
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780134484143
Author: Allan R. Hambley
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 4, Problem 4.67P
Solve for i(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure P4.67,, with R = 50
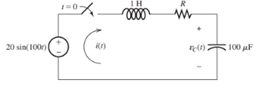
Figure P4.67
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
Report:-
1. Plot (total core loss / cycle) as a function of frequency.
2. Evaluate (K & K2 )corresponding to value of (voltage & frequency).
3. Calculate hysteresis and eddy current losses at rated voltage and
frequency.
Not use ai please
Help on this equation system?
Chapter 4 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
Ch. 4 - Suppose we have a capacitance C discharging...Ch. 4 - The dielectric materials used in real capacitors...Ch. 4 - The initial voltage across the capacitor shown in...Ch. 4 - A 100F capacitance is initially charged to 1000 V....Ch. 4 - At t = 0, a charged 10{ F capacitance is connected...Ch. 4 - At time t1 , a capacitance C is charged to a...Ch. 4 - Given an initially charged capacitance that begins...Ch. 4 - The initial voltage across the capacitor shown in...Ch. 4 - In physics, the half-life is often used to...Ch. 4 - We know that a 50F capacitance is charged to an...
Ch. 4 - We know that the capacitor shown in Figure P4.11...Ch. 4 - The purchasing power P of a certain unit of...Ch. 4 - Derive an expression for vC(t) in the circuit of...Ch. 4 - Suppose that at t= 0, we connect an uncharged 10 F...Ch. 4 - Suppose we have a capacitance C that is charged to...Ch. 4 - A person shuffling across a dry carpet can be...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.17PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.18. Prior...Ch. 4 - List the steps for dc steady-state analysis of RLC...Ch. 4 - Explain why we replace capacitances with open...Ch. 4 - Solve for the steady-state values of i1, i2, and...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.22. What...Ch. 4 - In the circuit of Figure P4.23, the switch is in...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.24 has been set up...Ch. 4 - Solve for the steady-state values of i1 , i2, i3,...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.26 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.27PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit of Figure P4.28 in which the...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Figure P4.29, the switch...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit of Figure P4.30 in which the...Ch. 4 - Give the expression for the time constant of a...Ch. 4 - A circuit consists of switches that open or close...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.33 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.34. The...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.34 given iL(0)=0A .Ch. 4 - Real inductors have series resistance associated...Ch. 4 - Determine expressions for and sketch is(t) to...Ch. 4 - For the circuit shown in Figure P4.38,, find an...Ch. 4 - The circuit shown in Figure P4.39 is operating in...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.40. A...Ch. 4 - Due to components not shown in the figure, the...Ch. 4 - The switch shown in Figure P4.42 has been closed...Ch. 4 - Determine expressions for and sketch vR(t) to...Ch. 4 - What are the steps in solving a circuit having a...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.45PCh. 4 - Solve for vC(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Solve for v(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.48PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown inFigure P4.49. The...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure P4.50. The...Ch. 4 - The voltage source shown in Figure P4.51 is called...Ch. 4 - Determine the form of the particular solution for...Ch. 4 - Determine the form of the particular solution for...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.54PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.55PCh. 4 - How can first-or second-order circuits be...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.57PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.58PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.59PCh. 4 - Sketch a step response for a second-order system...Ch. 4 - A dc source is connected to a series RLC circuit...Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.61 for R = 40 .Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.61 for R = 20 .Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.64PCh. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.64 for R=50 .Ch. 4 - Repeat Problem P4.64 for R=500 .Ch. 4 - Solve for i(t) for t > 0 in the circuit of Figure...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.68PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.69PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.70PCh. 4 - Use MATLAB to derive an expression for vc(t)in the...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.72PCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in FigureP4.50 in which...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.74PCh. 4 - Prob. 4.75PCh. 4 - Use MATLAB to solve for the mesh currents in the...Ch. 4 - The switch m the circuit shown in Figure T4.1 is...Ch. 4 - Prob. 4.2PTCh. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure T4.3. Figure...Ch. 4 - Consider the circuit shown in Figure T4.4 in which...Ch. 4 - Write the MATLAB commands to obtain the solution...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Transmitting and receiving antennas operating at 1 GHz with gains of 20 and 15 dB, respectively, are separated by a distance of 1 km. Find the power delivered to the load when the input power is 150 W. Assume the PLF = 1.arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forwardNEED HANDWRITTEN SOLUTION DO NOT USE AI OR CHATGPTarrow_forward
- 2) Determine the voltage gain of the follower depicted in Fig. 2. Assume Is= 7 × 10-16. B = 100, VA = 5 V. Also assume the capacitors are very large. (40 points)arrow_forwardCalculate the voltage gain and I/O impedance of circuits shown in Fig. 1. Assume (60 points- each section 20 points) J Vina кат Vb J Vina кат VCC VCC VCC Vino - Vout - Vout Rs w Q2 Q2 (c) (b) Q2 = (a) - Voutarrow_forwardNot use ai please letarrow_forward
- Use PSpice to create the circuit and show the circuit along with simulation results. Also please explicitly answer the question (i.e. have the answer make sense and not in parts where there is no final answer.)arrow_forwardProblem 5 Plot the impulse response of the system shown below. Hint: This is done graphically with 4 convolutions. x[n] D y[n]< D D D D D D D D D D Darrow_forwardUse PSpice to create the circuit. Also please explicitly answer whether the load line intersects the -0.7 line at the computed point.arrow_forward
- In class, we wrote on the blackboard a byte addressable memory where each element was 2 nibbles: For example: Main memory A Address Offset Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data Data 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 0 Ox10 0x00 0x02 0x2B Ox4F 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x11 0x12 0x20 0x10 0x10 0x00 OxFF Ox3E DxDD 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 0x00 7 0x1C 0x00 8 9 A 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x01 0x00 0x00 0x01 B с D E 0x00 0x05 0x04 0x03 0x02 0x00 Ox3D 0x00 0x1C Ox2F 0x00 Ox1F OxFF 0x03 0x02 F What is the contents of address 0x1C in main memory A for a 32 bit machine using Big Endian format? What is the contents of address 0x1C in main memory A for a 16 bit machine using Little Endian format? What is the contents of the indirect address at 0x04 in main memory A for a Big Endian 32 bit machine ((0x4))? What is the contents of 4(0x10) in main memory A for a 16 bit Little Endian machine? What is the contents of the address 16(0xC) for a 64 bit Little Endian machine?arrow_forwardProblem 4 Consider the system shown below where h₁[n] = {2,1,2} and h₂[n] = (n+1) u[n] (− means subtraction). h₂[n] x [n]- h₁[n] бел-27- h₂[n] y[n] (a) Determine the impulse response of the system and plot it for n = -3,...,6. (b) Determine graphically the response of the system to the following input. x[n] 2 4 5arrow_forwardNot use ai pleasearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
How Do Hall Effect Sensors Work? - The Learning Circuit; Author: element14 presents;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dgyB2-1VDI0;License: Standard Youtube License