
For the circuit in Figure P4.39,
(a)
The width to length ratio of the transistor in the given circuit.
Answer to Problem 4.40P
The width to length ratio of the transistors is given by
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A source follower depletion NMOS circuit with transistor parameters
Calculation:
Consider the given circuit in Figure 1 which consists a source follower depletion NMOS circuit .
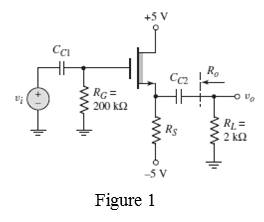
The gate terminal gets grounded when we consider the DC equivalent of the above circuit. The gate current is zero and gate source voltage is expressed as,
The drain to source voltage corresponding to operating point is,
Assuming the transistor is in saturation, the drain current at quiescent condition is given by,
Therefore the above equation can be rearranged to get the W/L ratio as,
Substituting the values of quiescent drain current ,gate-source voltage , threshold voltage and
(b)
The small signal voltage gain for a load resistance.
Answer to Problem 4.40P
The small signal voltage gain for
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A source follower depletion NMOS circuit with transistor parameters
Calculation:
For the circuit in Figure 1, the voltage gain is given by,
Here,
Substituting the value of width to length ratio from part (a) along with the voltages and
The transistor output resistance
Substituting these parameters along with the source resistance, the voltage gain can be calculated as,
(c)
The small signal output resistance
Answer to Problem 4.40P
The output voltage is given by
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A source follower depletion NMOS circuit with transistor parameters
Calculation:
For the circuit in Figure 1, the small signal output resistance is given by,
The transconductance of the circuit was obtained in previous part as
Substituting these parameters along with the source resistance, small signal output resistance can be calculated as,
(d)
The small signal voltage gain for a load resistance.
Answer to Problem 4.40P
The small signal voltage gain for
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
A source follower depletion NMOS circuit with transistor parameters
Calculation:
For the circuit in Figure 1, the voltage gain is given by,
The transconductance of the circuit was obtained in previous part as
Now, when there is a finite load resistance which is given here as
Substituting these parameters along with the load resistance resistance, the voltage gain can be calculated as,
It can be observed that, with a finite load resistance, the gain is less compared to the output with infinite load.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 4 Solutions
MICROELECT. CIRCUIT ANALYSIS&DESIGN (LL)
- Q2.A. It is planned to use the transformer shown in Fig. 1, a 12-pulse rectifier. Each secondary is connected to three phase controlled bridge rectifier. The two rectifiers are connected in series to supply a highly inductive load. 1. Based on the phasor relationship between different windings. If suitable turns ratio is selected, is it possible to use this transformer to produce 12 pulse output voltage? Show the reason behind your answer. 2. Assuming this arrangement is possible to be used in 12-pulse rectifier, draw the output voltage of the 1st and 2nd rectifier and give the relation of the total output voltage. 3. Use the Fourier analysis to show the harmonics in all line currents of the transformer. A B in C Fig. 1 b la a 2 b.arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answer.arrow_forward
- Q5.B How parallel connected DC-DC converters increase the effective switching frequency? Show the advantages and limitations in these converters.arrow_forwardQ4. Give the reasons for the following 1. In AC machines drives, the frequency modulation index should be integer regardless the value of switching frequency. 2. Variable de link voltage is adopted in inverter operating in square wave operation mode 3. Practical values of switch utilization factor is different from theoretical values 4. In three-phase inverter with my is odd and multiple of 3, the even and tripplen harmonics are zero. 5. The PSC-PWM is attractive for the modular multilevel converterarrow_forwardQ6.B. Answer the following questions 1. Does the steady state load current in a half bridge inverter has an average value and what is the adverse effect of the average current component? 2. Can the LPF of single phase bridge inverter based on bipolar PWM be used with single phase bridge inverter based on unipolar PWM? Explainarrow_forward
- Q3. Answer the following questions T 1. Compared to the bipolar voltage-switching scheme, the unipolar scheme is "effectively" doubling the switching frequency. Explain the statement's meaning and how this effect can be generated. 2. What are the properties of a good power switch, and what are its basic ratings? 3. What are the objectives of any PWM strategy for three-phase inverters? 4. Why is the current control PWM rectifier in the dq rotating reference frame preferred over the abc reference frame? 5. Define the switch utilization factor. Show how this factor can be calculated for different single-phase inverters for square wave operation mode at the maximum rated output.arrow_forwardQ1.B. Explain output control by voltage cancellation in a single-phase inverter. What are the advantages over square wave operation?arrow_forwardQ3.B. What is the problem of three-phase HW rectifier and how can be resolved?arrow_forward
- Q3-consider the unity feedback system shown below: a.Evaluate general formula of ess? b.Calculate the steady state error of the closed loop system due to R(s) unit step input, D(s)=0]? c.Calculate the steady-state response when D(s) and ramp and R(s)=0?arrow_forward- = 400KHZ. Q1. In a Boost converter, L = 25 μH, Vin = 12 V, D = 0.4, P = 25 W, and fs (i) if the output load is changing. Calculate the critical value of the output load P,below which the converter will enter the discontinuous conduction mode of operation. Assume the total turn-on loss is equal to 2 W. (ii) Assuming the input voltage fluctuates from 10 V to 14 V and the output voltage is regulated to 20 V. Calculate the critical value of the inductance L below which this Boost converter will enter the discontinuous conduction mode of operation at P = 5 W. (iii) Draw the waveforms for inductor voltage, inductor current, and the capacitor current for this Boost converter at the output load that causes it to operate at the border of continuous and discontinuous modes. vd tow 77 N₂ AT 22 1-1arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





