
3-23 Predict which ions are stable:
(a) 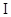
(b) 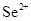
(c) 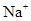
(d) 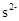
(e) 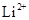
(f) 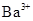
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Interpretation:
Whether
Concept Introduction:
Octet rule: generally all atoms will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 8 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element.
Duet rule: generally some atoms like hydrogen, lithium, beryllium will lose, gain or share electrons to attain 2 valence electrons; the electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium.
Answer to Problem 7P
Explanation of Solution
The atomic number or number of electrons of
When
The electronic configuration of the nearest noble element like helium, neon argon is the stable configuration hence the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Introduction to General, Organic and Biochemistry
- Draw the starting material that would be needed to make this product through an intramolecular Dieckmann reactionarrow_forwardDraw the major product of this reaction. Nitropropane reacts + pent-3-en-2-one reacts with NaOCH2CH3, CH3CHOHarrow_forwardIndicate whether the product formed in the reaction exhibits tautomerism. If so, draw the structure of the tautomers. OC2H5 + CoHs-NH-NH,arrow_forward
- Explain how substitutions at the 5-position of barbituric acid increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardExplain how substitutions at the 5-position of phenobarbital increase the compound's lipophilicity.arrow_forwardName an interesting derivative of barbituric acid, describing its structure.arrow_forward
- Briefly describe the synthesis mechanism of barbituric acid from the condensation of urea with a β-diketone.arrow_forwardGiven the hydrazones indicated, draw the structures of the enamines that can be formed. Indicate the most stable enamine (explain). C6H5 C6H5 H C6H5 Harrow_forward4. Propose a Synthesis for the molecule below. You may use any starting materials containing 6 carbons or less (reagents that aren't incorporated into the final molecule such as PhзP do not count towards this total, and the starting material can have whatever non-carbon functional groups you want), and any of the reactions you have learned so far in organic chemistry I, II, and III. Your final answer should show each step separately, with intermediates and conditions clearly drawn.arrow_forward
- Indicate the importance of the indole ring. Find a representative example and list 5 structures.arrow_forwardΌΗ 1) V2 CO 3 or Nalt In منهarrow_forward6. The equilibrium constant for the reaction 2 HBr (g) → H2(g) + Br2(g) Can be expressed by the empirical formula 11790 K In K-6.375 + 0.6415 In(T K-¹) - T Use this formula to determine A,H as a function of temperature. Calculate A,-H at 25 °C and at 100 °C.arrow_forward
 Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introduction to General, Organic and BiochemistryChemistryISBN:9781285869759Author:Frederick A. Bettelheim, William H. Brown, Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Omar TorresPublisher:Cengage Learning
