
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 13P
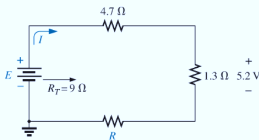
For each network in Fig. 5.100, constructed of standard values, determine:
- The current I.
- The source voltage E.
- The unknown resistance.
- The voltage across each element.
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Solve by Pen and Paper not using chatgpt or AI
You just got a job at Shin-Etsu Chemical growing Si crystals with different dopants. Howmuch Ga needs to be added to 800 kg of Si melt to achieve a 5-10 Ω.cm (measured at midheight) Si CZ crystal with the following characteristics: height: 7 ft, width: 12 inchesdiameter. Assume, angular rotation 10 RPM, melt viscosity 0.1 poise, pull velocity 2mm/min.a. Generate a plot of the doping distribution throughout the length of the crystal (CGa vs. fs ).b. If a second crystal were to be pulled out of the melt without replenishment of silicon nordopant what would be the average resistivity of this crystal (or resistivity at mid height)
DO NOT USE AI OR CHAT GPT NEED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION
Chapter 5 Solutions
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Ch. 5 - For each configuration in Fig. 5.88, find the...Ch. 5 - For each configuration in Fig. 5.89, find the...Ch. 5 - Find the total resistance RT for each...Ch. 5 - Find the total resistance RT for each...Ch. 5 - For each circuit board in Fig. 5.92, �nd the...Ch. 5 - For the circuit in Fig. 5.93, composed of standard...Ch. 5 - For each configuration in Fig. 5.94, determine the...Ch. 5 - Find the resistance R, given the ohmmeter reading...Ch. 5 - What is the ohmmeter reading for each...Ch. 5 - For the series configuration in Fig. 5.97,...
Ch. 5 - For the series configuration in Fig. 5.98,...Ch. 5 - Find the applied voltage necessary to develop the...Ch. 5 - For each network in Fig. 5.100, constructed of...Ch. 5 - For each configuration in Fig. 5.101, what are the...Ch. 5 - For each configuration of Fig. 5.102, find the...Ch. 5 - For the circuit in Fig. 5.103, constructed of...Ch. 5 - Find the unknown quantities for the circuit of...Ch. 5 - Find the unknown quantities for the circuit in...Ch. 5 - Eight holiday lights are connected in series as...Ch. 5 - For the conditions specified in Fig. 5.107,...Ch. 5 - Combine the series voltage sources in Fig. 5.108,...Ch. 5 - Determine the current I and its direction for each...Ch. 5 - Find {he unknown voltage source and resistor for...Ch. 5 - Using Kirchhoffs voltage law, find the unknown...Ch. 5 - Find the current I for the network of Fig. 5.112....Ch. 5 - Using Kirchhoffs voltage law, determine the...Ch. 5 - Using Kirchhoffs voltage law, find the unknown...Ch. 5 - Determine the values of the unknown resistors in...Ch. 5 - For the configuration in Fig. 5.116, with standard...Ch. 5 - Using the voltage divider rule, find the indicated...Ch. 5 - Using the voltage divider rule or Kirchhoffs...Ch. 5 - Using the voltage divider rule or Kirchhoffs...Ch. 5 - Using the information provided, find the unknown...Ch. 5 - Using the voltage divider rule, �nd the unknown...Ch. 5 - Design a voltage divider circuit that will permit...Ch. 5 - Design the voltage divider in Fig. 5.122 such that...Ch. 5 - Find the voltage across each resistor in Fig....Ch. 5 - Design the circuit in Fig. 5.124 such that...Ch. 5 - Determine the voltages Va,Vb, and Vab for the...Ch. 5 - Determine the current I (with direction) and the...Ch. 5 - For the network in Fig. 5.127 determine the...Ch. 5 - Given the information appearing in Fig. 5.128,...Ch. 5 - Determine the values of R1,R2,R3, and R4 for the...Ch. 5 - For the network in Fig. 5.130, determine the...Ch. 5 - For the integrated circuit in Fig. 5.131,...Ch. 5 - For the integrated circuit in Fig. 5.132,...Ch. 5 - Find the internal resistance of a battery that has...Ch. 5 - Find the voltage to the load (full-and conditions)...Ch. 5 - Determine the current through the circuit in Fig....Ch. 5 - Use the computer to verify the results of Example...Ch. 5 - Use the computer to verify the results of Example...Ch. 5 - Use the computer to verify the results of Example...
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
The job of the _____ is to fetch instructions, carry out the operations commanded by the instructions, and prod...
Starting Out With Visual Basic (8th Edition)
The solid steel shaft AC has a diameter of 25 mm and is supported by smooth bearings at D and E. It is coupled ...
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
How does a computers main memory differ from its auxiliary memory?
Java: An Introduction to Problem Solving and Programming (8th Edition)
What is an uninitialized variable?
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
1.2 Explain the difference between geodetic and plane
surveys,
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
What are the design issues for character string types?
Concepts Of Programming Languages
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 7. Complete the following problems for the circuit below. (a) When VDD = 120V, What is the voltage drop V1 across the 7Ω resistor? (b) If the voltage source VDD is set to obtain I1 = 2A, find the value of VDD. (c) If I1 = 100A, What is the value of I2arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =x12x2 + 9u1 dt dx2 =x1+x3+3u2 dt dx3 = 4x1 +5x2 - 12x3 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardCircuit Logic. Match each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light, or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a pushbutton whether it is a maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forward
- a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 = 4x1 = x2 dt dx2 =-3x12x2 +U1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardmatch each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a push button whether it is maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =-7x1 + x2 + 5u1 dt dx2 =-11x1+x3 + 2u1 dt dx3 = -8x16u1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forward
- Question 2 (20 points) a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 dt =x1- 2x2 dx2 = 3x1 - 4x2 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardStuck on the question. Please do not use AI, it will get the answer wrong.arrow_forwardConsider a particle confined in an infinite potential well as shown below and its wave function Solve the following problems. is derived as √(x) = A sin (TA), and energy E= H U 0 U=0 a x πλη 2ma² €30 (iii) Calculate the value of A. [Hint: The probability of finding the particle in 0arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forward8.19 In the circuit shown in Fig. P8.19, u(t) = 40cos(105t) V,R1 = 100 W, R2 = 500 W, C = 0.1 μF, and L = 0.5 mH.Determine the complex power for each passive element, and verifythat conservation of energy is satisfied.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, let R₁=7, R₂=12, R3=24, R4-2, V₁ =26, V2=104, and V3-78, to calculate the power delivered (or absorbed) by the circuit inside the box, as follows: {NOTE: On Multiple Choice Questions, like this problem, you have only one attempt } 1. The current I is equal to (choose the closed values in amperes) O 1.156 -1.156 -1.209 -4.622 1.209 0 (A) 4.622 2. The power delivered (or absorbed) (choose the closest value in watts) (W) -873.292 152.225 O 873.292 -122.181 -58.086 0 O 122.181 R₁ ww V₂ R₂ R3 V1 ww R4 √3arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Kirchhoff's Rules of Electrical Circuits; Author: Flipping Physics;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=d0O-KUKP4nM;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY