DFG. Calculate the support reactions due to pin supports and all internal hinge reactions. Show your calculation steps in detail and write your answers in the box below. E 1 m 3 kN/m B G 1 m F A -t-1 m-|-1 m--1 m- 2 m Darrow_forwardDetermine the forces in the members AD, CD, and AC of the truss shown below by using the method of joints. State whether each member is in tension or compression. (Note: You must show all the necessary free body diagrams. All members are weightless.)arrow_forward
- 1) A Warren bridge truss is shown to the below. (a) Determine the support reactions at A and K. (b) Determine the force in members CE, DE, and DF using method of joints. (c) Determine the force in members CE, DE, and DF using method of sections. (Note: A is a roller and K is a pin.) Ans: Ay = 8400 lb (1), K, = 0, Ky = 3600 lb (T), FCE = 8000 lb (T), FDE = 2600 lb (T), FDF = 9000 lb (C). [Intermediate answers for method of joints: FAB = 9100 lb (C), FAC = 3500 lb (T), FBC = 9100 lb (T), FBD = 7000 lb (C), FcD = 2600 lb (C)I %3D 6.25 ft 12.5 ft, 12.5 ft 12.5 ft, 12.5 ft В F H 15 ft K E 12.5 ft 12.5 ft 12.5 ft' 12.5 ft' 12.5 ft 6000 lb 6000 lbarrow_forwardFor the next Trusses, compute the axial forces in the selected sections. Compare the result with the method of joints. (Check the image for the trusses)arrow_forwardCalculate the rod forces BC, FC and FE in the truss system?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Engineering Basics - Statics & Forces in Equilibrium; Author: Solid Solutions - Professional Design Solutions;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dQBvQ2hJZFg;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY