
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
6th Edition
ISBN: 9780133840544
Author: George F. Limbrunner, Craig D'Allaird, Leonard Spiegel
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 5.45SP
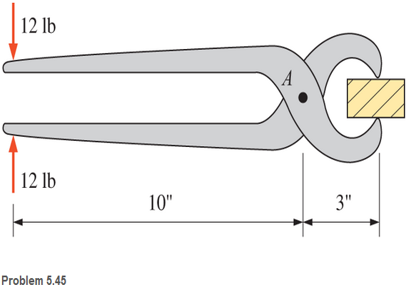
The tongs shown are used to grip an object. For an input force of 12 lb on each handle, determine the forces exerted on the object and the forces exerted on the pin at A.
Expert Solution & Answer
Learn your wayIncludes step-by-step video

schedule04:58
Students have asked these similar questions
State the following laws a) v/t = constant, (b) pv=constant c) pv^n=constant
Define Gas Constant and Universal Gas Constant
state Boyle's Law.
A receiver contains 0.25 m³ of air at a pressure of 1700 kPa and a temperature of 18 ° C . Calculate the final pressure after 2.5 kg of air is added if the final temperature is 20.5 ° C . Take R for air = 0.287 kJ / kg / ° K
Chapter 5 Solutions
Applied Statics and Strength of Materials (6th Edition)
Ch. 5 - through 5.7 Calculate the forces in all members of...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, DH, and HI for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, BE, and FE for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members BC, CH, and CG in...
Ch. 5 - For the Howe roof truss shown, determine the...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members DE, CE, and BC in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in members BC, BG, and FG for...Ch. 5 - Determine the forces in members CD, BD, BE, and CB...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected A-frame supports a load, as shown....Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - A bracket is pin connected at points A, B, and D...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected frame is loaded, as shown....Ch. 5 - The cylinder shown has a mass of 500 kg. Determine...Ch. 5 - A simple frame is pin connected at points A, B,...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - Using the method of sections, determine the forces...Ch. 5 - through 5.31 Calculate the forces in all members...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - Calculate the forces in all members of the trusses...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38, Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problem 5.32 through 5.38 , Calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - For Problems 5.32 through 5.38, calculate the...Ch. 5 - A pin-connected crane framework is loaded and...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at pins A, B, and D in...Ch. 5 - Determine the pin reactions at pins A, B, and C in...Ch. 5 - The wall bracket shown is pin-connected at points...Ch. 5 - Calculate the pin reactions at each of the pins in...Ch. 5 - The A-frame shown is pin-connected at A,B,C, and...Ch. 5 - The tongs shown are used to grip an object. For an...Ch. 5 - A toggle joint is a mechanism by which a...Ch. 5 - In the toggle joint of Problem 5.46 , assume that...Ch. 5 -
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
ICA 2-1
For each of the following situations, indicate whether you think the action is ethical or unethical or ...
Thinking Like an Engineer: An Active Learning Approach (4th Edition)
List for advantages of SQL-invoked routines.
Modern Database Management
In an inheritance relationship, this is the specialized class. a. superclass b. master class c. subclass d. par...
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Data Structures (4th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
How is the hydrodynamic entry length defined for flow in a pipe? Is the entry length longer in laminar or turbu...
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
Write a simple assignment statement with one arithmetic operator in some language you know. For each component ...
Concepts Of Programming Languages
What are some of the difficulties or limitations encountered in heat treating large, complex structures after w...
Degarmo's Materials And Processes In Manufacturing
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Heat energy is transferred to 1.36 kg of air which causes its temperature to increase from 40" CO 468°C. Calculate, for the two separate cases of heat transfer at (a) constant volume, (b) constant pressure: the quantity of heat energy transferred, (ii) the external work done, (iii) the increase in internal energy. Take cv and cp as 0.718 and 1.005 kJ/kgK respectivelyarrow_forwardA flat circular plate is 500 mm diameter. Calculate the theoretical quantity or heat radiated per hour when its temperature is 215°C and the temperature of its surrounds is 45°C. Take the value of the radiation constant to be 5.67 × 10^11 kJ/m2s K4.arrow_forwardDescribe Atmospheric Air and how it reacts with carbon in combustionarrow_forward
- 0.5 kg of ice at —5°C is put into a vessel containing 1.8kg of water at 17°C and mixed together, the result being a mixture of ice and water at 0°C. Calculate the final masses of ice and water, taking the water equivalent of the vessel to be 0.148 kg, specific heat of ice 2.04 kilkg K and latent heat of fusion 335 kJ/kg.arrow_forwardA condenser vacuum gauge reads 715 mmHg when the barometer stands at 757 mmHg. State the absolute pressure in the condenser in kN/m2 and bars.arrow_forwardSketch and Describe a timing diagram for a 2 stroke diesel enginearrow_forward
- Manipulate the formula for converting temperature from Fahrenheit to Celsiusarrow_forwardDefine Temperature, Pressure, and Absolute Temperature.arrow_forwardAn air reservoir contains 20 kg of air at 3200 kN/m2 gauge and 16°C. Calculate the new pressure and heat energy transfer if the air is heated to 35°C. Neglect any expansion of the reservoir, take R for air = 0.287 kJ/kgK, specific heat at constant volume c, = 0.718 kJFg K, and atmospheric pressure = 100 kN/m2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L
International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305501607Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan KiusalaasPublisher:CENGAGE L

International Edition---engineering Mechanics: St...
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781305501607
Author:Andrew Pytel And Jaan Kiusalaas
Publisher:CENGAGE L
How to balance a see saw using moments example problem; Author: Engineer4Free;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d7tX37j-iHU;License: Standard Youtube License