
Concept explainers
(a)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as a nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
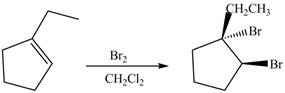
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction of
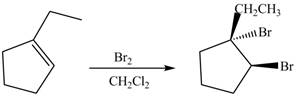
Figure 1
The product formed by reaction of
The reaction between
(b)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction,
The general view of
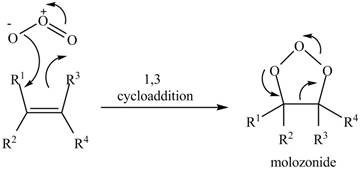
Figure 2
In the same manner,
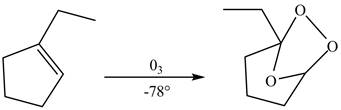
Figure 3
The product formed by the reaction between
(c)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on the reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof alkene with ozone, the oxidation of alkene takes place which leads to form molozonide product. This reaction takes place through
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
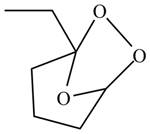
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The compound
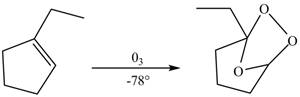
Figure 3
The molozonide formed is unstable in nature, therefore, it gets easily reduced by
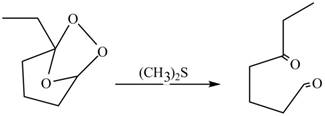
Figure 4
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
The reaction between
(d)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product obtained on the reaction of
Concept introduction:
In the reactionof alkene with ozone, the oxidation of alkene takes place which leads to form molozonide product. This reaction takes place through
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The compound
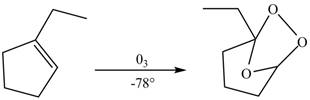
Figure 3
The molozonide formed is unstable in nature, therefore, it gets easily oxidized by
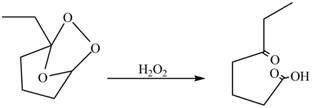
Figure 5
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
The reaction between
(e)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction between unsaturated alkene with
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
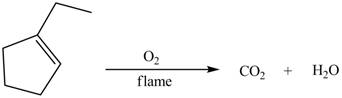
Figure 6
Therefore, the reaction between
The reaction between
(f)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In markovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction of
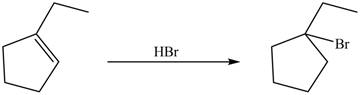
Figure 7
Therefore, the product formed by the reaction between
Thereaction between
(g)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
.In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction first reaction between
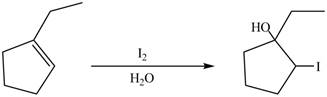
Figure 8
Therefore, the reaction between
The reaction between
(h)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In acatalytic hydrogenation reaction, palladium is used as a catalyst which accelerates the
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In this reaction, palladium is used as a catalyst which helps in accelerating the rate of hydrogenation reaction. This reaction leads to conversion of
The product formed by the reaction between
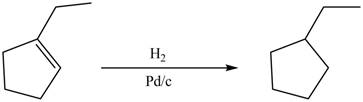
Figure 9
Theproduct formed by the reaction between
(i)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
In Anti-Markovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
Explanation of Solution
In thereaction, in presence of peroxides,
The product formed by the reaction between
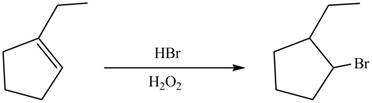
Figure 10
The product formed by the reaction between
(j)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of ![]() with
with
Concept introduction:
In hydroboration reaction, antimarkovnikov’s addition of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by thereaction of
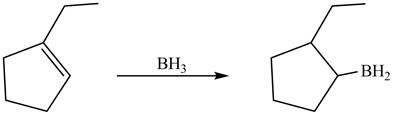
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
The product formed by thereaction between
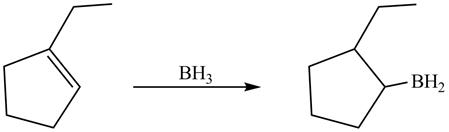
Figure 11
The product formed by the reaction between
(k)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the reaction of product of
Concept introduction:
In hydroboration reaction, antimarkovnikov’s addition of
The compound
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of boron substitued
Explanation of Solution
In the reaction,.the hydroxide group of
The product formed by the reaction between boron substitued
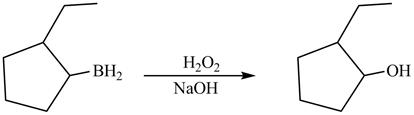
Figure 12
The product formed by thereaction between boron substitued
(l)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product on reaction of
Concept introduction:
Inan oxymercuration reaction,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed on reaction of
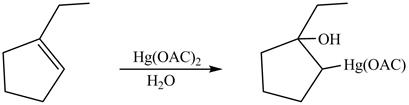
Explanation of Solution
This is an oxymercuration reaction in which
The product formed by the reaction between
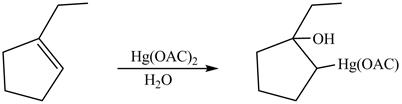
Figure 13
The product formed by thereaction between
(m)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an oxymercuration reaction,
In demercuration reaction,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The product formed by the reaction between
In demercuration reaction,
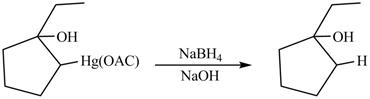
Figure 14
The product formed on reaction is
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
(n)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
In an electrophilic addition reaction, there is an addition of an electrophilic reagent on a nucleophilic group. The double bond and triple bond containing compounds act as a nucleophile. The addition of electrophilic reagent on nucleophilic compound leads to the dissociation of
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between
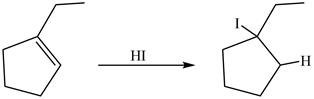
Figure 15
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
(o)
Interpretation:
Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Concept introduction:
The reaction between an alkene,
Answer to Problem 5.28AP
The Principal organic product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Explanation of Solution
The reaction between ![]() in presence of
in presence of
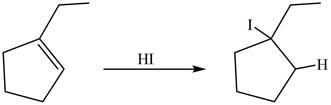
Figure 15
The product formed by the treatment of product of reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- At 90ºC the vapor pressure of ortho-xylene is 20 kPa and that of meta-xylene is 18 kPa. What is the composition of the vapor in equilibrium with a mixture in which the mole fraction of o-xylene is 0.60?arrow_forwardDraw the products of this reduction of a ketone with sodium borohydride. Use a dash or wedge bond to indicate the stereochemistry of substituents on asymmetric centers, where applicableIgnore any inorganic byproducts. 1) NaBH4 2) HCI/H2O Select to Drawarrow_forwardWhy do you think people who live at high altitudes are advised to add salt to water when boiling food like pasta? What mole fraction of NaCl is needed to raise the boiling point of H2O by 3˚C? Does the amount of salt added to water (typically about one teaspoon to four quarts of water) substantially change the boiling point? (Kb (H2O) = 0.51˚C/molal.)arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward9. Consider the following galvanic cell: Fe (s) | Fe(NO3)2 (aq) || Sn(NO3)2 (aq) | Sn (s) a. Write an equation for the half reactions occurring at the anode and cathode. b. Calculate the standard cell potential Show all of your work. c. Draw and label the galvanic cell, including the anode and cathode, direction of electron flow, and direction of ion migration.arrow_forward
- pls help asaparrow_forward11. Use the equation below to answer the following questions: 2 Al(s) + 3 Cd(NO3)2 (aq) → 2 Al(NO3)3 (aq) + 3 Cd(s) a. What is the net ionic equation for the reaction? b. Which species is a spectator ion in this reaction? Define a spectator ion. c. Identify the oxidizing agent and the reducing agent.arrow_forwardpls help asaparrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





