
Concept explainers
Which compound in each pair has the higher boiling point?
a. 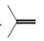 or
or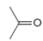 c.
c. 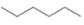 or
or
b. 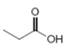 or
or 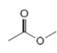 d.
d. 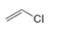 or
or 
(a)
Interpretation: In the given pair, the compound with the higher boiling point is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the compound is converted to a gaseous state.
The boiling point of compounds depends upon the molecular weight and the intermolecular forces present in the compounds. The intermolecular forces are the forces that exist in between the two or more atoms in a compound. Due to strong intermolecular forces, the molecule will require more energy to break the bonds. The compounds that have ionic bonding and hydrogen bonding will possess higher boiling point.
Answer to Problem 3.13P
In the given pair of compounds,
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
In
The increasing order of boiling point with intermolecular forces is,
Hence, the boiling point of
In the given pair of compounds,
(b)
Interpretation: In the given pair, the compound with the higher boiling point is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the compound is converted to a gaseous state.
The boiling point of compounds depends upon the molecular weight and the intermolecular forces present in the compounds. The intermolecular forces are the forces that exist in between the two or more atoms in a compound. Due to strong intermolecular forces, the molecule will require more energy to break the bonds. The compounds that have ionic bonding and hydrogen bonding will possess higher boiling point.
Answer to Problem 3.13P
In the given pair of compounds,
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
In
In the given pair of compounds,
(c)
Interpretation: In the given pair, the compound with the higher boiling point is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the compound is converted to a gaseous state.
The boiling point of compounds depends upon the molecular weight and the intermolecular forces present in the compounds. The intermolecular forces are the forces that exist in between the two or more atoms in a compound. Due to strong intermolecular forces, the molecule will require more energy to break the bonds. The compounds that have ionic bonding and hydrogen bonding will possess higher boiling point.
Answer to Problem 3.13P
In the given pair of compounds,
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
In both the compounds,
In the given pair of compounds,
(d)
Interpretation: In the given pair, the compound with the higher boiling point is to be predicted.
Concept introduction: Boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the compound is converted to a gaseous state.
The boiling point of compounds depends upon the molecular weight and the intermolecular forces present in the compounds. The intermolecular forces are the forces that exist in between the two or more atoms in a compound. Due to strong intermolecular forces, the molecule will require more energy to break the bonds. The compounds that have ionic bonding and hydrogen bonding will possess higher boiling point.
Answer to Problem 3.13P
In the given pair of compounds,
Explanation of Solution
The given compounds are
Van der Waals forces exist in both the compounds due to the presence of
In the given pair of compounds,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- " is The structure of the bicarbonate (hydrogen carbonate) ion, HCO3-, HCO3 best described as a hybrid of several contributing resonance forms, two of which are shown here. HO :0: :Ö: HO + Bicarbonate is crucial for the control of body pH (for example, blood pH: 7.4). A more self-indulgent use is in baking soda, where it serves as a source of CO2 CO₂ 2 gas, which gives bread and pastry their fluffy constituency. (i) Draw at least one additional resonance form. = (ii) Using curved "electron-pushing" arrows, show how these Lewis structures may be interconverted by movement of electron pairs. (iii) Determine which form or forms will be the major contributor(s) to the real structure of bicarbonate, explaining your answer on the basis of the criteria in Section 1-5.arrow_forwardWhich of these is the best use of a volumetric flask? measuring how much liquid it contains delivering a precise amount of liquid to another container holding solutions making solutions of precise concentrationarrow_forwardYou're competing on a Great British television game show, and you need to bake a cake. The quantity for each ingredient is given in grams, but you haven't been given a kitchen scale. Which of these properties would correlate with the mass of a baking ingredient like eggs or milk? Check all that apply. depth of color viscosity volume densityarrow_forward
- Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following species. Again, assign charges where appropriate. a. H-H¯ b. CH3-CH3 c. CH3+CH3 d. CH3 CH3 e. CH3NH3+CH3NH3 f. CH30-CH3O¯ g. CH2CH2 - h. HC2-(HCC) HC2 (HCC) i. H202×(HOOH) H₂O₂ (HOOH) Nortonarrow_forwardIs molecule 6 an enantiomer?arrow_forwardShow work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forward
- Use the vapor-liquid equilibrium data at 1.0 atm. for methanol-water (Table 2-8 ) for the following: If the methanol vapor mole fraction is 0.600, what is the methanol liquid mole fraction? Is there an azeotrope in the methanol-water system at a pressure of 1.0 atmospheres? If water liquid mole fraction is 0.350, what is the water vapor mole fraction? What are the K values of methanol and of water at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200? What is the relative volatility αM-W at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200?arrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. || |II***** Molecule 1 | Molecule 4 none of the above Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Х mm... C ---||| *** Molecule 5 Molecule 6arrow_forwardis SiBr4 Silicon (IV) tetra Bromine? is KClO2 potassium dihypochlorite ?arrow_forward
 Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Today: General, Organic, and Bioche...ChemistryISBN:9781305960060Author:Spencer L. Seager, Michael R. Slabaugh, Maren S. HansenPublisher:Cengage Learning
