
Concept explainers
Interpretation:The most acidic hydrogen in pair of molecules given below should be circled. Also, molecule that haslower value of
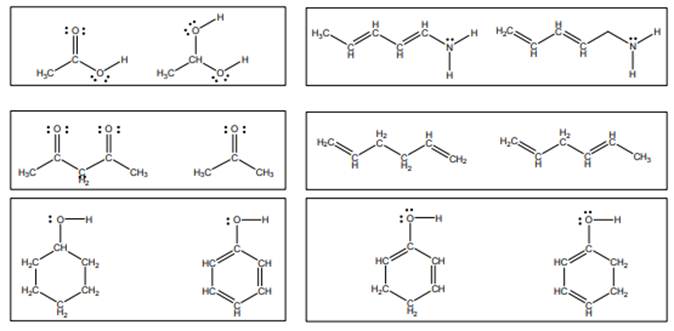
Concept introduction:Lewis structure is representation of molecule in which dots are shown to represent unshared electrons and lines are shown to represent bonds. These lines and dots represent distribution of the electrons in the molecule.
When one single structure is unable to describe all the properties of single molecule, a phenomenon called resonance comes into play. This arises when two or more than two Lewis structures are possible for one molecule. All such structures are called resonating structures and have same placement of atoms in them but these have different locations of bond pairs and lone pairs. The resonating structures are inter-convertible with each other. The resultant of all the resonating or contributing structures is called the resonance hybrid.
Rules to form resonance structure are as follows:
1. Use arrow types 1 and 2 for resonance structure of anions in movement of negative charge.
2. Use only arrow type 3 to move a positive charge for resonance structure of cations.
3. The sigma bond should not be broken. Any atom must not move from its place and total number of electrons must be same in all resonance structures.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Custom eBook for Organic Chemistry
- 20.44 The Diels-Alder reaction is not limited to making six-membered rings with only car- bon atoms. Predict the products of the following reactions that produce rings with atoms other than carbon in them. OCCH OCCH H (b) CH C(CH₂)s COOCH མ་ནས་བ (c) N=C H -0.X- (e) H C=N COOCHS + CH2=CHCH₂ →→arrow_forwardGiven the attached data, provide the drawing for the corresponding structure.arrow_forwardno Ai walkthroughsarrow_forward
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

