
a.
To create a model for h .
The equation for the model is
Given:
Given, Jacob and Emily ride a Ferris wheel at a carnival in Billings, Montana. The wheel has a 16-m diameter and turns at 3rpm with its lowest point 1 m above the ground. Assume that Jacob and Emily’s height h above the ground is a sinusoidal function of time t (in seconds), where
Calculation:
Since at
The diameter of the wheel is 16 m. So, the height of the rider changes from 8 feet below to 8 feet above the center i.e., -8 to 8. Hence the amplitude of the motion is 8.
Hence,
k is the vertical shift of the motion above the ground.
Here the shift of center of wheel above the ground is 1+8=9 m.
Hence,
Given the wheel completes 3 rotations in 1 minute i.e., 60 seconds. Hence, each rotation takes 60/3=20 seconds. So, the period is 20 seconds.
The frequency is given by:
Hence, the equation for the model is
Conclusion:
The equation for the model is
b.
To draw a graph of h for
The graph of h for
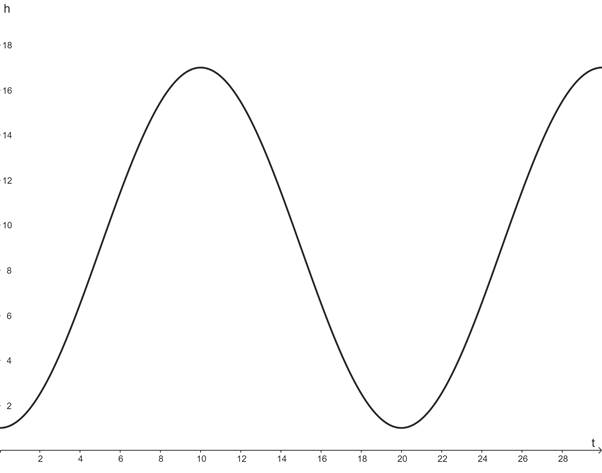
Given:
Given, Jacob and Emily ride a Ferris wheel at a carnival in Billings, Montana. The wheel has a 16-m diameter and turns at 3rpm with its lowest point 1 m above the ground. Assume that Jacob and Emily’s height h above the ground is a sinusoidal function of time t (in seconds), where
Calculation:
Graphing the equation using a graphing utility for
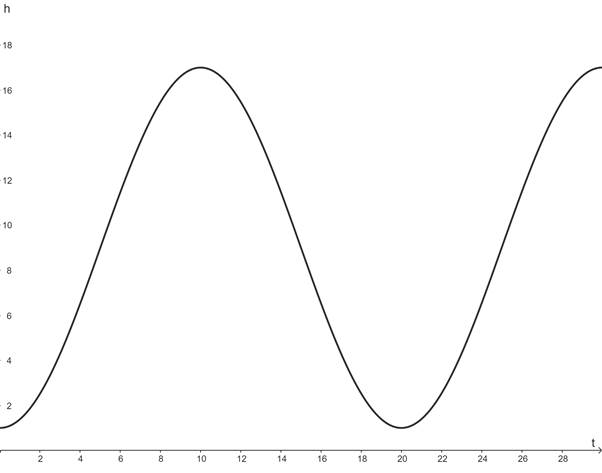
Conclusion:
The graph of h for
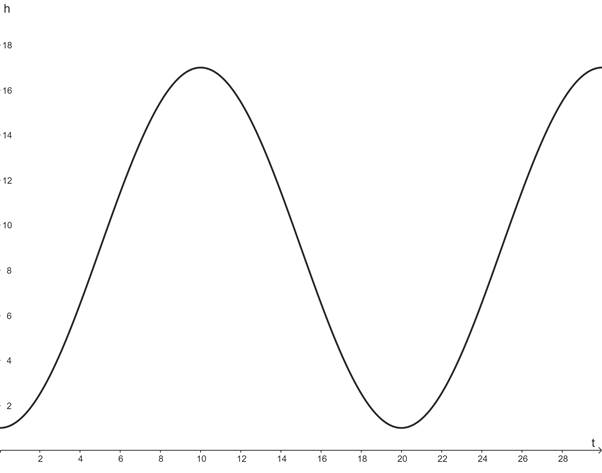
c.
To estimate the height of Jacob and Emily above the ground at
The height of Jacob and Emily above the ground at
Given:
Given, Jacob and Emily ride a Ferris wheel at a carnival in Billings, Montana. The wheel has a 16-m diameter and turns at 3rpm with its lowest point 1 m above the ground. Assume that Jacob and Emily’s height h above the ground is a sinusoidal function of time t (in seconds), where
Calculation:
The equation of the motion is
When
When
Hence, the height of Jacob and Emily above the ground at
Conclusion:
The height of Jacob and Emily above the ground at
Chapter 4 Solutions
PRECALCULUS:GRAPHICAL,...-NASTA ED.
- Consider the function f(x) = x²-1. (a) Find the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x=1 using the definition of the derivative. Show all your steps clearly. (b) Sketch the graph of f(x) around x = 1. Draw the secant line passing through the points on the graph where x 1 and x-> 1+h (for a small positive value of h, illustrate conceptually). Then, draw the tangent line to the graph at x=1. Explain how the slope of the tangent line relates to the value you found in part (a). (c) In a few sentences, explain what the instantaneous rate of change of f(x) at x = 1 represents in the context of the graph of f(x). How does the rate of change of this function vary at different points?arrow_forward1. The graph of ƒ is given. Use the graph to evaluate each of the following values. If a value does not exist, state that fact. и (a) f'(-5) (b) f'(-3) (c) f'(0) (d) f'(5) 2. Find an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = g(x) at x = 5 if g(5) = −3 and g'(5) = 4. - 3. If an equation of the tangent line to the graph of y = f(x) at the point where x 2 is y = 4x — 5, find ƒ(2) and f'(2).arrow_forwardDoes the series converge or divergearrow_forward
- Suppose that a particle moves along a straight line with velocity v (t) = 62t, where 0 < t <3 (v(t) in meters per second, t in seconds). Find the displacement d (t) at time t and the displacement up to t = 3. d(t) ds = ["v (s) da = { The displacement up to t = 3 is d(3)- meters.arrow_forwardLet f (x) = x², a 3, and b = = 4. Answer exactly. a. Find the average value fave of f between a and b. fave b. Find a point c where f (c) = fave. Enter only one of the possible values for c. c=arrow_forwardplease do Q3arrow_forward
- Use the properties of logarithms, given that In(2) = 0.6931 and In(3) = 1.0986, to approximate the logarithm. Use a calculator to confirm your approximations. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) (a) In(0.75) (b) In(24) (c) In(18) 1 (d) In ≈ 2 72arrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral. (Remember the constant of integration.) √tan(8x) tan(8x) sec²(8x) dxarrow_forwardFind the indefinite integral by making a change of variables. (Remember the constant of integration.) √(x+4) 4)√6-x dxarrow_forward
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning





