
College Physics
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168048
Author: Paul Peter Urone, OpenStax, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 34, Problem 17PE
The core of a star collapses during a supernova, forming a neutron star. 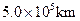 and it collapses to 10.0 km, find the neutron star’s
and it collapses to 10.0 km, find the neutron star’s
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
No chatgpt pls will upvote
A beam of alpha-particles of energy 7.3MeV is used.The protons emitted at an angle of zero degree are found to have energy of 9.34MeV.Find the Q-value of this reaction .
An aluminum rod and a copper rod have the same length of 100cm at 5C. At what temperatures would one of the rods be 0.5 mm longer than the other? Which rod is longer at such temperature?
Chapter 34 Solutions
College Physics
Ch. 34 - Explain why it only appears that we are at the...Ch. 34 - If there is no observable edge to the universe,...Ch. 34 - If the universe is infinite, does it have a...Ch. 34 - Another known cause of red shift in light is the...Ch. 34 - If some unknown cause of red shiftsuch as light...Ch. 34 - Olbers’s paradox poses an interesting question: If...Ch. 34 - If the cosmic microwave background radiation...Ch. 34 - The decay of one type of Kmeson is cited as...Ch. 34 - Distances to local galaxies are determined by...Ch. 34 - Distances to very remote galaxies are estimated...
Ch. 34 - If the smallest meaningful time interval is...Ch. 34 - Quantum gravity, if developed, would be an...Ch. 34 - Does observed gravitational lensing correspond to...Ch. 34 - Suppose you measure the red shifts of all the...Ch. 34 - What are gravitational waves, and have they yet...Ch. 34 - Is the event horizon of a black hole the actual...Ch. 34 - Suppose black holes radiate their mass away and...Ch. 34 - Discuss the possibility that star velocities at...Ch. 34 - How does relativistic time dilation prohibit...Ch. 34 - If neutrino oscillations do occur, will they...Ch. 34 - Lacking direct evidence of WIMPs as dark matter,...Ch. 34 - Must a complex system be adaptive to be of...Ch. 34 - State a necessary condition for a System to be...Ch. 34 - What is critical temperature Tc? Do all materials...Ch. 34 - Explain how good thermal contact with liquid...Ch. 34 - Not only is liquid nitrogen a cheaper coolant than...Ch. 34 - For experimental evidence particularly of...Ch. 34 - Discuss whether you think there are limits to what...Ch. 34 - Find the approximate mass of the luminous matter...Ch. 34 - Find the approximate mass of the dark and luminous...Ch. 34 - (a) Estimate the mass of the luminous matter in...Ch. 34 - If a galaxy is 500 Mly away from us, how fast do...Ch. 34 - On average, how far away are galaxies mat are...Ch. 34 - Our solar system orbits the center of the Milky...Ch. 34 - (a) What is the approximate speed relative to us...Ch. 34 - (a) Calculate The approximate age of the universe...Ch. 34 - Assuming a circular orbit for the Sun about the...Ch. 34 - (a) What is the approximate force of gravity on a...Ch. 34 - Andromeda galaxy is the closest large galaxy and...Ch. 34 - (a) A particle and its antiparticle are at rest...Ch. 34 - The average particle energy needed to observe...Ch. 34 - The peak intensity of the CMBR occurs at a...Ch. 34 - (a) What Hubble constant corresponds to an...Ch. 34 - Show that the velocity of a star orbiting its...Ch. 34 - The core of a star collapses during a supernova,...Ch. 34 - Using data from the previous problem, find the...Ch. 34 - Distances to the nearest stars (up to 500 by away)...Ch. 34 - (a) Use the Heisenberg uncertainty principle to...Ch. 34 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a star moving...Ch. 34 - What is the Schwarzschild radius of a blank hole...Ch. 34 - Black holes with masses smaller than muse formed...Ch. 34 - Supermassive black holes are thought to exist at...Ch. 34 - Construct Your Own Problem Consider a supermassive...Ch. 34 - The characteristic length of entities in...Ch. 34 - If the dark matter in the Milky Way were composed...Ch. 34 - The critical mass density needed to just halt the...Ch. 34 - Assume the average density of the universe is 0.1...Ch. 34 - To get an idea of how empty deep spam is on the...Ch. 34 - A section of superconducting wire carries a...
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Find more solutions based on key concepts
In humans, hemophilia A (OMIM 306700) is an X-linked recessive disorder that affects the gene for factor VIII p...
Genetic Analysis: An Integrated Approach (3rd Edition)
60. You are 9.0 m from the door of your bus, behind the bus, when it pulls away with an acceleration of 1.0 m/...
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: A Strategic Approach, Vol. 1 (Chs 1-21) (4th Edition)
Fibrous connective tissue consists of ground substance and fibers that provide strength, support, and flexibili...
Human Biology: Concepts and Current Issues (8th Edition)
Match each of the following items with all the terms it applies to:
Human Physiology: An Integrated Approach (8th Edition)
Q1. Which wavelength of light has the highest frequency?
a) 10 nm
b) 10 mm
c) 1 nm
d) 1 mm
Chemistry: A Molecular Approach (4th Edition)
Match the following examples of mutagens. Column A Column B ___a. A mutagen that is incorporated into DNA in pl...
Microbiology: An Introduction
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- ROTATIONAL DYNAMICS Question 01 A solid circular cylinder and a solid spherical ball of the same mass and radius are rolling together down the same inclined. Calculate the ratio of their kinetic energy. Assume pure rolling motion Question 02 A sphere and cylinder of the same mass and radius start from ret at the same point and more down the same plane inclined at 30° to the horizontal Which body gets the bottom first and what is its acceleration b) What angle of inclination of the plane is needed to give the slower body the same acceleration Question 03 i) Define the angular velocity of a rotating body and give its SI unit A car wheel has its angular velocity changing from 2rads to 30 rads seconds. If the radius of the wheel is 400mm. calculate ii) The angular acceleration iii) The tangential linear acceleration of a point on the rim of the wheel Question 04 in 20arrow_forwardQuestion B3 Consider the following FLRW spacetime: t2 ds² = -dt² + (dx² + dy²+ dz²), t2 where t is a constant. a) State whether this universe is spatially open, closed or flat. [2 marks] b) Determine the Hubble factor H(t), and represent it in a (roughly drawn) plot as a function of time t, starting at t = 0. [3 marks] c) Taking galaxy A to be located at (x, y, z) = (0,0,0), determine the proper distance to galaxy B located at (x, y, z) = (L, 0, 0). Determine the recessional velocity of galaxy B with respect to galaxy A. d) The Friedmann equations are 2 k 8πG а 4πG + a² (p+3p). 3 a 3 [5 marks] Use these equations to determine the energy density p(t) and the pressure p(t) for the FLRW spacetime specified at the top of the page. [5 marks] e) Given the result of question B3.d, state whether the FLRW universe in question is (i) radiation-dominated, (ii) matter-dominated, (iii) cosmological-constant-dominated, or (iv) none of the previous. Justify your answer. f) [5 marks] A conformally…arrow_forwardSECTION B Answer ONLY TWO questions in Section B [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-B sub question.] Question B1 Consider the line element where w is a constant. ds²=-dt²+e2wt dx², a) Determine the components of the metric and of the inverse metric. [2 marks] b) Determine the Christoffel symbols. [See the Appendix of this document.] [10 marks] c) Write down the geodesic equations. [5 marks] d) Show that e2wt it is a constant of geodesic motion. [4 marks] e) Solve the geodesic equations for null geodesics. [4 marks]arrow_forward
- Page 2 SECTION A Answer ALL questions in Section A [Expect to use one single-sided A4 page for each Section-A sub question.] Question A1 SPA6308 (2024) Consider Minkowski spacetime in Cartesian coordinates th = (t, x, y, z), such that ds² = dt² + dx² + dy² + dz². (a) Consider the vector with components V" = (1,-1,0,0). Determine V and V. V. (b) Consider now the coordinate system x' (u, v, y, z) such that u =t-x, v=t+x. [2 marks] Write down the line element, the metric, the Christoffel symbols and the Riemann curvature tensor in the new coordinates. [See the Appendix of this document.] [5 marks] (c) Determine V", that is, write the object in question A1.a in the coordinate system x'. Verify explicitly that V. V is invariant under the coordinate transformation. Question A2 [5 marks] Suppose that A, is a covector field, and consider the object Fv=AAμ. (a) Show explicitly that F is a tensor, that is, show that it transforms appropriately under a coordinate transformation. [5 marks] (b)…arrow_forwardHow does boiling point of water decreases as the altitude increases?arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forward
- 14 Z In figure, a closed surface with q=b= 0.4m/ C = 0.6m if the left edge of the closed surface at position X=a, if E is non-uniform and is given by € = (3 + 2x²) ŷ N/C, calculate the (3+2x²) net electric flux leaving the closed surface.arrow_forwardNo chatgpt pls will upvotearrow_forwardsuggest a reason ultrasound cleaning is better than cleaning by hand?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 3
Physics
ISBN:9781938168185
Author:William Moebs, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax