
Concept explainers
A dc source is connected to a series RLC circuit by a switch that closes at t = 0, as shown en Figure P4.61. The initial conditions are i(0 +) = 0 and
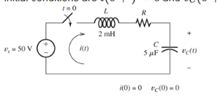
Figure P4.61
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 4 Solutions
Electrical Engineering: Principles & Applications (7th Edition)
Additional Engineering Textbook Solutions
Starting Out with Java: From Control Structures through Objects (7th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Experiencing MIS
Elementary Surveying: An Introduction To Geomatics (15th Edition)
Starting Out with Programming Logic and Design (5th Edition) (What's New in Computer Science)
Fluid Mechanics: Fundamentals and Applications
- a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =x12x2 + 9u1 dt dx2 =x1+x3+3u2 dt dx3 = 4x1 +5x2 - 12x3 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardCircuit Logic. Match each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light, or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a pushbutton whether it is a maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 = 4x1 = x2 dt dx2 =-3x12x2 +U1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forward
- match each statement to the proper circuit. All circuits have been drawn with a light (L) to represent the load, whether it is a motor, bell, light or any other load. In addition, each switch is illustrated as a push button whether it is maintained switch, momentary contact switch, pushbutton, switch-on target, or any other type of switch.arrow_forwarda) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 =-7x1 + x2 + 5u1 dt dx2 =-11x1+x3 + 2u1 dt dx3 = -8x16u1 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forwardQuestion 2 (20 points) a) In terms of n and p, how many state variables and how many inputs can you see in the system below? dx1 dt =x1- 2x2 dx2 = 3x1 - 4x2 dt b) Derive the state space representation for the above system c) Determine whether the system is stable or not.arrow_forward
- Stuck on the question. Please do not use AI, it will get the answer wrong.arrow_forwardConsider a particle confined in an infinite potential well as shown below and its wave function Solve the following problems. is derived as √(x) = A sin (TA), and energy E= H U 0 U=0 a x πλη 2ma² €30 (iii) Calculate the value of A. [Hint: The probability of finding the particle in 0arrow_forwardQ2: Using D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0.arrow_forward8.19 In the circuit shown in Fig. P8.19, u(t) = 40cos(105t) V,R1 = 100 W, R2 = 500 W, C = 0.1 μF, and L = 0.5 mH.Determine the complex power for each passive element, and verifythat conservation of energy is satisfied.arrow_forwardIn the circuit shown, let R₁=7, R₂=12, R3=24, R4-2, V₁ =26, V2=104, and V3-78, to calculate the power delivered (or absorbed) by the circuit inside the box, as follows: {NOTE: On Multiple Choice Questions, like this problem, you have only one attempt } 1. The current I is equal to (choose the closed values in amperes) O 1.156 -1.156 -1.209 -4.622 1.209 0 (A) 4.622 2. The power delivered (or absorbed) (choose the closest value in watts) (W) -873.292 152.225 O 873.292 -122.181 -58.086 0 O 122.181 R₁ ww V₂ R₂ R3 V1 ww R4 √3arrow_forwardFor the circuit shown, find the currents 11, 12, 16 and 17, given 13 =1 A, 14-19 A, 15 =-10 A, and Ig =5 A. = (A) 12 = (A) 16 = (A) 175 (A) (Based on Alexander Textbook, Chapter2) I5 12 14 18 13 16 • Round your values to 3-significant digits.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





