
(a)
Interpretation:
The number of unpaired electrons that is associated with electronic configuration
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom describes how many electrons are present in the shell. Many orbitals are present about the nucleus of an atom. In these orbitals the electrons do not occupy randomly. There are three rules for assigning the electrons to various shells, subshells, and orbitals. They are,
- The subshells are filled in increasing order of energy.
- In a subshell, the electrons occupy the orbital singly first in all orbitals before pairing up by the second electron. All the electrons that are in singly occupied orbitals have same spin.
- In a given orbital there cannot be more than two electrons and they have opposite spins.
Electronic configuration of an element is the one that gives information about how many electrons are present in each electron subshell of an atom. The electrons are added to the subshells in increasing order of energy. Electronic configurations are written in shorthand notation which uses a number‑letter combination. The shell is indicated by the number and subshell is indicated by the letter. Superscript that follows the subshell tells how many electrons are present in the subshell.
The order of filling up the electrons in the subshell is done as shown in the given figure below.
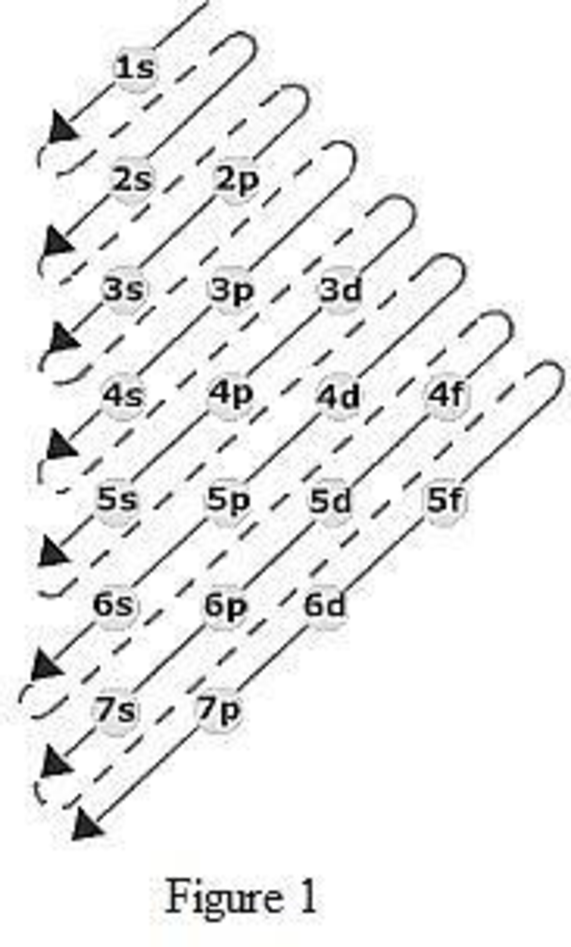
Orbital diagram is the one that gives information about the number of electrons present in the electron orbitals of an atom. The difference between electronic configuration and orbital diagram is that electronic configuration deals with the electrons occupancy in the subshell while orbital diagram deals with the electrons occupancy in the electron orbital. Electrons are paired up in the orbital only when all the orbitals in the subshell are singly filled.
(b)
Interpretation:
The number of unpaired electrons that is associated with electronic configuration
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom describes how many electrons are present in the shell. Many orbitals are present about the nucleus of an atom. In these orbitals the electrons do not occupy randomly. There are three rules for assigning the electrons to various shells, subshells, and orbitals. They are,
- The subshells are filled in increasing order of energy.
- In a subshell, the electrons occupy the orbital singly first in all orbitals before pairing up by the second electron. All the electrons that are in singly occupied orbitals have same spin.
- In a given orbital there cannot be more than two electrons and they have opposite spins.
Electronic configuration of an element is the one that gives information about how many electrons are present in each electron subshell of an atom. The electrons are added to the subshells in increasing order of energy. Electronic configurations are written in shorthand notation which uses a number‑letter combination. The shell is indicated by the number and subshell is indicated by the letter. Superscript that follows the subshell tells how many electrons are present in the subshell.
The order of filling up the electrons in the subshell is done as shown in the given figure below.
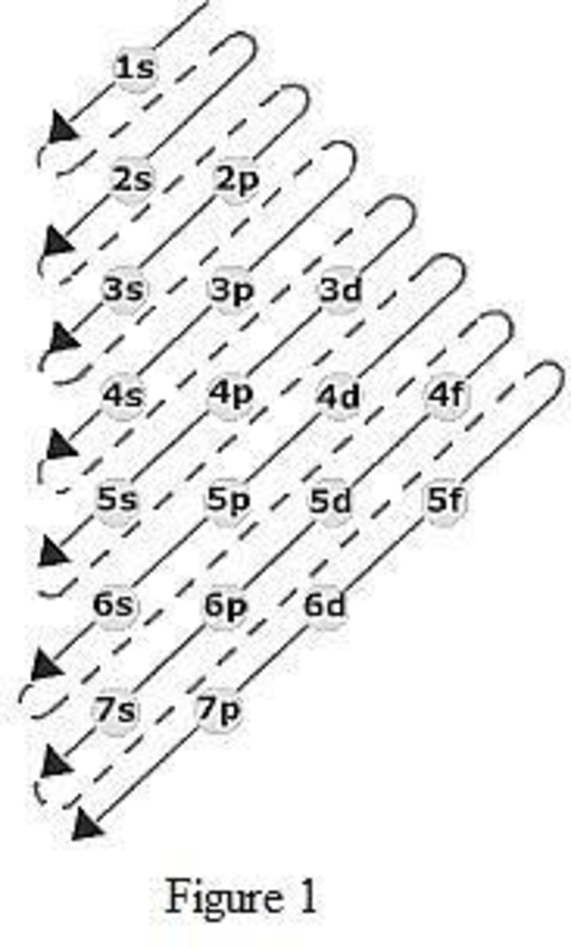
Orbital diagram is the one that gives information about the number of electrons present in the electron orbitals of an atom. The difference between electronic configuration and orbital diagram is that electronic configuration deals with the electrons occupancy in the subshell while orbital diagram deals with the electrons occupancy in the electron orbital. Electrons are paired up in the orbital only when all the orbitals in the subshell are singly filled.
(c)
Interpretation:
The number of unpaired electrons that is associated with electronic configuration
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom describes how many electrons are present in the shell. Many orbitals are present about the nucleus of an atom. In these orbitals the electrons do not occupy randomly. There are three rules for assigning the electrons to various shells, subshells, and orbitals. They are,
- The subshells are filled in increasing order of energy.
- In a subshell, the electrons occupy the orbital singly first in all orbitals before pairing up by the second electron. All the electrons that are in singly occupied orbitals have same spin.
- In a given orbital there cannot be more than two electrons and they have opposite spins.
Electronic configuration of an element is the one that gives information about how many electrons are present in each electron subshell of an atom. The electrons are added to the subshells in increasing order of energy. Electronic configurations are written in shorthand notation which uses a number‑letter combination. The shell is indicated by the number and subshell is indicated by the letter. Superscript that follows the subshell tells how many electrons are present in the subshell.
The order of filling up the electrons in the subshell is done as shown in the given figure below.
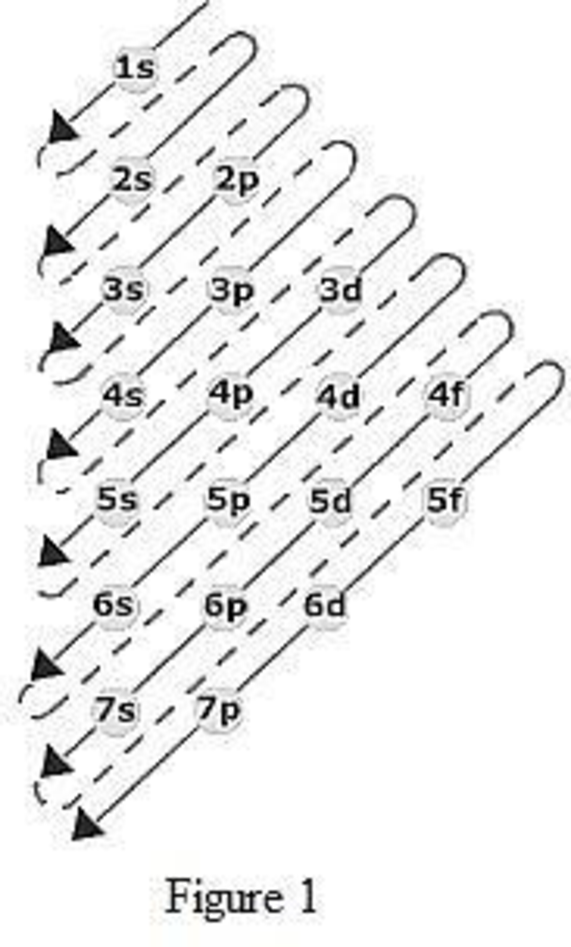
Orbital diagram is the one that gives information about the number of electrons present in the electron orbitals of an atom. The difference between electronic configuration and orbital diagram is that electronic configuration deals with the electrons occupancy in the subshell while orbital diagram deals with the electrons occupancy in the electron orbital. Electrons are paired up in the orbital only when all the orbitals in the subshell are singly filled.
(d)
Interpretation:
The number of unpaired electrons that is associated with electronic configuration
Concept Introduction:
Electronic configuration of an atom describes how many electrons are present in the shell. Many orbitals are present about the nucleus of an atom. In these orbitals the electrons do not occupy randomly. There are three rules for assigning the electrons to various shells, subshells, and orbitals. They are,
- The subshells are filled in increasing order of energy.
- In a subshell, the electrons occupy the orbital singly first in all orbitals before pairing up by the second electron. All the electrons that are in singly occupied orbitals have same spin.
- In a given orbital there cannot be more than two electrons and they have opposite spins.
Electronic configuration of an element is the one that gives information about how many electrons are present in each electron subshell of an atom. The electrons are added to the subshells in increasing order of energy. Electronic configurations are written in shorthand notation which uses a number‑letter combination. The shell is indicated by the number and subshell is indicated by the letter. Superscript that follows the subshell tells how many electrons are present in the subshell.
The order of filling up the electrons in the subshell is done as shown in the given figure below.
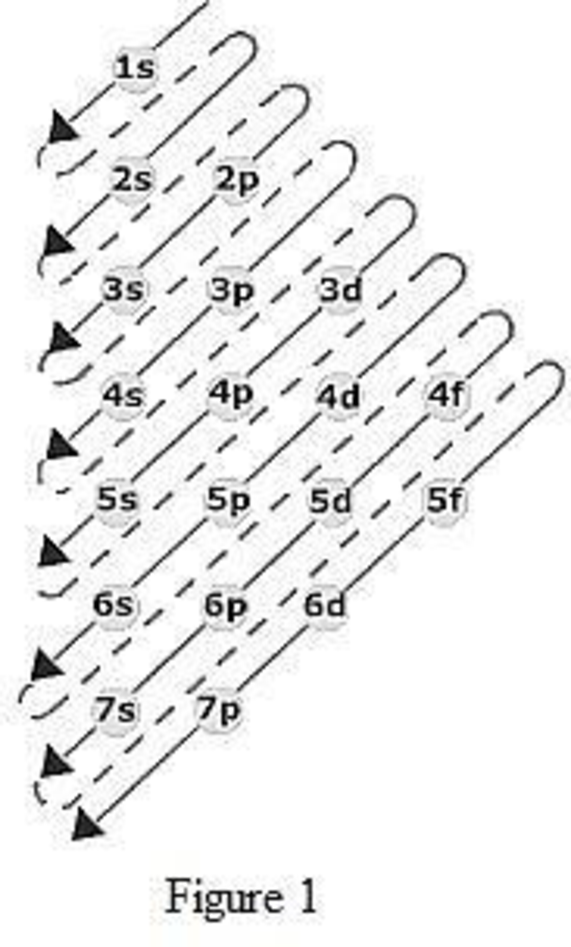
Orbital diagram is the one that gives information about the number of electrons present in the electron orbitals of an atom. The difference between electronic configuration and orbital diagram is that electronic configuration deals with the electrons occupancy in the subshell while orbital diagram deals with the electrons occupancy in the electron orbital. Electrons are paired up in the orbital only when all the orbitals in the subshell are singly filled.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 3 Solutions
Bundle: General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry, 7th + OWLv2 Quick Prep for General Chemistry, 4 terms (24 months) Printed Access Card
- You have identified a new species of a Gram-positive bacteria. You would like to screen their genome for all proteins that are covalently linked to the cell wall. You have annotated the genome, so that you identified all the promoters, operons, and genes sequences within the operons. Using these features, what would you screen for to identify a set of candidates for proteins covalently linked to the bacterial cell wall.arrow_forwardBelow is a diagram from a genomic locus of a bacterial genome. Each arrow represents a coding region, and the arrowheads indicate its orientation in the genome. The numbers are randomly assigned. Draw the following features on the diagram, and explain your rationale for each feature: 10 12 合會會會會長 6 a) Expected transcriptions, based on known properties of bacterial genes and operons. How many proteins are encoded in each of the transcripts? b) Location of promoters (include rationale) c) Location of transcriptional terminators (include rationale) d) Locations of Shine-Dalgarno sequences (include rationale)arrow_forwardSample excuse letter in school class for the reasons of headaches and dysmenorrhea caused by menstrual cyclearrow_forward
- How do the muscles on the foot work to balance on an ice skate, specifically the triangle of balance and how does it change when balancing on an ice skate? (Refer to anatomy, be specific)arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT an example of passive immunization? A. Administration of tetanus toxoid B. Administration of hepatitis B immunoglobulin C. Administration of rabies immunoglobulin D. Transfer of antibodies via plasma therapyarrow_forwardTranscription and Translation 1. What is the main function of transcription and translation? (2 marks) 2. How is transcription different in eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells? (2 marks) 3. Explain the difference between pre-mRNA and post-transcript mRNA. (2 marks) 4. What is the function of the following: (4 marks) i. the cap ii. spliceosome iii. Poly A tail iv. termination sequence 5. What are advantages to the wobble feature of the genetic code? (2 marks) 6. Explain the difference between the: (3 marks) i. A site & P site ii. codon & anticodon iii. gene expression and gene regulation 7. Explain how the stop codon allows for termination. (1 mark) 8. In your own words, summarize the process of translation. (2 marks)arrow_forward
- In this activity you will research performance enhancers that affect the endocrine system or nervous system. You will submit a 1 page paper on one performance enhancer of your choice. Be sure to include: the specific reason for use the alleged results on improving performance how it works how it affect homeostasis and improves performance any side-effects of this substancearrow_forwardNeurons and Reflexes 1. Describe the function of the: a) dendrite b) axon c) cell body d) myelin sheath e) nodes of Ranvier f) Schwann cells g) motor neuron, interneuron and sensory neuron 2. List some simple reflexes. Explain why babies are born with simple reflexes. What are they and why are they necessary. 3. Explain why you only feel pain after a few seconds when you touch something very hot but you have already pulled your hand away. 4. What part of the brain receives sensory information? What part of the brain directs you to move your hand away? 5. In your own words describe how the axon fires.arrow_forwardMutations Here is your template DNA strand: CTT TTA TAG TAG ATA CCA CAA AGG 1. Write out the complementary mRNA that matches the DNA above. 2. Write the anticodons and the amino acid sequence. 3. Change the nucleotide in position #15 to C. 4. What type of mutation is this? 5. Repeat steps 1 & 2. 6. How has this change affected the amino acid sequence? 7. Now remove nucleotides 13 through 15. 8. Repeat steps 1 & 2. 9. What type of mutation is this? 0. Do all mutations result in a change in the amino acid sequence? 1. Are all mutations considered bad? 2. The above sequence codes for a genetic disorder called cystic fibrosis (CF). 3. When A is changed to G in position #15, the person does not have CF. When T is changed to C in position #14, the person has the disorder. How could this have originated?arrow_forward
- hoose a scientist(s) and research their contribution to our derstanding of DNA structure or replication. Write a one page port and include: their research where they studied and the time period in which they worked their experiments and results the contribution to our understanding of DNA cientists Watson & Crickarrow_forwardhoose a scientist(s) and research their contribution to our derstanding of DNA structure or replication. Write a one page port and include: their research where they studied and the time period in which they worked their experiments and results the contribution to our understanding of DNA cientists Watson & Crickarrow_forward7. Aerobic respiration of a protein that breaks down into 12 molecules of malic acid. Assume there is no other carbon source and no acetyl-CoA. NADH FADH2 OP ATP SLP ATP Total ATP Show your work using dimensional analysis here: 3arrow_forward
 Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles Of Radiographic Imaging: An Art And A ...Health & NutritionISBN:9781337711067Author:Richard R. Carlton, Arlene M. Adler, Vesna BalacPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





