
Write the ground-state electron configurations for the following elements: B, V, C, As, I, Au.
(a)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Boron (
Put all the 5 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule
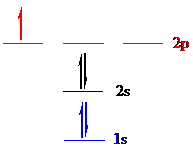
All the 5 electrons of boron (
There are 2 electrons present in
(b)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Vanadium (
The noble gas core for
Put all the 5 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
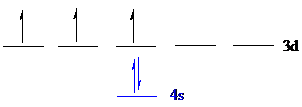
All the 5 electrons of vanadium (
There are 2 electrons present in
(c)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Carbon (
Put all the 6 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
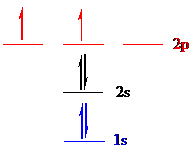
All the 6 electrons of carbon (
There are 2 electrons present in
(d)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Arsenic (
The noble gas core for
Put all the 15 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
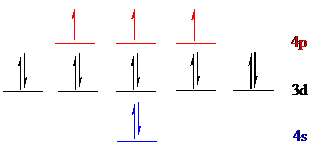
All the 15 electrons of arsenic (
There are 2 electrons present in
(e)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Iodine (
The noble gas core for
Put all the 17 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
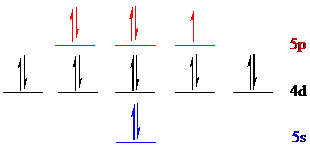
All the 17 electrons of iodine (
There are 2 electrons present in
(f)
Interpretation:
The ground-state electron configurations for the given elements should be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An orbital is an area of space in which electrons are orderly filled. The maximum capacity in any type of orbital is two electrons. An atomic orbital is defined as the region of space in which the probability of finding the electrons is highest. It is subdivided into four orbitals such as
There are three basic principles in which orbitals are filled by the electrons.
- 1. Aufbau principle: In German, the word 'aufbau' means 'building up'. The electrons are arranged in various orbitals in the order of increasing energies.
- 2. Pauli exclusion principle: An electron does not have all the four quantum numbers.
- 3. Hund’s rule: Each orbital is singly engaged with one electron having the maximum same spin capacity after that only pairing occurs.
The electron configuration is the allocation of electrons of an atom in atomic orbitals. Electronic configuration of a particular atom is written by following the three basic principles.
To find: Identify the ground-state electron configuration for
Answer to Problem 3.116QP
The ground-state electron configuration for
Explanation of Solution
Gold (
The noble gas core for
Put all the 25 electrons in the atomic orbitals by following Aufbau principle, Pauli exclusion principle and Hund’s rule.
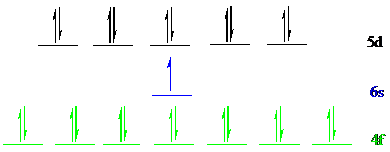
All the electrons of gold (
There are 14 electrons present in
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 3 Solutions
CHEMISTRY: ATOMS FIRST VOL 1 W/CONNECT
- For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects O donating O withdrawing O no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no resonance effects O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene Cl O donating O withdrawing ○ donating ○ withdrawing O no inductive effects O no resonance effects O Explanation Check O electron-rich O electron-deficient similar to benzene X © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessarrow_forwardIdentifying electron-donating and For each of the substituted benzene molecules below, determine the inductive and resonance effects the substituent will have on the benzene ring, as well as the overall electron-density of the ring compared to unsubstituted benzene. Molecule Inductive Effects NH2 ○ donating NO2 Explanation Check withdrawing no inductive effects Resonance Effects Overall Electron-Density ○ donating O withdrawing O no resonance effects O donating O withdrawing O donating withdrawing O no inductive effects Ono resonance effects O electron-rich electron-deficient O similar to benzene O electron-rich O electron-deficient O similar to benzene olo 18 Ar 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibilityarrow_forwardRank each of the following substituted benzene molecules in order of which will react fastest (1) to slowest (4) by electrophilic aromatic substitution. Explanation Check Х (Choose one) OH (Choose one) OCH3 (Choose one) OH (Choose one) © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Centerarrow_forward
- Assign R or S to all the chiral centers in each compound drawn below porat bg 9 Br Brarrow_forwarddescrive the energy levels of an atom and howan electron moces between themarrow_forwardRank each set of substituents using the Cahn-Ingold-Perlog sequence rules (priority) by numbering the highest priority substituent 1.arrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage LearningChemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning





