
Testing Biological Control Biological control agents are used to battle red imported fire ants. Researchers have enlisted the help of Thelohania solenopsae, a natural enemy of the ants. This microsporidian (Section 23.4) is a
Are these biological controls useful against imported fire ants? To find out, USDA scientists treated infested areas with either traditional pesticides or pesticides plus biological controls (both flies and the parasite). The scientists left some plots untreated as controls. FIGURE 45.16 shows the results.
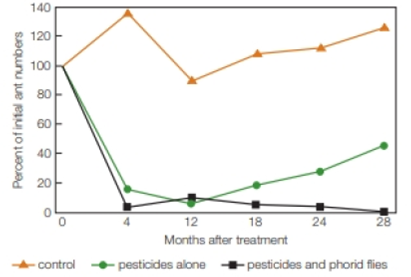
FIGURE 45.16 A comparison of two methods of controlling red imported fire ants. The graph shows the numbers of red imported fire ants over a 28-month period. Orange triangles represent untreated control plots. Green circles are plots treated with pesticides alone. Black squares are plots treated with pesticide and biological control agents (parasitoid flies and a microsporidian parasite).
How did
To determine: The variation in population size in the given control plots during the first four months of the study.
Introduction: Biological control agents are the natural enemies like predation, parasitism, and other methods that are used to control the pests like weeds, insects, mites, nematodes, and so on in order to generate a pest-free- yields. The biological control agent such as Thelohania solenopsae is a natural enemy of the red imported fire ants. This microsporidian can decline the ant’s colony by infecting and shrinking the ovaries of the queen which are the female reproducing ants.
Explanation of Solution
The USDA scientists conducted a study by treating the infected area by using the traditional pesticides and pesticides with biological controls. They kept some plots as controls that are untreated. They observed that the red imported fire ants over a period of 28 months.
Refer Fig. 45.16, “A comparison of two methods of controlling red imported fire ants” in the textbook. The graphical representation shows the percentage of the number of ants versus the months of treatment. The orange triangle indicates the control plots that are untreated. The green circle indicates the plots that treated using pesticides alone and the black square indicates the plots that treated using pesticide with biological control agents (using both parasite and flies).
During the first four months of the treatment, the variation in the population size of the control plots of fire ants increased. Initially, the percentage of the number of ants was 100%. However, after first four months, it had increased to 140%. Hence, there was a variation of about 40%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 45 Solutions
Biology: The Unity and Diversity of Life (MindTap Course List)
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
SEELEY'S ANATOMY+PHYSIOLOGY
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
HUMAN ANATOMY
Campbell Essential Biology (7th Edition)
- I'm struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? . Gonads . Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts . ⚫ Testes . Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) . Epididymis • Vas deferens ⚫ Seminal vesicles ⚫ 5-alpha reductase ⚫ DHT - Penis . Scrotum . Ovaries • Uterus ⚫ Fallopian tubes - Vagina - Clitoris . Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardRequisition Exercise A phlebotomist goes to a patient’s room with the following requisition. Hometown Hospital USA 125 Goodcare Avenue Small Town, USAarrow_forwardI’m struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? • Gonads • Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts • Testes • Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) • Epididymis • Vas deferens • Seminal vesicles • 5-alpha reductase • DHT • Penis • Scrotum • Ovaries • Uterus • Fallopian tubes • Vagina • Clitoris • Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forward
- I’m struggling with this topic and would really appreciate your help. I need to hand-draw a diagram and explain the process of sexual differentiation in humans, including structures, hormones, enzymes, and other details. Could you also make sure to include these terms in the explanation? • Gonads • Wolffian ducts • Müllerian ducts • Testes • Testosterone • Anti-Müllerian Hormone (AMH) • Epididymis • Vas deferens • Seminal vesicles • 5-alpha reductase • DHT • Penis • Scrotum • Ovaries • Uterus • Fallopian tubes • Vagina • Clitoris • Labia Thank you so much for your help!arrow_forwardOlder adults have unique challenges in terms of their nutrient needs and physiological changes. Some changes may make it difficult to consume a healthful diet, so it is important to identify strategies to help overcome these obstacles. From the list below, choose all the correct statements about changes in older adults. Select all that apply. Poor vision can make it difficult for older adults to get to a supermarket, and to prepare meals. With age, taste and visual perception decline. As people age, salivary production increases. In older adults with dysphagia, foods like creamy soups, applesauce, and yogurt are usually well tolerated. Lean body mass increases in older adults.arrow_forwardWhen physical activity increases, energy requirements increase also. Depending on the type, intensity, and duration of physical activity, the body’s requirements for certain macronutrients may change as well. From the list below, choose all the correct statements about the effects of increased physical activity or athletic training. Select all that apply. An athlete who weighs 70 kg (154 lb) should consume 420 to 700 g of carbohydrate per day. How much additional energy an athlete needs depends on the specific activity the athlete engages in and the frequency of the activity. Those participating in vigorous exercise should restrict their fat intake to less than 15%% of total energy intake. Athletes who are following energy-restricted diets are at risk for consuming insufficient protein. The recommendation to limit saturated fat intake to less than 10%% of total energy intake does not apply to athletes or those who regularly engage in vigorous physical activity.arrow_forward
- When taking vitamins and vitamin-mineral supplements, how can one be sure they are getting what they are taking?arrow_forwardHow many milligrams of zinc did you consume on average per day over the 3 days? (See the Actual Intakes vs. Recommended Intakes Report with all days checked.) Enter the number of milligrams of zinc rounded to the first decimal place in the box below. ______ mg ?arrow_forwardthe direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forward
- the direct output from molecular replacement is a coordinate file showing the orientation of the unknown target protein in the unit cell. true or false?arrow_forwardDid your intake of vitamin C meet or come very close to the recommended amount? yes noarrow_forwardWhich of the following statements about hydration is true? Absence of thirst is a reliable indication that an individual is adequately hydrated. All of these statements are true. Although a popular way to monitor hydration status, weighing yourself before and after intensive physical activity is not a reliable method to monitor hydration. Urine that is the color of apple juice indicates dehydration. I don't know yetarrow_forward
 Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology: The Dynamic Science (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305389892Author:Peter J. Russell, Paul E. Hertz, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning





