
(a)
Interpretation:
The three dimensional representation for
Concept introduction:
Electrons in an atom are present in particular orbitals. Sublevels contain orbitals which possess equivalent energy. Maximum two electrons are present in each orbital. The electrons present in
Answer to Problem 81E
The three dimensional representation for
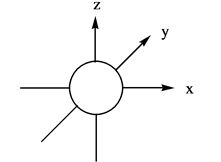
Explanation of Solution
The energy level possesses a sublevel that contains orbital. The sublevels are named as
The three dimensional representation for

Figure 1
The three dimensional representation for
(b)
Interpretation:
The three dimensional representation for
Concept introduction:
Electrons in an atom are present in particular orbitals. Sublevels contain orbitals which possess equivalent energy. Maximum two electrons are present in each orbital. The electrons present in
Answer to Problem 81E
The three dimensional representation for
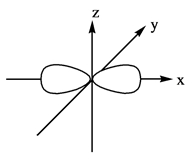
Explanation of Solution
The energy level possesses a sublevel that contains orbital. The sublevels are named as
The three dimensional representation for

Figure 2
The three dimensional representation for
(c)
Interpretation:
The three dimensional representation for
Concept introduction:
Electrons in an atom are present in particular orbitals. Sublevels contain orbitals which possess equivalent energy. Maximum two electrons are present in each orbital. The electrons present in
Answer to Problem 81E
The three dimensional representation for
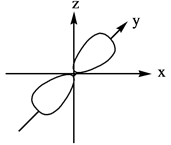
Explanation of Solution
The energy level possesses a sublevel that contains orbital. The sublevels are named as
The three dimensional representation for

Figure 3
The three dimensional representation for
(d)
Interpretation:
The three dimensional representation for
Concept introduction:
Electrons in an atom are present in particular orbitals. Sublevels contain orbitals which possess equivalent energy. Maximum two electrons are present in each orbital. The electrons present in
Answer to Problem 81E
The three dimensional representation for
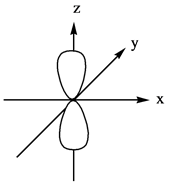
Explanation of Solution
The energy level possesses a sublevel that contains orbital. The sublevels are named as
The three dimensional representation for

Figure 4
The three dimensional representation for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Introductory Chemistry: Concepts and Critical Thinking (8th Edition)
- If some molecules in an excited state collide with other molecules in a ground state, this process1. can occur in solution and in the gas phase.2. can be treated as a bimolecular process.3. always results in collisional deactivation.4. does not compete with any other process.arrow_forwardRadiation of frequency v is incident on molecules in their ground state. The expected outcome is that1. the molecules do not change their state.2. the molecules transition to an excited state.3. the molecules undergo a secondary process.4. collisional deactivation occurs.arrow_forwardPredict the major product of the following reaction and then draw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 H₂SO heat : OH 90 Draw the structure of the major product. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. 3arrow_forward
- Draw a curved arrow mechanism for the reaction, adding steps as necessary. Be sure to include all electrons that are necessary to the mechanism and all nonzero formal charges. C Ö-H H + -S-OH .0. Add/Remove step X टे Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardDraw a curved arrow mechanism for its formation. You may need to re-draw structures to show certain bonds. Ensure that HSO is used as the base to deprotonate the ẞ carbon when necessary. C HO : OH HO: OH =s = + 1 Add/Remove step X Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhich of the following could 1,2-ethanediol be directly synthesized from? OH HO О 0 0. O ?arrow_forward
- Design a synthesis of 1,2-diethoxyethane from an alkene. Select the single best answer for each part. Part: 0/3 Part 1 of 3 Which of the following could 1,2-diethoxyethane be directly synthesized from? O HO 0 HO.... OH HO HO × 5 > ?arrow_forwardDraw the skeletal structure of the major organic product of each step of the reaction sequence. Part: 0/2 Part 1 of 2 Part: 1/2 Part 2 of 2 Continue OH NaH Na Na Br + Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : X G : Garrow_forwardpleasearrow_forward
- please help me please pleasearrow_forwardUsing reaction free energy to predict equilibrium composition Consider the following equilibrium: N2 (g) + 3H2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) AG⁰ = -34. KJ Now suppose a reaction vessel is filled with 8.06 atm of nitrogen (N2) and 2.58 atm of ammonia (NH3) at 106. °C. Answer the following questions about this system: ? rise Under these conditions, will the pressure of N2 tend to rise or fall? ☐ x10 fall Is it possible to reverse this tendency by adding H₂? In other words, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to rise, can that be changed to a tendency to fall by adding H₂? Similarly, if you said the pressure of N2 will tend to fall, can that be changed to a tendency to rise by adding H₂? If you said the tendency can be reversed in the second question, calculate the minimum pressure of H₂ needed to reverse it. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. yes no ☐ atm ☑ 5 00. 18 Ararrow_forwardi need help with the followingarrow_forward
 General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning
General, Organic, and Biological ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781285853918Author:H. Stephen StokerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





