
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780321934925
Author: Jeff Hardin, Gregory Paul Bertoni
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 1Q
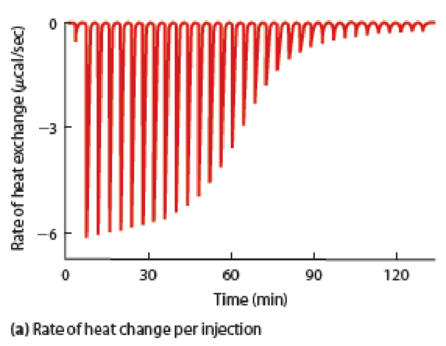
QUESTION: Why does the height of the spike get shorter after successive injections of ligand in Figure 5B-2a?
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Question 2
You are using molecular modelling software to examine the X-ray crystal structure of the
B2-adrenoceptor. You have access to two quality structural images of:
a B2-adrenoceptor bound to a full agonist (BI-167107), and
a B2-adrenoceptor bound to an inverse agonist (carazolol).
You would like to understand the nature and magnitude of the conformational changes made by the
B2-adrenoceptor as it moves from an inactive to active state.
Question 2a
What regions of the receptor would you expect to show the largest conformational changes?
Provide a rationale for your answer.
Question 2b
Describe how you could use information from the two X-ray crystal structures to determine what the
conformational changes are.
G protein-coupled receptors, such as the B2-adrenoceptor, normally only have a single C-terminus
end and a single N-terminus end. However, when examining the X-ray crystal structure of the B2-
adrenoceptor bound to the inverse agonist, there appear to be parts of the…
Drug 1-Ivacaftor (VX-770): Ivacaftor is a potentiator that increases CFTR channel opening time. We know from cell culture studies that this increases chloride transport by as much as 50% from baseline and restores it closer to what would be expected in wild type CFTR. Basically, the drug increases CFTR activity by unlocking the gate that allows for the normal flow of salt and fluids.
For which class of mutations do you think Ivacaftor will be most effective? Explain your choice.
2-89
The following is a block diagram for a sphingoglycolipid
where the building blocks are labeled with letters and the
linkages between building blocks are labeled with numbers.
A
1
2
B
C
a. Which building blocks are fatty acid residues?
b. Which building blocks are carbohydrate residues?
c. Which linkages are amide linkages?
d. Which linkages could involve a monosaccharide?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Becker's World of the Cell (9th Edition)
Ch. 5 - How do phototrophs and chemotrophs depend...Ch. 5 - How does the spontaneity of a chemical reaction...Ch. 5 - QUESTION: Why does the height of the spike get...Ch. 5 - For a chemical reaction happening in a cell, what...Ch. 5 - Prob. 5.1PSCh. 5 - QUANTITATIVE Photosynthetic Energy Transduction....Ch. 5 - Energy Conversion. Most cellular activities...Ch. 5 - Problem Set Enthalpy, Entropy, and Free Energy....Ch. 5 - Violating the Second Law? The second law of...Ch. 5 - QUANTITATIVE The Equilibrium Constant. The...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- = 20 nM. The rate of receptor-ligand complex formation with an A receptor-ligand complex has a dissociation constant of Ka added ligand concentration of 10 µM is 5 × 10³ s¯¹. What is the value of the reverse rate constant, k_₁ ? k_₁ = 8-1arrow_forwardWhy is COVID-19 a man made? (Brief explanation only atleast 3-5 sentences)arrow_forwardQuestion 7. What is the rate-limiting step in the formation of an actin microfilament?arrow_forward
- QUESTION 6 What is the three ketter code for each peptide(a) KFYV(b) ERSC(c) PIMFThe 3-letter code for Peptide (a) is: The 3-letter code for Peptide (b) is: The 3-letter code for Peptide (c) is:arrow_forwardquestion: A sustained decrease in MAP could result in decreased release of ACh by preganglionic neurons that innervate the adrenal medulla. answer should clearly state whether or not the statement is correct and then concisely explain why. the answer should be like more than three but less than 5 sentences and address all of the points in the statement. Here is an example: Both transmembrane carrier proteins and transmembrane channel proteins can mediate active transport of a hydrophilic solute through a cell plasma membrane. This statement is incorrect. Movement of a solute through a channel protein is always passive, whereas carrier-mediated transmembrane transport can be either passive or active. A transmembrane channel protein creates a pore through the membrane allowing for simple diffusion of a hydrophilic solute down a concentration gradient through the membrane. In contrast, transmembrane carrier protein interacts with and 'escorts' a hydrophilic solute through the…arrow_forwardQuestion 3. Someone conducted a kinetic study on insulin and insulin receptor binding. It is found that at an insulin concentration of 0.5 nM, half of the receptors are bound with insulin. Determine the binding dissociation constant between insulin and insulin receptor.arrow_forward
- 6. For a 1:1 ligand-receptor binding interaction that is modeled by X + Y XY : (A) Show how the fraction of ligand-receptor binding (fo) is represented by the [X] [X]+ K, equation of f, (i.e., derive this expression for this reaction beginning eg with the relationship for K = f([X].[X],[XY]) under equilibrium conditions). (B) shown to the right for this reaction, what is the estimated value of Keg? Give your answer in units of M. For the data plot 0.9 0.8 0.7 0.6 문 0.5 0.4 0.3 0.2 0.1 0.0000 0.0050 0.0100 0.0150 0.0200 0.0250 0.0300 0.0350 0.0400 [X) (mM)arrow_forwardQuestion:- Alpha-endorphin is a peptide with an amino acid sequence of YGGFMTSEKSQTPLVT. How many charges does it have at pH 7?arrow_forwardHow long does COVID-19 last on a doorknobarrow_forward
- ○ Transition state analog Uncompetitive Mechanism-based Affinity-based O Non-specificarrow_forwardQuestion :16, 17 .arrow_forwardQuestion: A sample of 5 mL of blood is tested for the enzyme creatine kinase (CK). The blood test reveals that the sample contains a total amount of 1.050 IU of CK. The normal range for CK in a blood test is 25-200 IU per liter. The patient from whom this blood was drawn then has creatine kinase levels that arearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax


Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning


Phlebotomy: Venipuncture Procedure; Author: Medical Lab Lady Gill;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LC9LABPts7M;License: Standard Youtube License