
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.21P
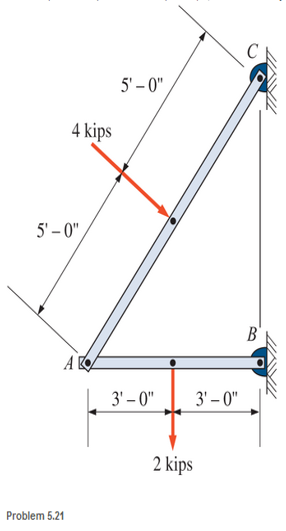
A simple frame is pin connected at points A, B, and C and is subjected to loads as shown. Compute the pin reactions at A, B, and C. Neglect the weights of the members.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
(b)
A steel 'hot rolled structural hollow section' column of length 5.75 m, has
the cross-section shown in Figure Q.5(b) and supports a load of 750 kN.
During service, it is subjected to axial compression loading where one end
of the column is effectively restrained in position and direction (fixed) and
the other is effectively held in position but not in direction (pinned).
i)
Given that the steel has a design strength of 275 MN/m², determine
the load factor for the structural member based upon the BS5950
design approach using Datasheet Q.5(b).
[11]
ii)
Determine the axial load that can be supported by the column
using the Rankine-Gordon formula, given that the yield strength of
the material is 280 MN/m² and the constant *a* is 1/30000.
[6]
300
600
2-300 mm
wide x 5 mm
thick plates.
Figure Q.5(b)
L=5.75m
Pinned
Fixed
Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤال
Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤال
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 5 - through 5.7 Calculate the forces in all members of...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, DH, and HI for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, BE, and FE for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, CH, and CG in...
Ch. 5 - For the Howe roof truss shown, determine the...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members DE, CE, and BC in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in members BC, BG, and FG for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, BD, BE, and CB...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected A-frame supports a load, as shown....Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - A bracket is pin connected at points A, B, and D...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected frame is loaded, as shown....Ch. 5 - The cylinder shown has a mass of 500 kg. Determine...Ch. 5 - A simple frame is pin connected at points A, B,...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - through 5.31 Calculate the forces in all members...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38, Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38 , Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected crane framework is loaded and...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at pins A, B, and D in...Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - The wall bracket shown is pin-connected at points...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - The A-frame shown is pin-connected at A,B,C, and...Ch. 5 - The tongs shown are used to grip an object. For an...Ch. 5 - A toggle joint is a mechanism by which a...Ch. 5 - In the toggle joint of Problem 5.46 , assume that...Ch. 5 -
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Q2: For the following figure, find the reactions of the system. The specific weight of the plate is 500 lb/ft³arrow_forwardQ1: For the following force system, find the moments with respect to axes x, y, and zarrow_forwardQ10) Body A weighs 600 lb contact with smooth surfaces at D and E. Determine the tension in the cord and the forces acting on C on member BD, also calculate the reaction at B and F. Cable 6' 3' wwwarrow_forward
- Help ارجو مساعدتي في حل هذا السؤالarrow_forwardQ3: Find the resultant of the force system.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 A three-blade propeller of a diameter of 2 m has an activity factor AF of 200 and its ratio of static thrust coefficient to static torque coefficient is 10. The propeller's integrated lift coefficient is 0.3.arrow_forward
- (L=6847 mm, q = 5331 N/mm, M = 1408549 N.mm, and El = 8.6 x 1014 N. mm²) X A ΕΙ B L Y Marrow_forwardCalculate the maximum shear stress Tmax at the selected element within the wall (Fig. Q3) if T = 26.7 KN.m, P = 23.6 MPa, t = 2.2 mm, R = 2 m. The following choices are provided in units of MPa and rounded to three decimal places. Select one: ○ 1.2681.818 O 2. 25745.455 O 3. 17163.636 O 4. 10727.273 ○ 5.5363.636arrow_forwardIf L-719.01 mm, = 7839.63 N/m³, the normal stress σ caused by self-weight at the location of the maximum normal stress in the bar can be calculated as (Please select the correct value of σ given in Pa and rounded to three decimal places.) Select one: ○ 1. 1409.193 2. 845.516 O 3. 11273.545 ○ 4.8455.159 ○ 5.4509.418 6. 2818.386 7.5636.772arrow_forward
- To calculate the rotation at Point B, a suitable virtual structure needs to be created. Which equation in the following choices most accurately represents the functional relationship between the bending moment, Mv2 ( Units: N.mm), of the virtual structure and the spatial coordinate x (Units: mm) if the applied unit virtual moment is clockwise? Select one: O 1. Mv2 1.000 O 2. Mv2=x+1.000 O 3. Mv2=x+0.000 4. Mv2 = -x-1.000 O 5. Mv2 -1.000 6. Mv2=-x+0.000arrow_forwardThe vertical deflection at Point B can be calculated as ( The following choices are provided in units of mm and rounded to three decimal places ; the downward deflection is negative and upward deflection is positive. ) Select one: 1. 1703.065 2. -1703.065 3. -2043.679 4.1362.452 5. -1362.452 6. 2043.679arrow_forwardThe second moments of area about z-axis, /z, and the second moments of area about y-axis, ly, can be calculated as Select one: O 1. I = Iz ○ 2. Ly ○ 3. ○ 4. ○ 5. = = Iz = *D' 64 I₁ = D, Iz Ly Ly = 32 *D' = = 3 Iz = *D' 32 = *D' O 6. Iy=D, Ly = D², Iz = 32 O 7. Ly = Iz D = 64 32arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
Types Of loads - Engineering Mechanics | Abhishek Explained; Author: Prime Course;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=4JVoL9wb5yM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY