
Identify the
amide, and
a. 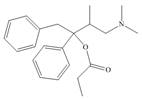 c.
c. 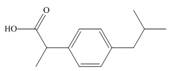 e.
e. 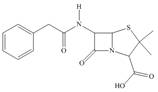
Darvon ibuprofen penicillin G
(analgesic) (analgesic) (an antibiotic)
b. 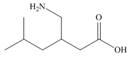 d.
d. 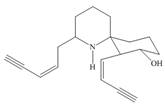 f.
f. 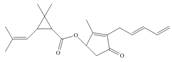
pregabalin histrionicotoxin pyrethrin I
trade name Lyrica (poison secreted by a (potent insecticide
(used in treating chronic south American frog) from chrysanthemum)
Pain)
(a)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in Darvon are shown below.
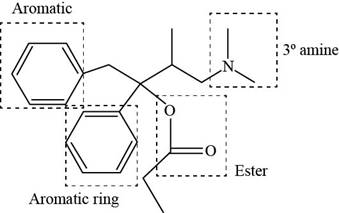
Explanation of Solution
The given compound is,
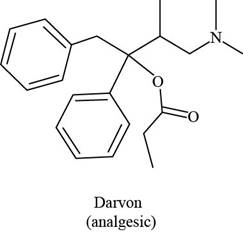
Figure 1
The functional groups present in Darvon are amine, ester and aryl group.
The structure of Darvon that shows the labeling of all functional groups is shown below.

Figure 2
The functional groups present in Darvon and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
(b)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in pregabalin are shown below.
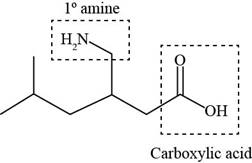
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is,
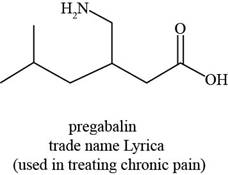
Figure 3
The functional groups present in pregabalin are amine, and carboxylic acid.
The structure of pregabalin that shows the classification of all functional group is shown below.

Figure 4
The functional groups present in pregabalin and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
(c)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in ibuprofen are shown below.
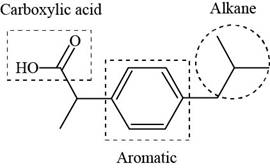
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is,
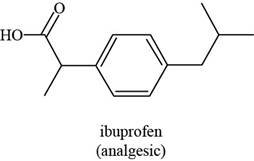
Figure 5
The functional groups present in ibuprofen are carboxylic acid, alkane and aryl.
The structure of ibuprofen that shows the classification of all functional group is shown below.

Figure 6
The functional groups present in ibuprofen and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
(d)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in histrionicotoxin are shown below.
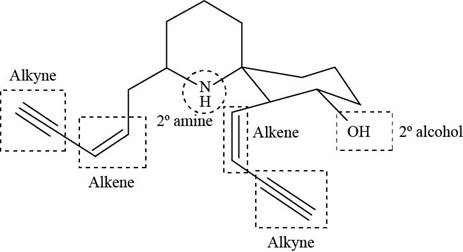
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is,
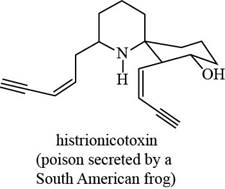
Figure 7
The functional groups present in histrionicotoxin are alkene, alkyne and alcohol. The structure of histrionicotoxin that shows the labeling of all functional group is shown below.

Figure 8
The functional groups present in histrionicotoxin and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
(e)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in penicillin G are shown below.
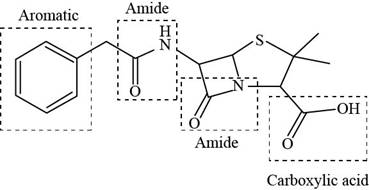
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is,
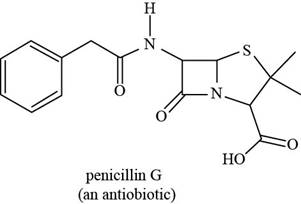
Figure 9
The functional groups present in penicillin G are carboxylic acid, amide, and aryl.
The structure of penicillin G that shows the labeling of all functional group is shown below.

Figure 10
The functional groups present in penicillin G and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
(f)
Interpretation: The functional groups present in the given molecule is to be classified and the classification of each alcohol, alkyl halide, amide, and amine as
Concept introduction: The table representing the general formula of different functional groups according to IUPAC convention is given below.
| General formula | Functional group | Functional group name |
| Alcohol | ||
| Aldehyde | ||
| Ketone | ||
| Amine | ||
| Ether | ||
| Ester | ||
| Alkyl halide | ||
| Double bond | ||
| Carboxylic acid |
The classification of alcohols or alkyl halides depend upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains hydroxyl group or alkyl halide. In case of primary alcohol,
The classification of amines or amides also depends upon the number of carbon atoms attached to the carbon that contains nitrogen atom.
Answer to Problem 3.32P
The functional groups present in pyrethrin I are shown below.
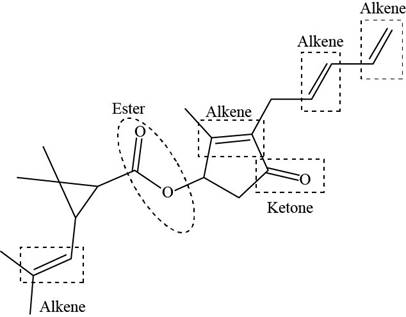
Explanation of Solution
The given structure is,
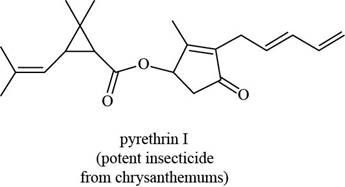
Figure 11
The functional groups present in pyrethrin I are ester, ketone, and alkene.
The structure of pyrethrin I that shows the labeling of all functional group is shown below.

Figure 12
The functional groups present in pyrethrin I and the classification of each alcohol, amide, alkyl halide and amine as primary, secondary, and tertiary are rightfully stated.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
Package: Loose Leaf for Organic Chemistry with Biological Topics with Connect Access Card
- Saved v Question: I've done both of the graphs and generated an equation from excel, I just need help explaining A-B. Below is just the information I used to get the graphs obtain the graph please help. Prepare two graphs, the first with the percent transmission on the vertical axis and concentration on the horizontal axis and the second with absorption on the vertical axis and concentration on the horizontal axis. Solution # Unknown Concentration (mol/L) Transmittance Absorption 9.88x101 635 0.17 1.98x101 47% 0.33 2.95x101 31% 0.51 3.95x10 21% 0.68 4.94x10 14% 24% 0.85 0.62 A.) Give an equation that relates either the % transmission or the absorption to the concentration. Explain how you arrived at your equation. B.) What is the relationship between the percent transmission and the absorption? C.) Determine the concentration of the ironlll) salicylate in the unknown directly from the graph and from the best fit trend-line (least squares analysis) of the graph that yielded a straight…arrow_forwardDon't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardCalculate the differences between energy levels in J, Einstein's coefficients of estimated absorption and spontaneous emission and life time media for typical electronic transmissions (vnm = 1015 s-1) and vibrations (vnm = 1013 s-1) . Assume that the dipolar transition moments for these transactions are in the order of 1 D.Data: 1D = 3.33564x10-30 C m; epsilon0 = 8.85419x10-12 C2m-1J-1arrow_forward
- Don't used Ai solutionarrow_forwardPlease correct answer and don't used hand raitingarrow_forwardIn an induced absorption process:a) the population of the fundamental state is diminishingb) the population of the excited state decreasesc) the non-radiating component is the predominant oned) the emission radiation is consistentarrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





