
Concept explainers
GO Figure 30-44a shows a wire that forms a rectangle (W = 20 cm, H = 30 cm) and has a resistance of 5.0 mΩ. Its interior is split into three equal areas, with magnetic fields
![]() components Bz of the three fields with time t; the vertical axis scale is set by Bs = 4.0 μT and Bb = −2.5Bs, and the horizontal axis scale is set by ts = 2.0 s. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the current induced in the wire?
components Bz of the three fields with time t; the vertical axis scale is set by Bs = 4.0 μT and Bb = −2.5Bs, and the horizontal axis scale is set by ts = 2.0 s. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction of the current induced in the wire?
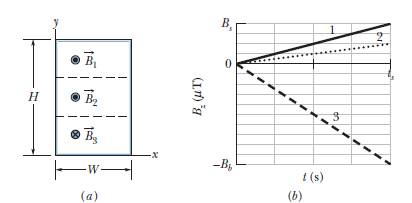
Figure 30-44 Problem 16.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 30 Solutions
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (3rd Edition)
Biology: Life on Earth with Physiology (11th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Anatomy & Physiology (6th Edition)
Principles of Anatomy and Physiology
- 8. With the aid of a diagram draw the following electric circuit and use the resistor as the load, (a) Closed circuit (b) Open circuitarrow_forwardLab 8 Part 3 PHET Wave Interface simulation. I am having trouble with this part of the lab.arrow_forwardMick and Rick are twins born on Earth in the year 2175. Rick grows up to be an Earth-bound robotics technician while Mick becomes an intergalactic astronaut. Mick leaves the Earth on his first space mission in the year 2200 and travels, according to his clock, for 10 years at a speed of 0.75c. Unfortunately, at this point in his journey, the structure of his ship undergoes mechanical breakdown and the ship explodes. How old is Rick when his brother dies?arrow_forward

 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill





