
a)
Interpretation : The approximate boiling points for the C2, C4, C6, and C8
Concept Introduction : A measure of an object's heat or cold is its temperature. The temperature of an object determines how heat is transferred.
a)
Answer to Problem 92A
The approximate boiling points for the C2, C4, C6, and C8 alkanes are
Explanation of Solution
The graph is plotted between the number of carbon atoms and the boiling points.
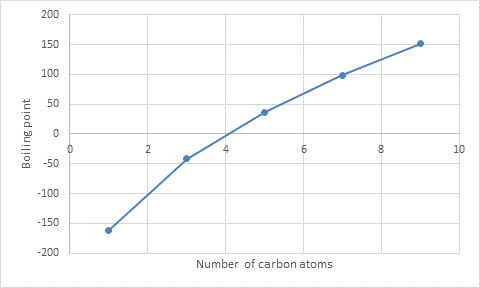
With the help of a graph, the boiling point of C2, C4, C6, and C8 alkanes are obtained.
The approximate boiling point of C2 alkane is
The approximate boiling point of C4alkane is
The approximate boiling point of C6 alkane is
The approximate boiling point of C8alkane is
b)
Interpretation : The nine alkanes that are gases at room temperature are to be identified.
Concept Introduction : A measure of an object's heat or cold is its temperature. The temperature of an object determines how heat is transferred.
b)
Answer to Problem 92A
The alkanes that are gases at room temperature are C1, C2, C3, and C4 alkanes.
Explanation of Solution
The alkanes beyond their boiling point become gaseous.
The alkanes are liquid when it is below their boiling point.
From the graph, the alkanes that are gases at room temperature can be identified.
When the boiling point of alkanes is less than the room temperature, those alkanes become gases at that room temperature.
The alkanes such as C1, C2, C3, and C4 alkanes have less boiling point than room temperature so they become gaseous.
c)
Interpretation : The nine alkanes that are liquid at 350 K are to be identified.
Concept Introduction : A measure of an object's heat or cold is its temperature. The temperature of an object determines how heat is transferred.
c)
Answer to Problem 92A
The alkanes that are liquid at 350 K are C7, C8, and C9 alkanes.
Explanation of Solution
The alkanes beyond their boiling point become gaseous.
The alkanes are liquid when it is below their boiling point.
From the graph, the alkanes that are liquid at 350 K can be identified.
The temperature is 350 K means
When the boiling point of alkanes is higher than 350 K, those alkanes are liquid at that temperature.
The alkanes such as C7, C8, and C9 alkanes have high boiling point than 350 K so they are liquid at that temperature.
d)
Interpretation : The approximate increase in boiling point per additional carbon atom in these alkanes is to be identified.
Concept Introduction : A measure of an object's heat or cold is its temperature. The temperature of an object determines how heat is transferred.
d)
Answer to Problem 92A
The approximate increase in boiling point per additional carbon atom in these alkanes is
Explanation of Solution
With the help of the graph, the approximate increase in boiling point is calculated.
There is approximately
Chapter 3 Solutions
Chemistry 2012 Student Edition (hard Cover) Grade 11
- fcrip = ↓ bandwidth Il temp 32. What impact (increase, decrease, or no change) does each of the following conditions have on the individual components of the van Deemter equation and consequently, band broadening? Increase temperature Longer column Using a gas mobile phase instead of liquid Smaller particle stationary phase Multiple Paths Diffusion Mass Transferarrow_forward34. Figure 3 shows Van Deemter plots for a solute molecule using different column inner diameters (i.d.). A) Predict whether decreasing the column inner diameters increase or decrease bandwidth. B) Predict which van Deemter equation coefficient (A, B, or C) has the greatest effect on increasing or decreasing bandwidth as a function of i.d. and justify your answer. Figure 3 Van Deemter plots for hydroquinone using different column inner diameters (i.d. in μm). The data was obtained from liquid chromatography experiments using fused-silica capillary columns packed with 1.0-μm particles. 35 20 H(um) 큰 20 15 90 0+ 1500 100 75 550 01 02 594 05 μ(cm/sec) 30 15 10arrow_forwardelow are experimentally determined van Deemter plots of column efficiency, H, vs. flow rate. H is a quantitative measurement of band broadening. The left plot is for a liquid chromatography application and the night is for gas chromatography. Compare and contrast these two plots in terms of the three band broadening mechanisms presented in this activity. How are they similar? How do they differ? Justify your answers.? 0.4 H (mm) 0.2 0.1- 0.3- 0 0.5 H (mm) 8.0 7.0 6.0 5.0 4.0- 3.0 T +++ 1.0 1.5 0 2.0 4.0 Flow Rate, u (cm/s) 6.0 8.0 Flow Rate, u (cm/s)arrow_forward
- Predict the products of this organic reaction: + H ZH NaBH3CN H+ n. ? Click and drag to start drawing a structure. Xarrow_forwardWhat is the missing reactant R in this organic reaction? + R H3O+ + • Draw the structure of R in the drawing area below. • Be sure to use wedge and dash bonds if it's necessary to draw one particular enantiomer. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forwardWhat would be the best choices for the missing reagents 1 and 3 in this synthesis? 1 1. PPh3 2. n-BuLi 2 • Draw the missing reagents in the drawing area below. You can draw them in any arrangement you like. • Do not draw the missing reagent 2. If you draw 1 correctly, we'll know what it is. • Note: if one of your reagents needs to contain a halogen, use bromine. Click and drag to start drawing a structure.arrow_forward
- The product on the right-hand side of this reaction can be prepared from two organic reactants, under the conditions shown above and below the arrow. Draw 1 and 2 below, in any arrangement you like. 1+2 NaBH₂CN H+ N Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X $arrow_forwardExplain what is the maximum absorbance of in which caffeine absorbs?arrow_forwardExplain reasons as to why the amount of caffeine extracted from both a singular extraction (5ml Mountain Dew) and a multiple extraction (2 x 5.0ml Mountain Dew) were severely high when compared to coca-cola?arrow_forward
- Protecting Groups and Carbonyls 6) The synthesis generates allethrolone that exhibits high insect toxicity but low mammalian toxicity. They are used in pet shampoo, human lice shampoo, and industrial sprays for insects and mosquitos. Propose detailed mechanistic steps to generate the allethrolone label the different types of reagents (Grignard, acid/base protonation, acid/base deprotonation, reduction, oxidation, witting, aldol condensation, Robinson annulation, etc.) III + VI HS HS H+ CH,CH,Li III I II IV CI + P(Ph)3 V ༼ Hint: no strong base added VI S VII IX HO VIII -MgBr HgCl2,HgO HO. isomerization aqeuous solution H,SO, ༽༽༤༽༽ X MeOH Hint: enhances selectivity for reaction at the S X ☑arrow_forwardDraw the complete mechanism for the acid-catalyzed hydration of this alkene. esc 田 Explanation Check 1 888 Q A slock Add/Remove step Q F4 F5 F6 A བྲA F7 $ % 5 @ 4 2 3 & 6 87 Click and drag to start drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Ce W E R T Y U S D LL G H IK DD 요 F8 F9 F10 F1 * ( 8 9 0 O P J K L Z X C V B N M H He commandarrow_forwardExplanation Check F1 H₂O H₂ Pd 1) MCPBA 2) H3O+ 1) Hg(OAc)2, H₂O 2) NaBH4 OH CI OH OH OH hydration halohydrin formation addition halogenation hydrogenation inhalation hydrogenation hydration ☐ halohydrin formation addition halogenation formation chelation hydrogenation halohydrin formation substitution hydration halogenation addition Ohalohydrin formation subtraction halogenation addition hydrogenation hydration F2 80 F3 σ F4 F5 F6 1 ! 2 # 3 $ 4 % 05 Q W & Å © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. F7 F8 ( 6 7 8 9 LU E R T Y U A F9arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





